这道题目可以在leetcode找到
https://leetcode.com/problems/lru-cache/
============================================================================
Amazon OA中的题面是:
给一个array, 给一个cache max size, 输出miss count. 什么时候hit, 什么时候miss的情况写好就好了。
example: size = 4, input array 【1,2,3,4,5,4,1】
1 miss 2 miss 3 miss 4 miss 5 miss 替换 1
4 hit 把4提前到第一位 1 miss 替换 2
============================================================================
一亩三分地中大家说的这个题目我没太看明白。。。使用了4,4放到第一个,然后使用了1,1不是应该在第一个吗?干嘛要替换2?
到前4个应该是[4,3,2,1]-》[5,4,3,2]-》[4,5,3,2]-》[1,4,5,3]我是这么理解的
============================================================================
所以我们翻回去看看操作系统好了
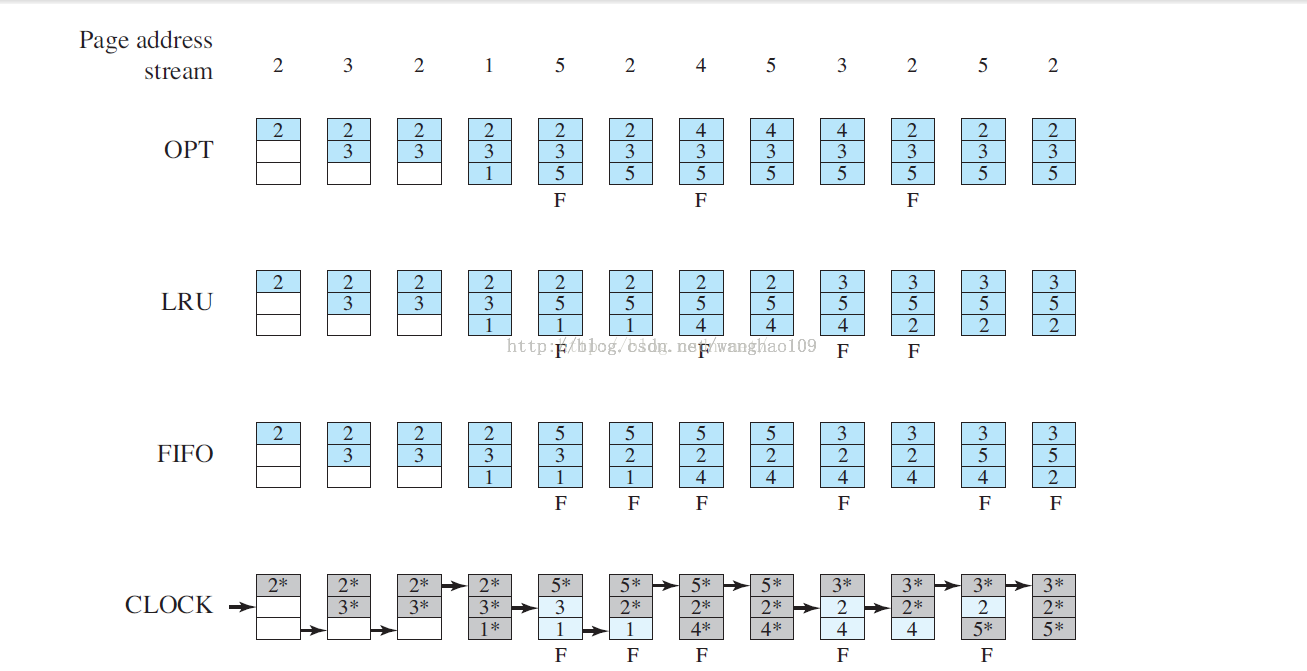
这里只关注LRU
LRU:最近最少使用(Least Recently Used).替换上次使用距离当前最远的页。根据局部性原理:替换最近最不可能 访问到的页。核心思想是,如果最近被访问,那么以后被访问的几率大。
性能最接近OPT,但难以实现。可以维护一个关于访问页的栈或者给每个页添加最后访问的时间标签,但开销都很大。
分析:(F表示页帧最初填满时出现page fault)
a.需要页面2,内存中还有空闲位置,直接加入页面2
b.需要页面3,内存中还有空闲位置,直接加入页面3
c.需要页面2,内存中已经存在页面2,不加入任何页面,这里重置了2的最近历史访问记录
d.需要页面1,内存中还有空闲位置,直接加入页面1
e.需要页面5,页面2,3,1距离最近一次历史访问的距离依次为2,3,1(步骤c中重置了2的访问记录).所以替换掉页 面3.
f.需要页面2,内存中已经存在页面2,不加入任何页面,重置页面2的访问记录
g.需要页面4,页面2,5,1距离最近一次历史访问的距离依次是1,2,3,所以替换掉页面1
h.需要页面5,内存中存在页面5,不改变,重置页面5的访问记录
i.需要页面3,页面2,5,4距离最近一次历史访问的距离依次为3,1,2,所以替换掉页面2
j.需要页面2,页面3,5,4距离最近一次历史访问的距离依次为1,2,3,所以替换掉页面4
k.需要页面5,内存中存在页面5,不改变
L.需要页面2,内存中存在页面2,不改变
我选择了使用HashMap和List。
这里给出的算法是Leetcode中刷题的。之后在Eclipse中再写一个补上。
public class LRUCache {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map;
ArrayList<Integer> list;
int max;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(capacity);
list = new ArrayList<Integer>(capacity);
max = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(map.containsKey(key))
{
list.remove(new Integer(key));
list.add(key);
return map.get(key);
}
else
return -1;
}
public void set(int key, int value) {
if(map.containsKey(key))
{
map.put(key, value);
list.remove(new Integer(key));
list.add(key);
}
else
{
if(map.size() < max)
{
map.put(key,value);
list.add(key);
}else
{
int leastkey = list.remove(0);
list.add(key);
map.remove(leastkey);
map.put(key, value);
}
}
}
}
给出完整的实现,还是用的之前的hashmap和list实现的方法
package quinn;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LRUcache {
static HashMap<Integer, Integer> map;
static ArrayList<Integer> list;
int capacity;
public LRUcache(int capacity_val)
{
capacity = capacity_val;
map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(capacity);
list = new ArrayList<Integer>(capacity);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[] array = {4,3,4,2,3,1,4,2};
int max = 3;
LRUcache MemoA = new LRUcache(max);
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
MemoA.set(array[i], i);
outputlist();
}
int findx = MemoA.get(4);
if(findx == -1)
System.out.println("Do not have now");
else
{
System.out.println("result is: "+findx);
outputlist();
}
}
private static void outputlist() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.print("[ ");
for(int j=0; j < list.size();j++)
{
System.out.print(list.get(j)+" ");
}
System.out.print("]\n");
}
private int set(int key, int i2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(map.size() < capacity)
{
if(map.containsKey(key))
{
map.put(key, i2);
list.remove(new Integer(key));
list.add(key);
}else
{
map.put(key, i2);
list.add(key);
}
}
else
{
int lastkey = list.get(0);
list.remove(0);
map.remove(lastkey);
list.add(key);
map.put(key, i2);
}
return key;
}
private int get(int key) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(map.containsKey(key))
{
list.remove(new Integer(key));
list.add(key);
return map.get(key);
}else
return -1;
}
}
给出一个LinkedHashMap的实现,来自于:
http://yikun.github.io/2015/04/03/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0%E4%B8%80%E4%B8%AALRU-Cache%EF%BC%9F/
简便很多。
package quinn;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class LRUCache2 {
private int capacity;
private static Map<Integer, Integer> cache;
public LRUCache2(final int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.cache = new java.util.LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> (capacity, 0.75f, true) {
// 定义put后的移除规则,大于容量就删除eldest
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
return size() > capacity;
}
};
}
public int get(int key) {
if (cache.containsKey(key)) {
return cache.get(key);
} else
return -1;
}
public void set(int key, int value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[] array = {4,3,4,2,3,1,4,2};
int max = 3;
LRUCache2 MemoA = new LRUCache2(max);
for(int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
MemoA.set(array[i], i);
}
}
}
























 5527
5527











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








