相关文章:
【网络编程socket】图解 Java NIO BIO MIO AIO 四大IO模型与原理
【网络编程socket】BIO & Socket和ServerSocket API & 入门例子
【网络编程socket】java NIO编程示例以及流程详解
1. NIO架构图

2. 服务端代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class ServerSocketChannels implements Runnable {
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
protected Selector selector;
private volatile boolean stop;
public ServerSocketChannels() {
}
public ServerSocketChannels(int port) {
try {
//创建多路复用器selector,工厂方法
selector = Selector.open();
//创建ServerSocketChannel,工厂方法
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定ip和端口号,默认的IP=127.0.0.1,对连接的请求最大队列长度设置为backlog=1024,
// 如果队列满时收到连接请求,则拒绝连接
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port), 1024);
//设置非阻塞方式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//注册serverSocketChannel到selector多路服用器上面,监听accept请求
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("the time is start port = " + port);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
public void stop() {
this.stop = true;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//如果server没有停止
while (!stop) {
try {
//selector.select()会一直阻塞到有一个通道在你注册的事件上就绪了
//selector.select(1000)会阻塞到1s后然后接着执行,相当于1s轮询检查
selector.select(1000);
//找到所有准备接续的key
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
key = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
//处理准备就绪的key
handle(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (key != null) {
//请求取消此键的通道到其选择器的注册
key.cancel();
//关闭这个通道
if (key.channel() != null) {
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (selector != null) {
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void handle(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
//如果key是有效的
if (key.isValid()) {
//监听到有新客户端的接入请求
//完成TCP的三次握手,建立物理链路层
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
doAccept(key);
}
//监听到客户端的读请求
if (key.isReadable()) {
doReadable(key);
}
}
}
/**
* 处理客户端连接事件
*
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
public void doAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) ssc.accept();
//设置客户端链路为非阻塞模式
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//将新接入的客户端注册到多路复用器Selector上
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
public void doReadable(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
//获得通道对象
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//从channel读数据到缓冲区
int readBytes = sc.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0) {
//Flips this buffer. The limit is set to the current position and then
// the position is set to zero,就是表示要从起始位置开始读取数据
readBuffer.flip();
//eturns the number of elements between the current position and the limit.
// 要读取的字节长度
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
//将缓冲区的数据读到bytes数组
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": the time server receive order: " + body);
String currenttime = "query time order".equals(body) ? new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "bad order";
doWrite(sc, currenttime);
} else if (readBytes < 0) {
key.channel();
sc.close();
}
}
public void doWrite(SocketChannel channel, String response) throws IOException {
if (response != null && !"".equals(response)) {
byte[] bytes = response.getBytes();
//分配一个bytes的length长度的ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer write = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
//将返回数据写入缓冲区
write.put(bytes);
write.flip();
//将缓冲数据写入渠道,返回给客户端
channel.write(write);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8010;
ServerSocketChannels server = new ServerSocketChannels(port);
// ServerSocketChannels2 server = new ServerSocketChannels2(port);
new Thread(server, "timeserver-001").start();
}
}
3. 客户端代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class TimeClientHandler implements Runnable {
//服务器端的ip
private String host;
//服务器端的端口号
private int port;
//多路服用选择器
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
public TimeClientHandler(String host, int port){
this.host = host == null ? "127.0.0.1": host;
this.port = port;
try {
//初始化一个Selector,工厂方法
selector = Selector.open();
//初始化一个SocketChannel,工厂方法
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//设置非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
/**
* 首先尝试连接服务端
* @throws IOException
*/
public void doConnect() throws IOException {
//如果连接成功,像多路复用器selector监听读请求
if(socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(this.host, this.port))){
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//执行写操作,像服务器端发送数据
doWrite(socketChannel);
}else {
//监听连接请求
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
}
public static void doWrite(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException {
//构造请求消息体
byte [] bytes = "query time order".getBytes();
//构造ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer write = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
//将消息体写入发送缓冲区
write.put(bytes);
write.flip();
//调用channel的发送方法异步发送
sc.write(write);
//通过hasRemaining方法对发送结果进行判断,如果消息全部发送成功,则返回true
if(!write.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println("send order to server successd");
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
doConnect();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
while (!stop){
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> its =keys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (its.hasNext()){
key = its.next();
its.remove();
try {
handle(key);
}catch (Exception e){
if(key != null){
key.cancel();
if(key.channel() != null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
public void handle(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
if(key.isValid()){
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if(key.isConnectable()){
//如果连接成功,监听读请求
if(sc.finishConnect()){
sc.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//像服务端发送数据
doWrite(sc);
}else{
System.exit(1);
}
}
//监听到读请求,从服务器端接受数据
if(key.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = sc.read(byteBuffer);
if(readBytes > 0){
byteBuffer.flip();
byte [] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.remaining()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("now body is "+ body);
stop = true;
}else if(readBytes < 0){
key.cancel();
sc.close();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8010;
TimeClientHandler client = new TimeClientHandler("",port);
new Thread(client,"client-001").start();
}
}
4. 运行
4.1 非nio客户端
启动服务端后,可以用任意的方式给服务端发送数据,而客户端可以是telnet,可以是原始的sokety,也是nio写的客户端。
客户端向服务器发送一个非字符串“query time order”,然后服务器回错误提示“bad order”,意思是错误的请求。
我们直接telnet localhost 8010,分别输入一些字符,分别输入“a,1,3”查看:
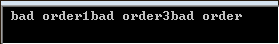
服务端控制台输出:
timeserver-001: the time is start port = 8010
timeserver-001: the time server receive order: a
timeserver-001: the time server receive order: 1
timeserver-001: the time server receive order: 3
4.2 nio客户端
nio客户端向服务器发送一个字符串“query time order”,然后服务器回写一个日期。
服务端控制台输出:
the time is start port = 8010
timeserver-001: the time server receive order: query time order
客户端控制台输出:
send order 2 server successd
now body is Tue Jun 15 10:39:03 CST 2021 '收到了服务器端发来的日期'
参考:
《java NIO示例以及流程详解》 参考主体
《Java Nio服务端怎么发送数据给Socket Io》
《Socket+NIO实现客户端与服务器的通信的Demo》
《NIO包下SocketChannel的用法》
























 1205
1205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








