原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u010132427/article/details/52157430
在上一篇文章中简单分析了fork、pause等系统调用的实现,怀着对fork在父子进程中返回不同值的好奇,本文中将深入分析fork的执行过程以及如何实现在父子进程中返回不一样的值(父进程---子进程ID,子进程----0)。
为了分析fork,可以从它定义处开始一步一步的分析它执行的过程以及堆栈内容的变化。下面从syscall0(int,fork)展开后的结果:
- static inline int fork(void)
- {
- long __res;
- __asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
- : "=a" (__res) \
- : "0" (__NR_fork)); \
- if (__res >= 0) \
- return (int) __res; \
- errno = -__res; \
- return -1; \
- }
从上面第2行代码可知,fork执行过程的起点为“int $0x80” ,通过调用系统中断0x80从而跳转到_system_call中去执行。返回值__res从eax寄存器中得到,当__res >= 0时返回__res值,否则报错并返回-1 。在调用系统中断0x80时,CPU保存现场,自动把一些寄存器的值按顺序压入栈,此时栈内的内容如下图所示,把ss、esp、eflags、cs寄存器入栈,在调用system_call函数时把返回程序的入口地址也入栈。
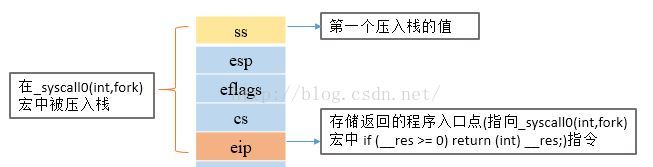
接下来,程序跳转进入/kernel/system_call.S文件中system_call系统调用入口函数_system_call处执行。
- .align 2
- reschedule:
- pushl $ret_from_sys_call
- jmp _schedule
- .align 2
- _system_call:
- cmpl $nr_system_calls-1,%eax
- ja bad_sys_call
- push %ds
- push %es
- push %fs
- pushl %edx
- pushl %ecx # push %ebx,%ecx,%edx as parameters
- pushl %ebx # to the system call
- movl $0x10,%edx # set up ds,es to kernel space
- mov %dx,%ds
- mov %dx,%es
- movl $0x17,%edx # fs points to local data space
- mov %dx,%fs
- call _sys_call_table(,%eax,4)
- pushl %eax
- movl _current,%eax
- cmpl $0,state(%eax) # state
- jne reschedule
- cmpl $0,counter(%eax) # counter
- je reschedule
- ret_from_sys_call:
- movl _current,%eax # task[0] cannot have signals
- cmpl _task,%eax
- je 3f
- cmpw $0x0f,CS(%esp) # was old code segment supervisor ?
- jne 3f
- cmpw $0x17,OLDSS(%esp) # was stack segment = 0x17 ?
- jne 3f
- movl signal(%eax),%ebx
- movl blocked(%eax),%ecx
- notl %ecx
- andl %ebx,%ecx
- bsfl %ecx,%ecx
- je 3f
- btrl %ecx,%ebx
- movl %ebx,signal(%eax)
- incl %ecx
- pushl %ecx
- call _do_signal
- popl %eax
- 3: popl %eax
- popl %ebx
- popl %ecx
- popl %edx
- pop %fs
- pop %es
- pop %ds
- iret
在__system_call中,先把ds,es,fs,edx,ecx,ebx压入栈,再把call _sys_call_table(,%eax,4)指令的返回入口地址入栈,然后调转到sys_fork函数处执行,此时栈内的内容为:
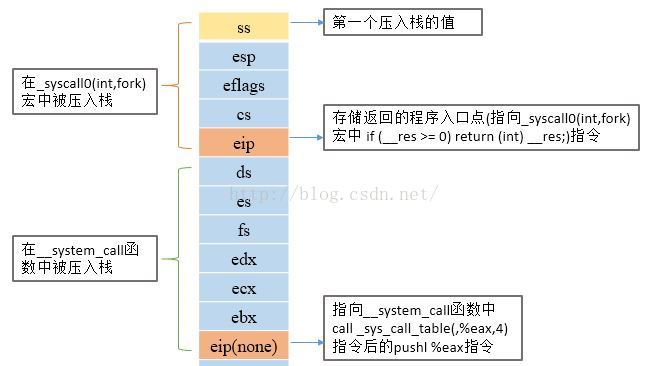
- .align 2
- _sys_fork:
- call _find_empty_process
- testl %eax,%eax
- js 1f
- push %gs
- pushl %esi
- pushl %edi
- pushl %ebp
- pushl %eax
- call _copy_process
- addl $20,%esp
- 1: ret
在sys_fork中,首先调用find_empty_process函数取得不重复的进程号,其返回值在eax寄存器中;然后把gs,esi,edi,ebp,eax寄存器的值压栈,然后,以前面压入栈内的ss到eax(nr)这些值为参数调用copy_process函数,此时栈内的内容为:
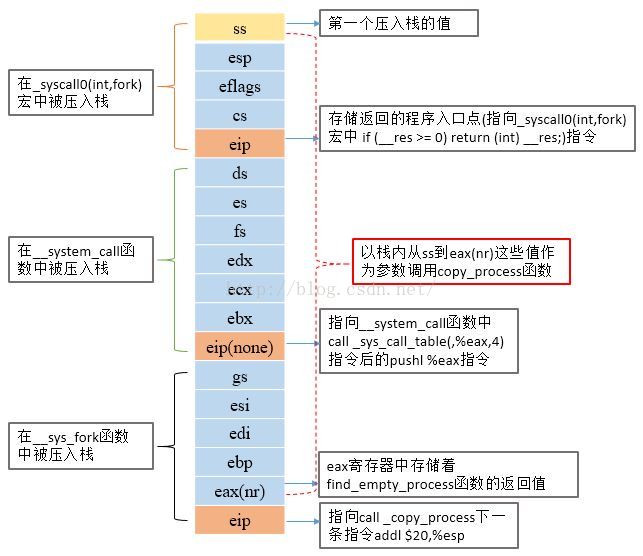
在copy_process函数中有如下两行代码对于fork生成的子进程很关键:
- p->tss.eip = eip;
- ...
- p->tss.eax = 0;
执行完copy_process函数后,返回addl $20,%esp指令处,把栈顶指针esp上移20(栈内的5个项* 4 字节 = 20),刚好把gs,esi,edi,ebp,eax(nr)的空间忽略掉。然后使用ret指令返回eip(none)中的地址,即
__system_call函数中的pushl %eax指令处,把eax寄存器的值(为copy_process 返回的子进程号)入栈。此时栈内的内容变为:
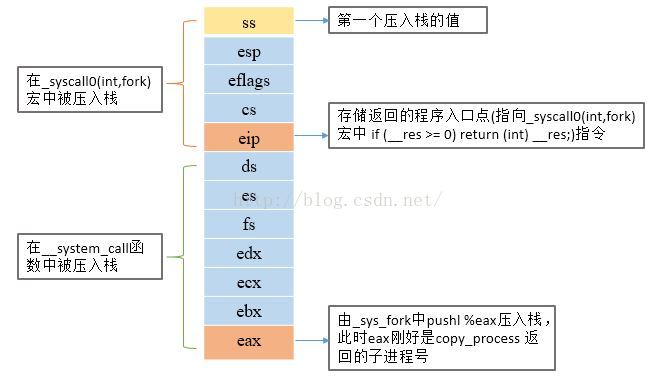
此时,程序返回到_system_call中,接下来判断是否进行进程调度:
- movl _current,%eax
- cmpl $0,state(%eax) # state
- jne reschedule
- cmpl $0,counter(%eax) # counter
- je reschedule
这些代码的意思是:先比较当前current,即子进程的状态是否可以运行,如果当前进程不再就绪状态就去执行调度程序,如果该任务在就绪状态但时间片用完了,也就执行调度程序。所有后续的情况是,我们无法确定进程0或者进程1先执行,但是返回值已经明显确定了。
a. 对于进程0(父进程)而言,接下来会执行ret_from_sys_call后的指令,进行system_call系统调用的退出和信号处理,其中call _do_signal后面的popl %eax 表示把 子进程号 出栈存到eax中,返回到syscall0时传递给__res,表示进程0(父进程)的fork返回的子进程号。
b. 对于进程1(子进程)而言,在schedule函数中调度到子进程运行时,由前面copy_process函数可知,子进程会返回到syscall0中if(__res >= 0) return (int) __res;)指令处,__res为 0,即子进程的fork返回0 ,其过程如下:
- .align 2
- reschedule:
- pushl $ret_from_sys_call
- jmp _schedule
先把_ret_from_sys_call的地址压入栈,再跳转到schedule函数执行,在schedule函数最后会调用switch_to宏:
- #define switch_to(n) {\
- struct {long a,b;} __tmp; \
- __asm__("cmpl %%ecx,_current\n\t" \
- "je 1f\n\t" \
- "movw %%dx,%1\n\t" \
- "xchgl %%ecx,_current\n\t" \
- "ljmp %0\n\t" \
-
-
- "cmpl %%ecx,_last_task_used_math\n\t" \
- "jne 1f\n\t" \
- "clts\n" \
- "1:" \
- ::"m" (*&__tmp.a),"m" (*&__tmp.b), \
- "d" (_TSS(n)),"c" ((long) task[n])); \
- }
switch_to宏的核心是"ljmp %0\n\t"指令,它实现任务的切换。当它切换到子进程时,由于子进程的tss.eip指向syscall0中if(__res >= 0) return (int) __res;)指令处,且tss.eax = 0,所以子进程中fork会返回0值。


























 1583
1583

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








