Vector
-
数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢
-
JDK1.0版本,运行效率慢、线程安全,JDK1.2之后也实现了List接口
-
Vector与ArrayList的共同点
- 都是由数组结构实现的
- 都可以初始化数组长度
-
Vector与ArrayList的区别
- Vector是线程安全的(synchronized);ArrayList不是线程安全的
- Vector在创建对象时可以设置容量增量(capacityIncrement)大小,capacityIncrement默认为initialCapacity,initialCapacity默认为10;ArrayList不可以通过参数设置容量增量,默认增量为10
- Vector有Element相关的方法,addElement,removeElementAt等,ArrayList没有Element相关方法
-
源码分析
-
默认参数
参数 解释 默认值 elementData 元素数据 elementCount 元素个数 capacityIncrement 容量增量 -
构造方法
-
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
- addElement()方法
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
- 案例一,initialCapacity为10, capacityIncrement为10,elementCount为0
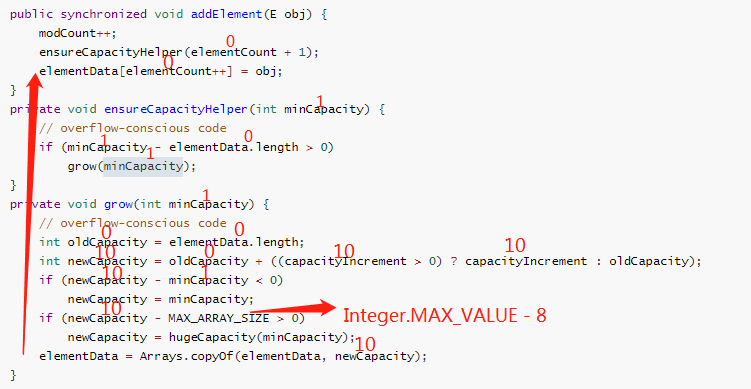
- 案例二,initialCapacity为10, capacityIncrement为10,elementCount为10
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-21m3uyTw-1602057436909)(https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EsonW/picgo/master/image-20201005170228720.png)]
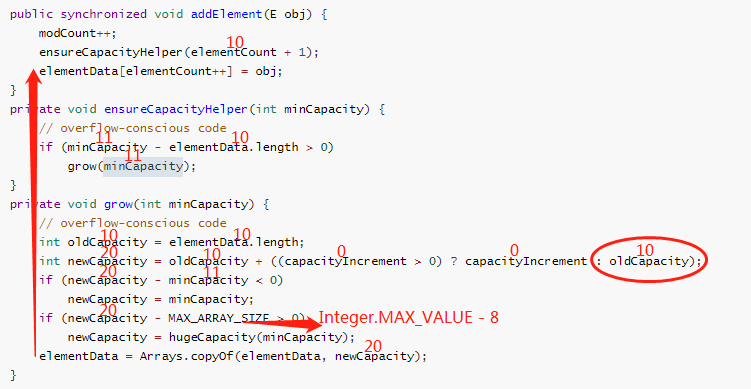
- 案例三,initialCapacity为10, capacityIncrement为0,elementCount为10
- add()方法,与addElement()方法基本相同,只是多了一个添加成功与否的返回值
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
- removeElementAt()方法
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
- removeElements()方法
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
int i = indexOf(obj); //找到数组中第一个与给定对象相同对象的索引
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
- remove()方法
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == -1)
throw new IllegalStateException();
synchronized (Vector.this) {
checkForComodification();
Vector.this.remove(lastRet);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
/**
Copies an array from the specified source array, beginning at the specified position, to the specified position of the destination array. A subsequence of array components are copied from the source array referenced by `src` to the destination array referenced by `dest`. The number of components copied is equal to the `length` argument. The components at positions `srcPos` through `srcPos+length-1` in the source array are copied into positions `destPos` through `destPos+length-1`, respectively, of the destination array.If the `src` and `dest` arguments refer to the same array object, then the copying is performed as if the components at positions `srcPos` through `srcPos+length-1` were first copied to a temporary array with `length` components and then the contents of the temporary array were copied into positions `destPos` through `destPos+length-1` of the destination array.
* @param src the source array.
* @param srcPos starting position in the source array.
* @param dest the destination array.
* @param destPos starting position in the destination data.
* @param length the number of array elements to be copied.
**/
/**
从指定的源数组将数组从指定位置开始复制到目标数组的指定位置。数组组件的子序列从“src”引用的源数组复制到“dest”引用的目标数组。复制的组件数等于“length”参数。源数组中位置为“srcPos”到“srcPos+length-1”的组件将分别复制到目标的位置“destPos”到“destPos+length-1”数组。如果“src”和“dest”参数引用同一个数组对象,然后执行复制,就好像首先将位置为“srcPos”到“srcPos+length-1”的组件复制到具有“length”组件的临时数组中,然后将临时数组的内容复制到目标数组的“destPos”到“destPos+length-1”的位置。
*@param src源数组。
*@param srcPos源数组中的起始位置。
*@param dest目标数组。
*@param destPos目标数据中的起始位置。
*@param length要复制的数组元素数。
**/
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);






















 925
925

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








