图
1.表示
用邻接矩阵表示:
带权的图用无穷大初始化矩阵
—意思:顶点不可到达,
但是自己可以到达自己,距离是0 。
不带权的图用0 就可以。



 上面的查找顶点用散列改进比较好。
上面的查找顶点用散列改进比较好。
邻接矩阵的用法:
无向图:
邻接表:
这里默认A,B,C,D都是起点
与其他点邻接,则拓展一个单链表。
 ### 二、有向图的邻接表
### 二、有向图的邻接表
这里是分为正向和逆向的邻接表
 ### 三、网络带权图的连接表
### 三、网络带权图的连接表

这里讲第三种的具体代码实现
第一步:
1.构建结点( 存相邻的结点 (包括位置下标 , 权重 , 指针域 ) )
 2.构建类(就是单链表的类)
2.构建类(就是单链表的类)
包括指针域和数据域。
指针指向的结点类型是 Edge ( 边结点类型 )
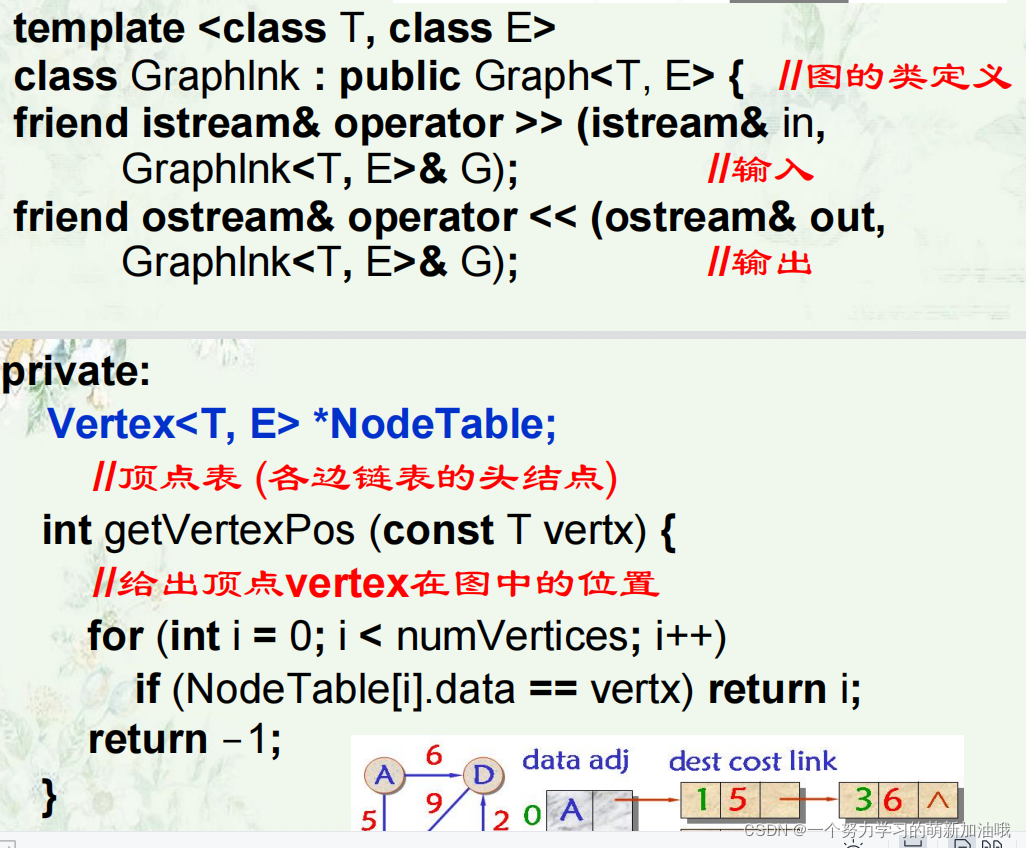
顶点表、
有头指针、
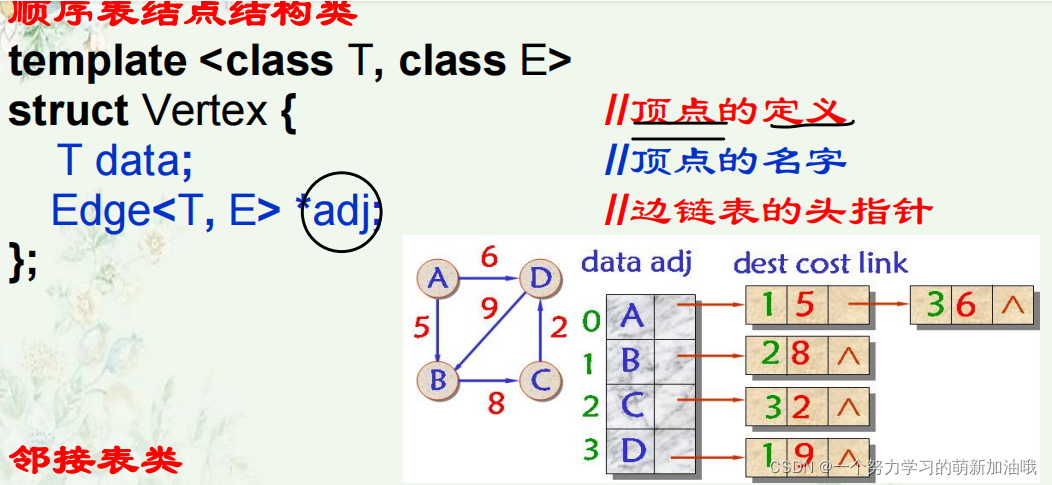
data域是存该结点的值,比如图中的 A , B ,C ,D 等。
 析构需要先析构链表,再析构数组
析构需要先析构链表,再析构数组
=====================
下面是创建

完整代码:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//图的邻接表结构
const int DefaultVertices = 30;//默认最大顶点数
//边结点
template<class T>//T为顶点名字
struct Edge {
int dest;//边的另一个顶点的位置
int cost;//边上的权值
Edge<T>* link;//这个点的下一条边
Edge() { dest = -1; cost = 0; link = NULL; }
Edge(int num, int weight) { dest = num; cost = weight; link = NULL; }
};
//顶点
template<class T>//T为数据
struct Vertex {
T data;//顶点名字
Edge<T>* adj;//边链表的头指针
};
//图
template<class T>//T为顶点名字
class Graph {
public:
int maxVertices;//图中最大顶点数
int numEdges;//当前边数
int numVertices;//当前顶点数
Vertex<T>* NodeTable;//顶点表(各边链表的头指针)
int getVertexPos(T vetrex) {//给出顶点vetrex在图中的位置
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
if (NodeTable[i].data == Vertex)return i;
}
return -1;
}
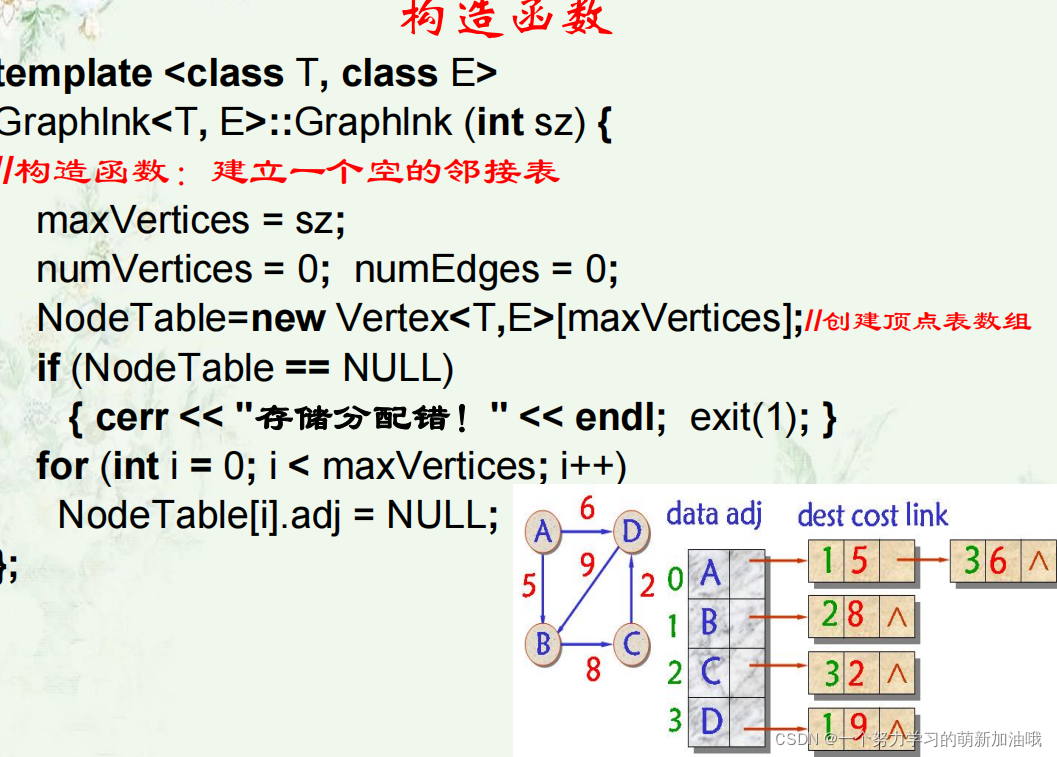
Graph(int sz = DefaultVertices) {//初始化
maxVertices = sz; numVertices = 0; numEdges = 0;
NodeTable = new Vertex<T>[maxVertices];//创建顶点表数组
for (int i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++) {
NodeTable[i].adj = NULL;//边链表头指针赋空
}
}
~Graph() { delete[]NodeTable; }
//图输入
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Graph<T>& G) {
int n,v1pos, v2pos;//序号
T v1, v2; int w;
cout << "请输入序号选择图的类型:1.无向图 2.有向图" << endl;
in >> n;//输入序号
switch (n) {
case 1:
cout << "请输入无向图的顶点总数:"; in >> G.numVertices;
while (G.numVertices > G.maxVertices || G.numVertices < 0) {
cout << "顶点总数不能超过30个,也不能是负数,请重新输入:"; in >> G.numVertices;
}
cout << "请输入各顶点的名字:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertices; i++) {
in >> G.NodeTable[i].data;
}
cout << "请输入边的总数:"; in >> G.numEdges;
while (G.numVertices < 0) {
cout << "边的总不能是负数,请重新输入:"; in >> G.numEdges;
}
cout << "请输入各边连接的两个顶点:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numEdges; i++) {
int f = 0;
in >> v1 >> v2;
for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertices; j++) {
//判断输入顶点是否在图内
if (v1 == G.NodeTable[j].data) {
f++; v1pos = j;//记录顶点在顶点表的位置
}
if (v2 == G.NodeTable[j].data) {
f++; v2pos = j;
}
if (f == 2)break;
}
if (f < 2) {
cout << "有顶点不存在图内,请重新输入两个顶点和边的权值:";
i--;
}
else {
Edge<T>* p = G.NodeTable[v1pos].adj;
//v1顶点添加边
if (p == NULL) {//该顶点还没有边时
p = new Edge<T>;//创建边
G.NodeTable[v1pos].adj = p;//p为边链表的头结点
}
else {
while (p->link != NULL)p = p->link;//来到最后一个结点
Edge<T>* t = new Edge<T>;//创建边
p->link = t;
p = t;
}
p->dest = v2pos;//边的另一个顶点的位置
//p->cost = w;//边的权值
p->link = NULL;//下一条边赋值为空
//v2顶点添加边
p = G.NodeTable[v2pos].adj;
if (p == NULL) {//该顶点还没有边时
p = new Edge<T>;//创建边
G.NodeTable[v2pos].adj = p;//p为边链表的头结点
}
else {
while (p->link != NULL)p = p->link;//来到最后一个结点
Edge<T>* t = new Edge<T>;//创建边
p->link = t;
p = t;
}
p->dest = v1pos;//边的另一个顶点的位置
//p->cost = w;//边的权值
p->link = NULL;//下一条边赋值为空
}
}
break;
case 2:
cout << "请输入有向图的顶点总数:"; in >> G.numVertices;
while (G.numVertices > G.maxVertices || G.numVertices < 0) {
cout << "顶点总数不能超过30个,也不能是负数,请重新输入:"; in >> G.numVertices;
}
cout << "请输入各顶点的名字:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertices; i++) {
in >> G.NodeTable[i].data;
}
cout << "请输入边的总数:"; in >> G.numEdges;
while (G.numVertices < 0) {
cout << "边的总不能是负数,请重新输入:"; in >> G.numEdges;
}
cout << "请输入各边连接的始顶点、终顶点:"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numEdges; i++) {
int f = 0;
in >> v1 >> v2;
for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertices; j++) {
//判断输入顶点是否在图内
if (v1 == G.NodeTable[j].data) {
f++; v1pos = j;//记录顶点在顶点表的位置
}
if (v2 == G.NodeTable[j].data) {
f++; v2pos = j;
}
if (f == 2)break;
}
if (f < 2) {
cout << "有顶点不存在图内,请重新输入两个顶点和边的权值:";
i--;
}
else {
Edge<T>* p = G.NodeTable[v1pos].adj;
//v1始顶点添加边
if (p == NULL) {//该顶点还没有边时
p = new Edge<T>;//创建边
G.NodeTable[v1pos].adj = p;//p为边链表的头结点
}
else {
while (p->link != NULL)p = p->link;//来到最后一个结点
Edge<T>* t = new Edge<T>;//创建边
p->link = t;
p = t;
}
p->dest = v2pos;//边的终顶点的位置
// p->cost = w;//边的权值
p->link = NULL;//下一条边赋值为空
}
}
break;
default:cout << "序号输入错误!" << endl;
}
return in;
}
//图的输出
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Graph<T>& G) {
cout << "顶点集合:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertices;i++) {
cout << G.NodeTable[i].data << ' ';
}
cout << endl << "边集合:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertices;i++) {
Edge<T>* p = G.NodeTable[i].adj;
if (p != NULL) {//顶点有边时
cout << "与" << G.NodeTable[i].data << "相连的边有:";
while (p != NULL) {
cout << "(" << G.NodeTable[i].data << "," << G.NodeTable[p->dest].data << ") ";
p = p->link;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
return out;
}
//u的第一个邻接顶点的位置
int getFirstNeigbor(int u) {
if (u<0 || u>=numVertices)return -1;
if (NodeTable[u].adj != NULL)return NodeTable[u].adj->dest;
else return -1;
}
//v的邻接顶点w的下一个邻接顶点的位置
int getNextNeigbor(int v, int w) {
if (v >= 0 && v < numVertices) {
Edge<T>* p = NodeTable[v].adj;
//寻找w
while (p != NULL && p->dest != w) p = p->link;
if (p != NULL && p->link != NULL)return p->link->dest;//找到
}
return -1;//没找到
}
void PrintPath(int u, int v, bool* visited,int* path,int pLen) {
int w;
visited[u] = 1;//记录u被访问,防止死循环
pLen++; path[pLen] = u;//路径长度++,顶点u加入到路径中
if (u == v&&pLen>0) {//找到一条u->v的路径
for (int i = 0; i < pLen; i++) {
cout << NodeTable[path[i]].data << "->";
}
cout << NodeTable[path[pLen]].data << endl;
return;//找到一条路径之后返回
}
w = getFirstNeigbor(u);//第一个邻接顶点的位置
while (w != -1) {//w存在
//如果w未被访问过,递归访问w
if (!visited[w]) {
PrintPath(w, v, visited, path, pLen);
visited[w] = 0;//回退之后要重置
}
//当w被访问过,且w是终点,且路径>0,说明路径构成回路
else if (w == v && pLen > 0) {//打印回路
for (int i = 0; i <= pLen; i++) {
cout << NodeTable[path[i]].data << "->";
}
cout << NodeTable[w].data << endl;
}
w = getNextNeigbor(u, w);//访问下一个邻接顶点
}
}
};
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Graph.h"
using namespace std;
void hasFalse(bool* visited,int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
visited[i] = false;//数组初始化为false
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
Graph<char>G;
cin >> G;//图的输入
cout << G;//图的输出
//求有向图的简单路径
bool *visited=new bool[G.numVertices];//判断顶点是否已经被访问
int* path = new int[G.numVertices];//顶点路径
hasFalse(visited, G.numVertices);//数组初始化
//打印第i个位置的顶点到第j个位置的顶点的路径
cout << "该图的简单路径为:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertices; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < G.numVertices; j++) {
if (i == j)continue;//回路不是简单路径,不打印
else G.PrintPath(i, j, visited, path, -1);
hasFalse(visited, G.numVertices);//数组初始化
}
}
cout << endl<<"该图的简单回路有:"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertices; i++) {
hasFalse(visited, G.numVertices);//数组初始化
G.PrintPath(i, i, visited, path, -1);
}
delete[]visited; delete[]path;
return 0;
}
/*
6
A B C D E F
8
A F
A B
F B
B C
B E
C D
D E
C A
*/























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








