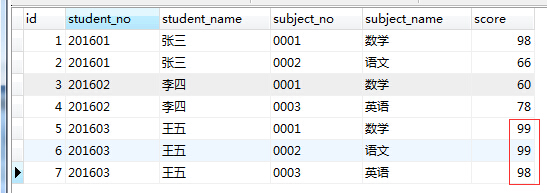
1、用一条SQL 语句 查询出每门课都大于80 分的学生姓名。(表结构如下图)
这里写图片描述
答案可以有如下两种:
select distinct student_name from table_test_one where student_name not in
(select distinct student_name from table_test_one where score<=80);
或者
select student_name from table_test_one group by student_name having min(score)>80;
第二种方法是group by 、min函数 结合 having的使用,w3school教程里面也提到过(在 SQL 中增加 HAVING 子句原因是,WHERE 关键字无法与合计函数一起使用)
建表然后倒入初始数据:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS
table_test_one;
CREATE TABLEtable_test_one(
idint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
student_novarchar(10) NOT NULL,
student_namevarchar(10) NOT NULL,
subject_novarchar(10) NOT NULL,
subject_namevarchar(10) NOT NULL,
scoreint(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO
table_test_oneVALUES (‘1’, ‘201601’, ‘张三’, ‘0001’, ‘数学’, ‘98’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_oneVALUES (‘2’, ‘201601’, ‘张三’, ‘0002’, ‘语文’, ‘66’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_oneVALUES (‘3’, ‘201602’, ‘李四’, ‘0001’, ‘数学’, ‘60’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_oneVALUES (‘4’, ‘201602’, ‘李四’, ‘0003’, ‘英语’, ‘78’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_oneVALUES (‘5’, ‘201603’, ‘王五’, ‘0001’, ‘数学’, ‘99’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_oneVALUES (‘6’, ‘201603’, ‘王五’, ‘0002’, ‘语文’, ‘99’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_oneVALUES (‘7’, ‘201603’, ‘王五’, ‘0003’, ‘英语’, ‘98’);
可以运行一下上面两个语句试试结果是不是你想要的。
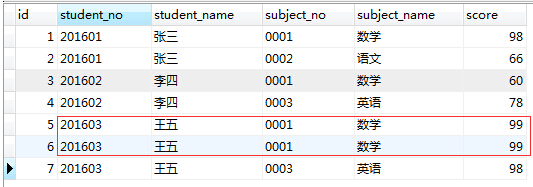
2、删除除了id不同, 其他都相同的学生冗余信息,表如下:
答案:
delete table_test_one where id not in
(select min(id) from table_test_one group by
student_no, student_name, subject_no, subject_name, score);
是否有看懂?如果没能看懂的话,继续往下看:
先来造数据,题1中的数据只需要执行如下SQL就变成题2中的数据了:
update table_test_one set subject_no = ‘0001’, subject_name = ‘数学’ where id = 6;
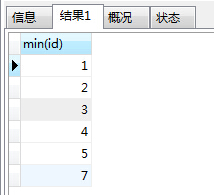
然后我们先执行这个看看:
select min(id) from table_test_one group by
student_no, student_name, subject_no, subject_name, score
这个的执行结果如下:
如果还不懂就再看看几次吧。
PS:GROUP BY 语句用于结合合计函数,根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组。刚刚就是GROUP BY 对多列的使用场景。
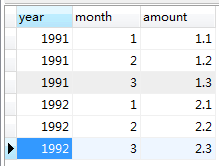
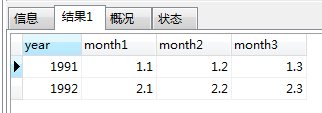
3、行转列:
表数据如下:
希望查询到结果如下:
答案:
select year,
(select amount from table_test_two t where t.month = 1 and t.year = table_test_two.year) as month1,
(select amount from table_test_two t where t.month = 2 and t.year = table_test_two.year) as month2,
(select amount from table_test_two t where t.month = 3 and t.year = table_test_two.year) as month3
from table_test_two group by year;
利用group by 实现行转列,这种场景在数据统计的时候经常用到。
猿友可以造数据自己运行试试:
Table structure for table_test_two
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS
table_test_two;
CREATE TABLEtable_test_two(
yearint(11) NOT NULL,
monthint(11) NOT NULL,
amountdecimal(10,1) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (year,month,amount)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Records of table_test_two
INSERT INTO
table_test_twoVALUES (‘1991’, ‘1’, ‘1.1’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_twoVALUES (‘1991’, ‘2’, ‘1.2’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_twoVALUES (‘1991’, ‘3’, ‘1.3’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_twoVALUES (‘1992’, ‘1’, ‘2.1’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_twoVALUES (‘1992’, ‘2’, ‘2.2’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_twoVALUES (‘1992’, ‘3’, ‘2.3’);
4、复制表( 只复制结构, 源表名:table_test_two 新表名:table_test_three)
答案:
create table table_test_three as
select * from table_test_two where 1=2;
PS:如果需要将数据也复制过去,则上面改成where 1=1
5、复制表数据(将表 table_test_two 的数据复制到表table_test_three 里面)
答案:
insert into table_test_three (year,month,amount)
select year,month,amount from table_test_two;
6、两张关联表,删除主表中已经在副表中没有的信息
答案:
delete from table_test_student where not exists
(select * from table_test_class where table_test_student.class_id = table_test_class.calss_id);
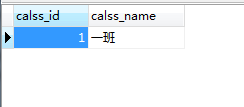
我们先造点数据吧:
Table structure for table_test_class
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS
table_test_class;
CREATE TABLEtable_test_class(
calss_idint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
calss_namevarchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (calss_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Records of table_test_class
INSERT INTO
table_test_classVALUES (‘1’, ‘一班’);
Table structure for table_test_student
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS
table_test_student;
CREATE TABLEtable_test_student(
student_idint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
student_namevarchar(10) CHARACTER SET utf8 NOT NULL,
class_idint(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (student_id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
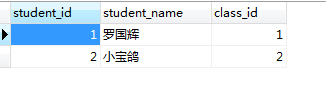
Records of table_test_student
INSERT INTO
table_test_studentVALUES (‘1’, ‘罗国辉’, ‘1’);
INSERT INTOtable_test_studentVALUES (‘2’, ‘小宝鸽’, ‘2’);
执行后数据如下:
显然副表student中小宝鸽这条数据的calss_id,主表没有对应的class_id.
执行对应SQL语句就会把小宝鸽这条数据删除掉了。






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








