文章目录
JAVAEE之多线程初
1.线程的概念
一个线程就是一个"执行流",每个线程之间都可以按照顺序执行自己的代码.多个线程之间"同时"执行着多份代码
2.进程与线程的区别
- 进程包含线程.每个进程至少有一个线程存在,即主线程
- 进程有独立的内存空间和文件描述符表.同一个进程中的多个线程之间,共享同一份地址空间和文件描述表
- 进程是操作系统资源分配的基本单位,线程是操作系统调度执行的基本单位
- 进程之间具有独立性,一个进程挂了,不会影响到别的进程;同一个进程里的多个线程之间,一个线程挂了,可能会把整个进程带走,影响到 其他线程.
3.Java代码如何创建线程
- 继承Thread重写run
- 实现runnable,重写run
- 继承Thread,匿名内部类
- 实现Runnable,匿名内部类
- lambda
4.Thread
1.多线程程序和普通程序的区别
Java 标准库中提供了一个Thread 能够表示一个 线程
class Mythread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello world")
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先创建MyThread实例 t 的引用实际上是指向子类的实例
Thread t = new MyThread();
//启动线程,在进程中形成了另外一个流水线,新的流水线开始并发的执行
t.start;
}
上述代码涉及两个线程:
- main 方法所对应的线程(一个进程里至少有一个线程) 也可以成为 主线程
- 通过 t.start 创建的新的线程
start 方法:创建一个线程,新的线程将会执行 run 方法
run 方法: 表示了线程的入口方法是啥.(线程启动起来,要执行哪些逻辑)(不是让程序员调用,要交给系统去自动调用)
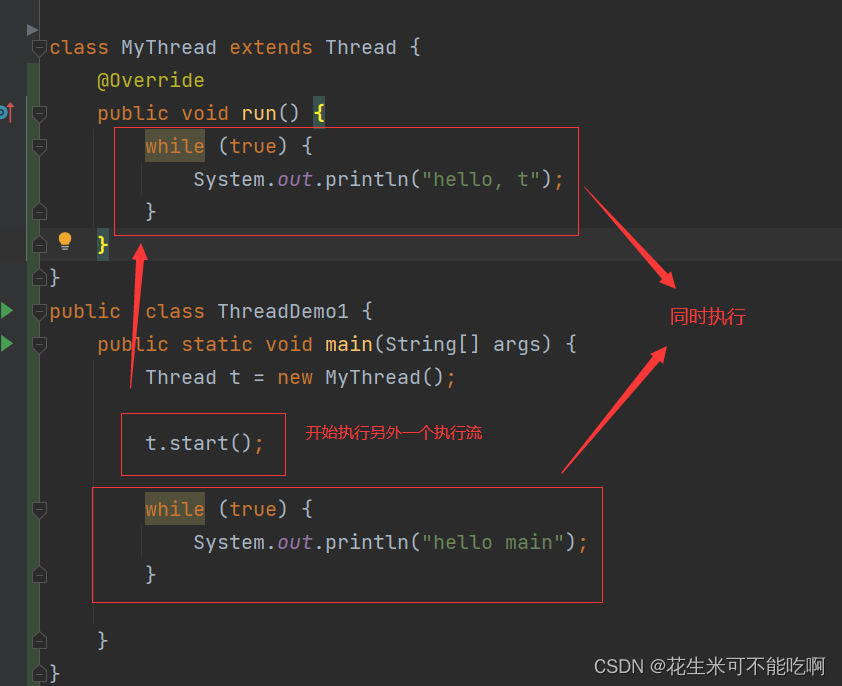
以下体会:每个线程是一个独立的执行流
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello, t");
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new MyThread();
t.start();
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello main");
}
}
}
此时,hello t 和 hello main 都能打印出来
]
2.创建线程方法一 继承Thread类 重写 run
run 不是一个随便的方法, 是重写了父类的方法 , 这种重写一般就是 功能的扩展
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello ,t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//sleep 睡眠过程中,还没到点的就提前唤醒
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new MyThread();
//start 会创建新的线程
//run 不会创建新的线程.run 是在 main 线程中执行的~
t.run();
t.start();//调用系统api ,创建新线程,新的线程里面调用 t.run
while(true) {
System.out.println("hello,main");
Thread.sleep(1000);
//sleep 是 Thread 的静态方法 参数单位是 ms
}
}
}
3.创建线程方法二 实现 runnable 接口 重写 run
Runnable 字面意思是可运行的.使用 Runnable 描述一个具体的任务
通过 run 方法来描述
方法一是使用 Thread 的 run 描述线程入口
方法二是使用 Runnable interface 来描述线程入口
//runnbale字面意思是可运行的
class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread t = new Thread(runnable);
t.start();
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4.创建线程方法三 继承 Thread 使用匿名内部类
//匿名内部类
public class ThreadDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t.start();
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5.创建线程方法四 实现Runnable 使用匿名内部类
//实现runnable 匿名内部类
public class ThreadDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new MyRunnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
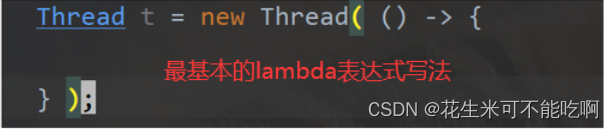
6.lambda 表达式
lamdba 表达式, 本质就是一个匿名函数(没有名字的函数)
Java 里面,函数(方法)是无法脱离的
lambda 表达式基本写法
() -> {
}
解释: () 里面放参数,如果只有一个参数,() 可以省略
{ } 里面放函数体,写Java 代码 若只有一行代码,也可省略 { }
//lambda
public class ThreadDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread( () -> {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello t");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello main");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
7.Thread 类里面的其他方法
每个线程都有一个唯一的 Thread 对象与之关联 .Java 代码中的 Thread 对象和操作系统中的线程是一一对应的
| Thread() |
|---|
| Thread(Runnable target) |
| Thread(String name) |
| Thread(Runnable target,String name) |
name 参数 ,是给线程起了个名字.这里的名字不影响程序执行,只是方便在调试的时候,快速找到线程
| 属性 | 获取方法 |
|---|---|
| ID | getId() |
| 名称 | getName() |
| 状态 | getState() |
| 优先级 | getPriority() |
| 是否后台线程 | isDaemon() |
| 是否存活 | isAlive() |
| 是否被中断 | isInterrupted() |
isDaemon() : true 表示的是 后台进程
false 表示的是前台进程
前台线程会阻止 Java 进程结束,必须得 Java 进程中所有的前台线程都执行完 , Java 进程才能结束 . 创建的线程默认是前台的 , 可以通过 setDaemon 设置成后台的
isAlive() : 描述 系统内核 里的那个线程是否存活的
线程的入口方法执行完毕,此时系统中的对应线程就没了,此时调用该线程 isAlive 就是 false.
系统对于线程的调度 , 是随机的 . 假设你的机器上面有很多的线程和进程 . 此时cpu 调度了一圈 , 消耗的时间就可能非常长 . 此时就可能导致某个线程隔了很久也没有调度上去.;例如"电脑卡了"
统中的对应线程就没了,此时调用该线程 isAlive 就是 false.
系统对于线程的调度 , 是随机的 . 假设你的机器上面有很多的线程和进程 . 此时cpu 调度了一圈 , 消耗的时间就可能非常长 . 此时就可能导致某个线程隔了很久也没有调度上去.;例如"电脑卡了"





















 700
700











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








