synchronized实现线程同步,让多个线程排队以此获取某个资源,保证数据不会出错。
synchronized到底锁定的是什么元素?
修饰方法
-
静态方法(锁定的是类)
-
非静态方法( 锁定的是方法的调用者)
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
//线程A
new Thread(()->{
data.func1();
},"A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//休眠一秒后启动线程B
new Thread(()->{
data.func2();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Data{
public void func1(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("1....");
}
public void func2(){
System.out.println("2....");
}
}
不加锁:一秒之后执行B线程,再等两秒指向A线程
class Data{
public synchronized void func1(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("1....");
}
public synchronized void func2(){
System.out.println("2....");
}
}
- 加锁之后,等3秒后执行A,B线程同时输出
- A,B线程同时争夺,data是调用者被锁住,data只能依次执行
- 若func2不加上
synchronized,那么A,B不会竞争
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
//线程A
new Thread(()->{
data.func1();
},"A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//休眠一秒后启动线程B
new Thread(()->{
data.func2();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Data{
public synchronized static void func1(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("1....");
}
public synchronized static void func2(){
System.out.println("2....");
}
}
A.B会排队
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data1 = new Data();
Data data2 = new Data();
//线程A
new Thread(()->{
data1.func1();
},"A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//休眠一秒后启动线程B
new Thread(()->{
data2.func2();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Data{
public synchronized static void func1(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("1....");
}
public synchronized static void func2(){
System.out.println("2....");
}
}
不同对象调用,AB仍然会排队
修饰代码块
锁定的是传入的对象
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data2 data2 = new Data2();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
new Thread(()->{
data2.func();
}).start();
}
}
}
class Data2{
public void func(){
System.out.println("start...");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end...");
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data2 data2 = new Data2();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
new Thread(()->{
data2.func();
}).start();
}
}
}
class Data2{
public void func(){
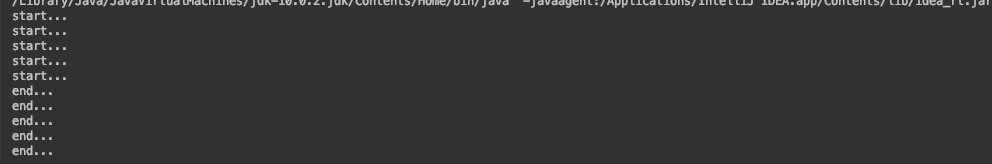
synchronized (this){ // 争夺资源,调用的对象
System.out.println("start...");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end...");
}
}
}
排队,争夺data2对象
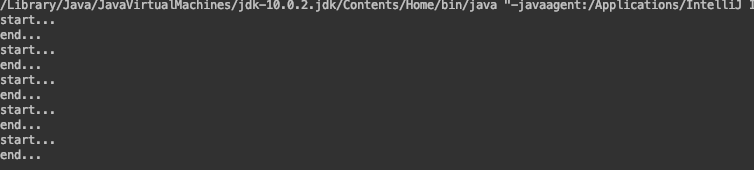
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
new Thread(()->{
new Data2().func();
}).start();
}
这样就不会争夺了,不用排队
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
new Thread(()->{
new Data2().func();
}).start();
}
}
}
class Data2{
public void func(){
synchronized (Data2.class){ // 争夺资源
System.out.println("start...");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end...");
}
}
}
锁Data2运行时类,会排队
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
new Thread(()->{
new Data2().func();
}).start();
}
}
}
class Data2{
public void func(){
Integer num = 1;
synchronized (num){ // 争夺资源
System.out.println("start...");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end...");
}
}
}
仍然排队,说明num在内存中只有一份
还有其他的题目,关键是看争夺的对象在内存中有几份






















 383
383











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








