文章目录
- 前置要求
- 线程基础知识复习
- CompletableFutrue
- 说说Java"锁"事
-
- 大厂面试题复盘
- 从轻松的乐观锁和悲观锁开始
- 通过8种情况演示锁运行案例,看看我们到底锁的是什么
- 公平锁和非公平锁
- 可重入锁(又名递归锁)
- 死锁及排查
- 写锁(独占锁)/ 读锁(共享锁)
- 自旋锁SpinLock
- 无锁->独占锁->读写锁->邮戳锁
- 无锁->偏向锁->轻量锁->重量锁
- 其他细节
- LockSupport与线程中断
- Java内存模型值JMM
- volatile与Java内存模型
- CAS
- 原子操作类之18罗汉增强
- 聊聊ThreadLocal
- Java对象内存布局和对象头
- Synchronized与锁升级
- AbstractQueuedSynchronizer之AQS
- ReentrantLock、ReentrantReadWriteLock、StampedLock
- 总结与回顾
前置要求
线程基础知识复习
Futrue和Callable接口
Future接口定义了操作异步任务执行一些方法,如获取异步任务的执行结果、取消任务的执行、判断任务是否被取消、判断任务执行是否完毕等。
Callable接口定义了需要有返回的任务需要实现的方法。
比如主线程让一个子线程去执行任务,子线程可能比较耗时,启动子线程开始执行任务后,主线程就去做其他事了,过了一会儿去取子任务的执行结果。
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+
"\t"+"===come in.");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return 1024;
});
new Thread(futureTask).start();
System.out.println("======阳哥继续讲课=====");
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
}
}
运行结果:
======阳哥继续讲课=====
Thread-0 ===come in.
1024
推荐 futureTask.get() 放在最后,如果不放在最后的话,我们再来看:
new Thread(futureTask).start();
// 只要出现future.get()方法,不管是否计算完成都阻塞,等待结果出来再运行
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
System.out.println("======阳哥继续讲课=====");
运行结果:
Thread-0 ===come in.
1024
======阳哥继续讲课=====
针对上面说的 futrure.get()方法:
// 只要出现future.get()方法,不管是否计算完成都阻塞,等待结果出来再运行
// 工作中别用这个,别给自己挖坑
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
// 过时不候
System.out.println(futureTask.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
那么,如何避免阻塞呢?
答:用轮询来代替阻塞。
小总结:不见不散 - 过时不候 - 轮询
从之前的FutureTask说
如果要做一些复杂的任务呢?比如:
应对Future的完成时间,完成了可以告诉我,也就是我们的回调通知。
将两个异步计算合成一个异步计算,这两个异步计算互相对立,同时第二个又依赖第一个的结果。
当Future集合中某个任务最快结束时,返回结果。
等待Future结合中的所有任务都完成。
。。。。。。。。。。
对Future的改进
CompetableFuture和CompletionStage源码分别介绍
类架构说明
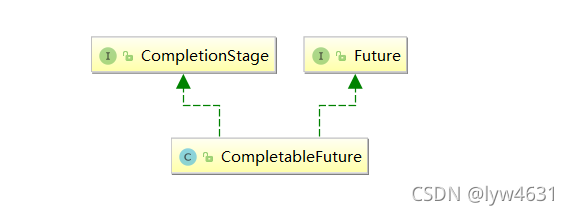
接口CompletionStage是什么
CompletionStage代表异步计算过程中的某一阶段,一个阶段完成以后可能会触发另外一个阶段。
一个阶段的计算执行可以是一个Function,Consumer或者Runnable。
一个阶段的执行可能是被单个阶段的完成触发,也可能是有多个阶段一起触发。
代表异步计算过程中的某一个阶段,一个阶段完成以后可能会触发另外一个阶段,有些类似Linux系统的管道分隔符

类CompletableFuture是什么
在Java8中,CompletableFuture提供了非常强大的Future的扩展功能,可以帮助我们简化异步编程的复杂性,并且提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,也提供了转换和组合CompletableFuture的方法。
它可以代表一个明确完成的Future,也有可能代表一个完成阶段(CompletionStage),它支持计算完成以后触发一些函数或执行某些动作。
它实现了Future和CompletionStage接口。
核心的四个静态方法,来创建一个异步操作
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "===come in.");
});
// 线程池用在哪些地方?
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "===come in.");
}, threadPoolExecutor);
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
运行结果
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 ===come in.
pool-1-thread-1 ===come in.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 20, 1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(50), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "===come in.");
return 11;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future4 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "===come in.");
return 12;
}, threadPoolExecutor);
threadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
运行结果:
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-1 ===come in.
pool-1-thread-1 ===come in.
Executor参数说明:
没有指定Executor的方法,直接使用默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
如果指定线程池,则使用我们自定义的或者特别指定的线程池执行异步代码。
| 函数式接口名称 | 方法名称 | 参数 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Runnable | run | 无 | 无 |
| Function | apply | 7 | 有 |
| Consume | appept | 7 | 无 |
| Supplier | get | 无 | 有 |
| BiConsumer | accept | 2 | 无 |
案例精讲-从电商网站的比价需求说
函数式编程已经成为主流
先说说join和get对比
get()
public static void main(String[] args)
throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
return 1;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("==result==" + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}).get());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
join()
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
return 1;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("==result==" + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}).join());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
发现了什么
get和join是一样的,只是,join不抛出异常
大厂业务需求说明
案例说明:电商比价需求
- 同一款产品,同时搜索出同款商品在各大电商的售价
- 同一款商品,同时搜索出本产品在某一个电商平台下,各个入驻门店的售价是多少
出来结果是同款产品的在不同地方的价格清单列表,返回一个list
e.g.
《MySQL》in jd price is 88.05
《MySQL》in pdd price is 86.11
《MySQL》in taobao price is 90.43 - 要求深刻理解
3.1 函数式编程
3.2 链式编程
3.3 Stream流式计算
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<NetMall> list =
Arrays.asList(new NetMall("jd"), new NetMall("ebay"),
new NetMall("pdd"), new NetMall("taobao"),
new NetMall("dangdang"),new NetMall("tmall"),
new NetMall("suning"),new NetMall("amazon"));
long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list1 = getPriceByStep(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list1) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end1-start1)+"毫秒");
long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list2 = getPriceByStep(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list2) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long end2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end2-start2)+"毫秒");
}
// 一步步走
public static List<String> getPriceByStep(List<NetMall> list, String mallName) {
return list.stream()
.map(netMall -> String.format("%s in %s price is %.2f",
mallName,
netMall.getMallName(),
netMall.getPrice()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// 万箭齐发
public static List<String> getPriceByAsync(List<NetMall> list, String mallName) {
return list.stream().
map(netMall ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> String.format("%s in %s price is %.2f",
mallName,
netMall.getMallName(),
netMall.getPrice())))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
class NetMall {
private String mallName;
public NetMall(String mallName) {
this.mallName = mallName;
}
public double getPrice() {
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() * 2 + "mysql".charAt(0);
}
public String getMallName() {
return this.mallName;
}
}
CompletableFutrue常用方法
获得结果和触发计算
get()
getNow()
public static void main(String[] args) {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
return 1;
});
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// 立即返回,如果获取不到值,则返回自己定义的默认值
System.out.println(future.getNow(999));
System.out.println("============================================");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
return 1;
});
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// 立即返回,如果获取不到值,则返回自己定义的默认值
System.out.println(future2.getNow(999));
System.out.println("=============================================");
CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
return 1;
});
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// 立即返回,如果获取不到值,则返回自己定义的默认值
System.out.println(future3.getNow(999));
}
运行结果:
999
============================================
999
=============================================
1
boolean complete(T value)
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(20); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
return 1;
});
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// 是否打断上面的线程,如果打断,则返回打断后自定义的值
System.out.println(future.complete(-44) + "\t" + future.get());
}
运行结果:
-44
对计算结果进行处理
thenApply
由于存在依赖关系(当前步错,不走下一步),当前步骤有异常的话就叫停
先来看看正常的:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer num = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f + 2;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f + 3;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("result is " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}).join();
System.out.println("num is " + num);
}
运行结果:
result is 6
num is 6
那么,如果中途发生异常呢?
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer num = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
// 抛出异常
int i = f / 0;
return f + 2;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("result is " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}).join();
System.out.println("num is " + num);
}
运行结果:
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.encodeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:273)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:280)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.uniApply(CompletableFuture.java:604)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.uniApplyStage(CompletableFuture.java:614)
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.thenApply(CompletableFuture.java:







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 837
837











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








