二级指针:
二级指可以理解为一个二维数组,但有不能完全等于二维数组,因为其使用方式是指向动态分配的二维空间。
下面函数通过传递输出参数的方式应用二级指针:
void func2(char**args, int &num, int* lens)
{
int count = 3;
const char *iface[] = {"getStatus",
"setStatus",
"getUserName"};
//iface就是一个指针形式的二维数组,像不像,第一行是getStatus
num = count;
for( int i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
lens[i] = strlen(iface[i]);//一级指针
}
if( args == NULL )
return;
for( int i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
strcpy(args[i], iface[i]);
//args[i]就是*(args+i),其实就是第i行
//iface[i]等于*(iface+i),一维指针数组和二级指针效果一样
}
三级指针:
void func(char*** args, int &c)
{
int count = 3;
c = count;
const char *iface[] = {"getStatus", "setStatus", "getUserName"};
*args = (char**)malloc(count*sizeof(char*));//二级指针*args指向大小为count*sizeof(char*)的二维空间
//若是三级指针呢,照猫画虎,args = char(***)malloc(3*sizeof(char **));,这里面args是三级指针,其指向大小为3个byte的三维空间或链表。
for( int i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
cout << iface[i] << endl;
int len = strlen(iface[i])+1;
(*args)[i] = (char*)malloc(len*sizeof(char));//循环申请一维空间
memset((*args)[i], 0, len);
strcpy((*args)[i], iface[i]);
}
}
//运行一下,看看效果:
//说明一下,visual studio2015以上的版本需要在stdafx.h中加入#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS或这加入
//#pragma warning( disable : 4996)
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <cstring>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char **array = NULL;
int count = -1;
func(&array, count);//“三级指针&array”作为参数传递,注意是形式上的三级指针,array本身是二级指针变量
//经过func函数的运行,里面的二维数组信息传递给了array
vector<string> ifaceList;
cout << "count = " << count << endl;
for( int i = 0; i < count; i++ )
{
cout << array[i] << endl;//打印出二维数组信息
ifaceList.push_back(array[i]);
if( array[i] != NULL )
{
free(array[i]);//因为func函数里面申请了空间,需要在这里循环手动释放
array[i] = NULL;// array[i] 一级指针指向NULL
}
}
if( array != NULL )
{
free(array);//释放func中申请的空间
array = NULL;
}
//注意循环里释放了count次,这个地方释放了一次。func中申请空间和这里的释放空间是对称的。
//三级指针的应用时func中申请空间,main函数中释放空间。
//下面二级指针的应用则是func2中不申请空间,只把指针指向二维空间首地址。当应用时在main函数中申请空间,用完释放空
//间。
cout << "----------------" << endl;
for( vector<string>::iterator iter = ifaceList.begin(); iter != ifaceList.end(); iter++ )
{
//cout << *iter << endl;
}
cout << "======= who allocate who free ==========" << endl;
char** pIfaceList = NULL;
int num = -1;
int lens[100] = {-1};
func2(pIfaceList, num, lens);//传递二级指针参数pIfaceList
cout << "num = " << num << endl;
for( int i = 0; i < num; i++ )
{
cout << "len[" << i << "] = " << lens[i] << endl;//输出func2函数中二维数组中的信息
}
//allocate memory
pIfaceList = (char**)malloc(num*sizeof(char*));//分配空间num byte
for(int i = 0 ; i < num; i++)
{
int nLen = lens[i]+1;
pIfaceList[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*nLen);//分配nLen byte空间,pIfaceList[i] 指向这部分空间
memset(pIfaceList[i], 0, sizeof(char)*nLen);
}
func2(pIfaceList, num, lens);//再次调用func2
vector<string> ifaceList2;
for( int i = 0; i < num; i++ )
{
cout << "pIfaceList[" << i << "] = " << pIfaceList[i] << endl;//按行输出
ifaceList2.push_back(pIfaceList[i]);
if(pIfaceList[i] != NULL)
{
free(pIfaceList[i]);
pIfaceList[i] = NULL;
}
}
if( pIfaceList != NULL )
{
free(pIfaceList);
pIfaceList = NULL;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
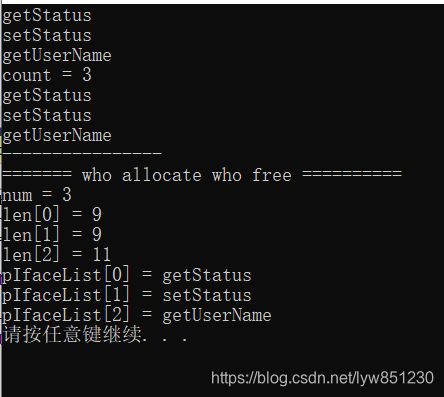
下面是运行效果:





















 569
569











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








