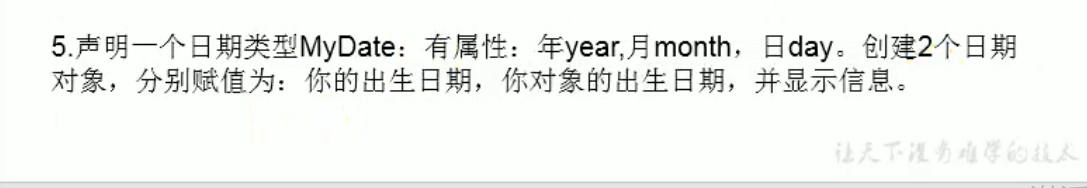
- 什么是类的成员?
package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
class Person {
// 属性=成员变量
String name;
boolean isMarried;
// 构造器
public Person() {
}
public Person(String n, boolean im) {
name = n;
isMarried = im;
}
// 方法或函数
public void walk() {
System.out.println("人走路");
}
public String display() {
return "名字是:" + name + ",Married:" + isMarried;
}
// 代码块
{
name = "HanMeiMei";
age = 17;
isMarried = true;
}
// 内部类
class pet {
String name;
float weight;
}
}
}
}
方法、属性、构造器、接口、代码块。
- 什么是面向对象的三大特征?
封装性、继承性、多态性。 - 如何创建对象并调用类的属性、方法?
package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建Person类的对象 = 类的实例化 = 实例化类
Person p1 = new Person();
// 调用属性:对象.属性
p1.name = "zzf";
System.out.println(p1.name);
// 调用方法:对象.方法
p1.eat();
Person p2 = new Person();
System.out.println(p2.name);//null
Person p3 = p1;//同一个地址值,赋值
System.out.println(p3.name);//zzf
}
}
class Person {
// 属性/成员变量
String name;
int age = 1;
boolean isMale;
// 方法
public void eat() {
System.out.println("人可以吃饭!");
}
}
-
对象的内存如何解析?


-
权限修饰符有什么不同?
属性(成员变量):可以在声明属性时,指明其权限,使用权限修饰符。
常用的权限修饰符:public、private、缺省、protected.
局部变量不可以使用权限修饰符。 -
局部变量和属性有哪些区别?
package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u = new User();
//属性(成员变量)有默认的初始化值
//局部变量没有默认初始化值
System.out.println(u.name);//null
System.out.println(u.age);//0
//特别的,形参调用时初始化即可
u.talk("chinese");
}
}
class User {
// 属性(成员变量):直接定义在类的一对{}内
// 局部变量:声明在方法内、方法形参、代码块内、构造形参、构造器内部的变量。
//属性加载到堆中(非static),局部变量加载到栈中
// 属性(成员变量)
String name;
int age;
boolean isMale;
public void talk(String language) {// language形参,也是局部变量
System.out.println("我们使用" + language + "进行交流");
}
public void eat() {
String food = "烙饼";// 局部变量
System.out.println("我们喜欢吃" + food);
}
}
- 练习

package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.age = 18;
p1.name = "Tom";
p1.sex = 1;
p1.study();
p1.showAge();
p1.addAge(2);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
int sex;
public void study(){
System.out.println("studying");
}
public void showAge(){
System.out.println(age);
}
public int addAge(int i){
age += i;
return age;
}
}
- 利用面向对象的编程方法,设计计算圆的面积。
package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 利用面向对象的编程方法,设计计算圆的面积。
Customer c1 = new Customer();
double s1 = c1.getCircle(2);//有返回值所以用变量储存
System.out.println(s1);
c1.circle(3);
}
}
// 方式一:
class Customer {
public double getCircle(double r) {
double s = r * r * Math.PI;
return s;
}
}
// 方式二:
class Customer {
double r;
public void circle(double r) {
double s = r * r * Math.PI;// 没有返回值,所以要先输出
System.out.println(s);
}
}

package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JuXing j1 = new JuXing();
// j1.method();
int s = j1.method(11,11);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
//声明一个method方法,在方法中打印一个10 * 8的*型矩形,
//在main方法中调用该方法。
class JuXing{
// public void method(){
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
// System.out.print("*" + "\t");
// }
// System.out.println();
//
// }
// }
//修改上一个程序,在method方法中,除打印一个10 * 8的*型矩形,再计算该矩形
//的面积,并将其作为方法的返回值。在main方法中调用该方法,
//接收返回的面积值并打印。
// public int method(){
// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
// System.out.print("*" + "\t");
// }
// System.out.println();
//
// }
// return 10 * 8;
//
// }
//修改上一个程序,在main方法中提供m和n两个参数,方法中打印一个m * n的矩形,
//再计算该矩形的面积,并将其作为方法的返回值。在main方法中调用该方法,
//接收返回的面积值并打印。
public int method(int m,int n){
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
System.out.print("*" + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
return m * n;
}
}

package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//声明Student类型的数组
Student[] s1 = new Student[20];//String[] arr = new String[20];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
//给数组元素赋值
s1[i] = new Student();
//给Student对象的属性赋值
s1[i].number = i + 1;
s1[i].state = (int) (Math.random() * 10) + 1;
s1[i].score = (int) (Math.random() * 90) + 10;
//打印出年级为3(state)的学生信息。
if (s1[i].state == 3) {
System.out.println(s1[i].info());
System.out.println();
}
}
System.out.println("**************");
//使用冒泡排序进行排序
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < s1.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (s1[j].score > s1[j + 1].score) {
//如果需要换序,交换的是数组的元素,Student对象。
Student temp = s1[j];
s1[j] = s1[j + 1];
s1[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
//遍历对象数组
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s1[i].info());
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class Student {
int number;//学号
int state;//年级
int score;//分数
//调用属性
public String info(){
return "学号:" + number +'\t' + "年级:" +
state + '\t' + "分数:" + score;
}
}
完善后`
package com.atguigu.contact;
public class ZhuShi {
//无论在哪个类声明的属性、方法,都要在main方法中创建对象并调用。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 声明Student类型的数组
Student[] s1 = new Student[20];// String[] arr = new String[20];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
// 给数组元素赋值
s1[i] = new Student();
s1[i].number = i + 1;
s1[i].score = (int)(Math.random()*90 )+ 10;
s1[i].state = (int)(Math.random()*10) + 1;
}
ZhuShi z1 = new ZhuShi();
z1.print(s1);//有返回值用接收
z1.searchState(s1, 3);
z1.maoPao(s1);
}
/**
*
* @Description 遍历数组
* @param s1要遍历的数组
*
*/
public void print(Student[] s1) {
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s1[i].info());
System.out.println();
}
}
/**
*
* @Description 输出指定年级的信息的方法
* @param s1 要遍历的数组
*
* @param state指定的年级的变量
*
*/
public void searchState(Student[] s1, int state) {
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
if (s1[i].state == state) {
System.out.println(s1[i].info());
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/**
*
* @Description 对数组进行冒泡排序的方法
* @param s1 要排序的数组
* @param score 要比较的分数
*/
public void maoPao(Student[] s1){
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < s1.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (s1[j].score > s1[j + 1].score) {
// 如果需要换序,交换的是数组的元素,Student对象。
Student temp = s1[j];
s1[j] = s1[j + 1];
s1[j + 1] = temp;
s1[i].info();
}
}
}
}
}
class Student {
int number;// 学号
int state;// 年级
int score;// 分数
// 调用属性
public String info() {
return "学号:" + number + '\t' + "年级:" + state + '\t' + "分数:" + score;
}
}






















 211
211











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








