一、数据准备
1、字段解释
| orderID | 订单ID |
| userID | 用户ID |
| goodsID | 商品ID |
| orderAmount | 订单金额 |
| payment | 支付金额 |
| channelID | 销售渠道 |
| platformType | 支付方式 |
| orderTime | 下单时间 |
| payTime | 支付时间 |
| chargeback | 拒付 |
2、导入相应的包
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'].insert(0, 'SimHei')
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'3、读如数据并且用index_col='id'将id设为索引列,读出数据10万条
orders_df = pd.read_excel('data/某电商平台2021年订单数据.xlsx',index_col='id')
orders_df
4、修改渠道字段的列名为channelID,平台字段的列名为platformType
orders_df.rename(columns={'chanelID':'channelID','platfromType':'platformType'},inplace=True)5、筛选出2021年的订单(orderTime在2021年)
先将年份不在2021年的数据的数据索引获取出来再在原表中删除将其对应的索引。
index = orders_df[orders_df.orderTime.dt.year != 2021].index
orders_df.drop(index = index,inplace=True)6、删除支付金额(payment)小于0的订单,删除支付金额(payment)大于订单金额(orderAmount)的订单,删除支付时间(payTime)早于下单时间(orderTime)的订单,删除支付时长超过30分钟的订单
1)、先删除支付金额(payment)小于0的订单,和删除支付时间(payTime)早于下单时间(orderTime)的订单
index = orders_df[(orders_df.payment < 0) | (orders_df.payTime < orders_df.orderTime)].index
orders_df.drop(index = index,inplace= True)
orders_df2)删除支付时长超过30分钟的订单
先将订单的支付时长按秒统计出来并且筛选
index = orders_df[(orders_df.payTime - orders_df.orderTime).dt.total_seconds() > 1800].index
orders_df.drop(index = index,inplace=True)3)支付金额(payment)大于订单金额(orderAmount)的订单,将支付金额修改为订单金额乘以平均折扣
先算出订单的平均折扣率
a,b = orders_df[orders_df.payment <= orders_df.orderAmount][['orderAmount','payment']].sum()
mean_discount = b / a发现折扣率基本在0.95上。最后用where将支付金额进行修改
# Series.where - 满足条件的保留原来的值,不满足条件用第二个参数值
# Series.mask - 满足条件的被替换掉,不满足条件保留原来的值
orders_df['payment'] = orders_df.payment.where(
orders_df.payment <= orders_df.orderAmount,
(orders_df.orderAmount * mean_discount).round(2)
)7、将渠道(channelID)字段的空值填充为众数
# 找出字段的众数在用fillna进行填充
mode_value = orders_df.channelID.mode()[0]
orders_df.channelID.fillna(mode_value,inplace=True)
orders_df.info()8、处理掉平台(platformType)字段的异常值(最后只有四种值:微信、支付宝、App、Web)

orders_df['platformType'] = orders_df.platformType.str.replace(
r'[·\s]','',regex = True
).str.title().replace(
r'薇信|Vx','微信',regex = True
).str.replace(
r'网页|网站','Web',regex = True
)二、数据分析
1、统计出核心指标,包括:GMV、净销售额、客单价、拒退率、复购率
GVM = orders_df.orderAmount.sum()
sales = orders_df.query('not chargeback').payment.sum()
# 客单价 用户数量进行去重nunique()
arppu = sales / orders_df.userID.nunique()
brate = orders_df.query('chargeback').orderID.count() / orders_df.orderID.nunique()temp = pd.pivot_table(
orders_df.query('not chargeback'),
index = 'userID',
values = 'orderID',
aggfunc='nunique'
).rename(columns= {'orderID':'orderCount'})
ser = temp.orderCount.map(lambda x: 1 if x > 1 else 0)
rrate = ser.sum() / ser.count()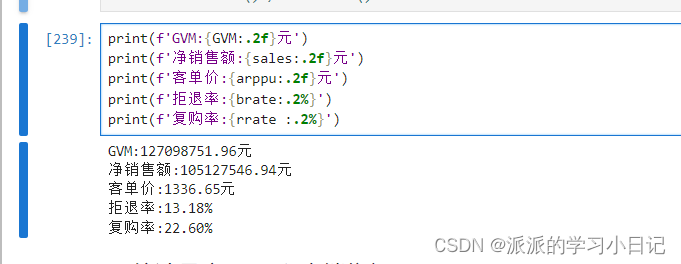
2、 统计月度GMV和净销售额
先分别创建
temp1 = pd.pivot_table(
orders_df,
index = 'month',
values= 'orderAmount',
aggfunc='sum'
).rename(columns={'orderAmount':'GMV'})
temp2 = pd.pivot_table(
orders_df.query('not chargeback'),
index = 'month',
values = 'payment',
aggfunc = 'sum'
).round(2).rename(columns={'payment':'净销售额'})
# temp = pd.concat((temp1,temp2),axis = 1)
temp = pd.merge(temp1,temp2,how = 'inner',left_index = True,right_index= True)
temp两个指标的透视表在用merge对数据进行重塑

对数据进行可视化
temp.plot(kind = 'line',figsize = (10,4),marker = '*',linewidth = 0.5,linestyle = '--')
plt.ylim(0,14000000)
plt.xticks(temp.index)
plt.legend(loc = 'lower right')
plt.show()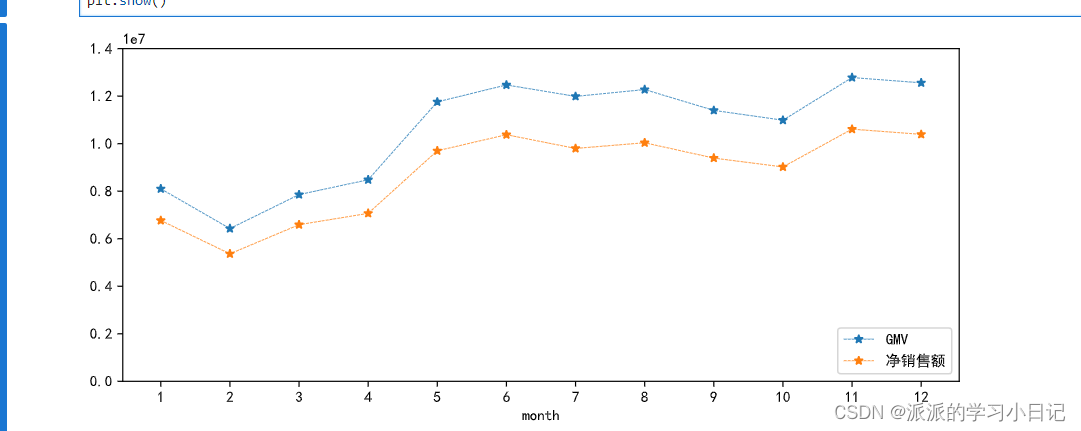
3、统计各渠道对流量(订单量)的贡献占比
先创建透视表
temp5 = orders_df.pivot_table(
index = 'channelID',
values= 'orderID',
aggfunc='count'
).rename(columns={'orderID':'orderID_count'})
temp5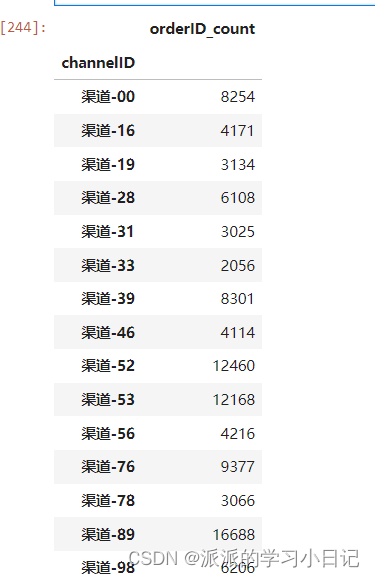
数据进行可视化

4、 统计星期几用户下单量最高
先用weekday找出星期几并且添加
orders_df['weekday'] = (orders_df.orderTime.dt.weekday + 1) % 7tem4 = orders_df.pivot_table(
index='weekday',
values='orderID',
aggfunc='nunique'
)
temp4.plot(kind='bar', figsize=(8, 4), xlabel='', legend=False)
for i in np.arange(7):
plt.text(i, temp4.orderID[i] + 100, temp4.orderID[i], ha='center', fontdict=dict(size=9))
plt.xticks(np.arange(7), labels=[f'星期{x}' for x in '日一二三四五六'], rotation=0)
plt.show()
5、 统计每天哪个时段用户下单量最高
先对时间用对时间字段进行向下取整,并提出时间的时分
orders_df['time'] = orders_df.orderTime.dt.floor('30T').dt.strftime('%H:%M')
temp6 = pd.pivot_table(
orders_df,
index = 'time',
values='orderID',
aggfunc='nunique'
)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4),dpi = 200)
plt.bar(temp6.index,temp6.orderID,color = np.random.random((8,3)),width = 0.5)
plt.xticks(rotation = 75)
plt.show()
6、以自然月为窗口计算每个月的复购率
直接创建透视表
temp7 = pd.pivot_table(
orders_df.query('not chargeback'),
columns='month',
index = 'userID',
values = 'orderID',
aggfunc='nunique'
)
temp7 = temp7.map(lambda x: x if np.isnan(x) else (1 if x > 1 else 0))
temp7.sum()/temp7.count()
# temp7.sum()有复购行为的人数,temp7.count()有购买行为的人数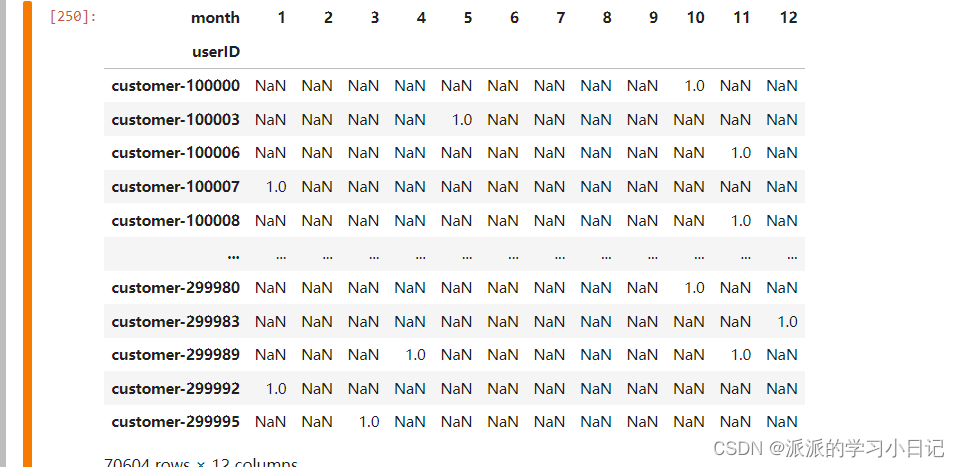

8、用RFM模型实现用户价值分群
1、r recency:用户的新近性,最后一次消费时间体现。
2、f frequency:用户的消费频率
3、m monetary:用户的消费金额
所以这里直接创建的是透视表对orderTim下单时间求最大值作为用户消费的最近时间R,'orderID'订单编号用count计算用户的消费频率F,用sum计算'payment'用户的总消费金额M
rfm_model_df = pd.pivot_table(
orders_df.query('not chargeback'),
index = 'userID',
values=['orderTime','orderID','payment'],
aggfunc={
'orderTime':'max',
'orderID':'nunique',
'payment':'sum'
}
).rename(columns={'orderTime':'R','orderID':'F','payment':'M'})
rfm_model_df在计算出用户距离2021年12月31日59时59分的间隔天数,再对列进行排序
from datetime import datetime
rfm_model_df['R'] = (datetime(2021,12,31,23,59,59) - rfm_model_df.R).dt.days
# reindex- 调整行索引或列索引的顺序(也可用花式索引来调整)
rfm_model_df = rfm_model_df.reindex(columns=['R','F','M'])
rfm_model_df将RFM模型的原始数据处理为对应的等级
def handle_r(value):
if value <= 14:
return 5
elif value <= 30:
return 4
elif value <= 90:
return 3
elif value <= 180:
return 2
return 1
def handle_f(value):
if value >= 5:
return 5
return value
def handle_m(value):
if value < 500:
return 1
elif value < 800:
return 2
elif value < 1200:
return 3
elif value < 2500:
return 4
return 5
使用 apply() 方法将 handle_r、 handle_f、handle_m函数应用到 R 列的每一个值上,并将处理后的值赋值回 rfm_model_df 中的 R、F、M列
rfm_model_df['R'] = rfm_model_df.R.apply(handle_r)
rfm_model_df['F'] = rfm_model_df.F.apply(handle_f)
rfm_model_df['M'] = rfm_model_df.M.apply(handle_m)
Pandas 的 map() 函数和 lambda 表达式,将每一列中高于平均值的数据点替换为 ‘高’,低于平均值的数据点替换为 ‘低’。
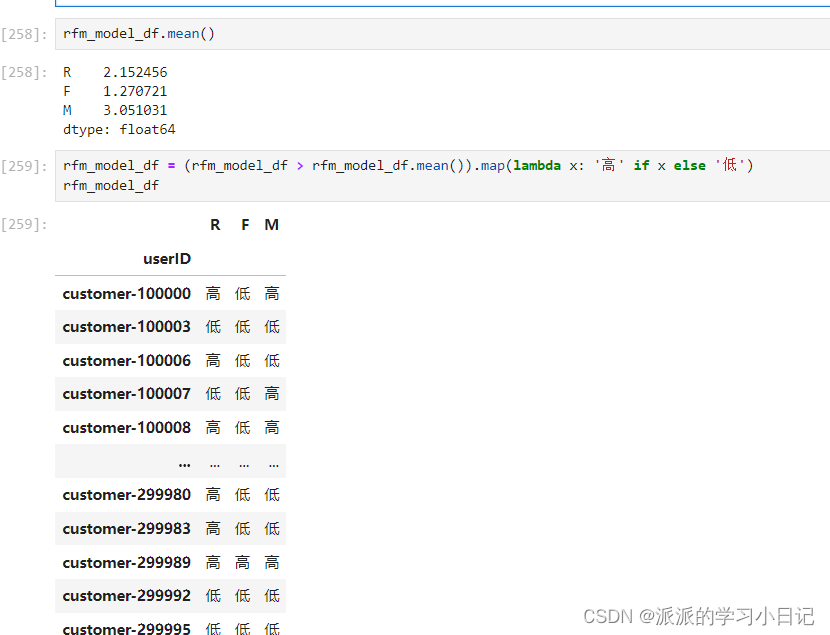 对群体打上标签并对不同的客户群体进行计数判断客户的价值
对群体打上标签并对不同的客户群体进行计数判断客户的价值




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








