1.安装开发工具
•sudo apt install build-essential
•sudo apt install qemu # install QEMU
•sudo apt install libncurses5-dev bisonflex libssl-dev libelf-dev
2.下载内核源代码
•sudo apt install axel
•axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
•xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
•tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar
•cd linux-5.4.34
3.配置内核选项
•make defconfig # Default configuration is based on 'x86_64_defconfig'
•make menuconfig
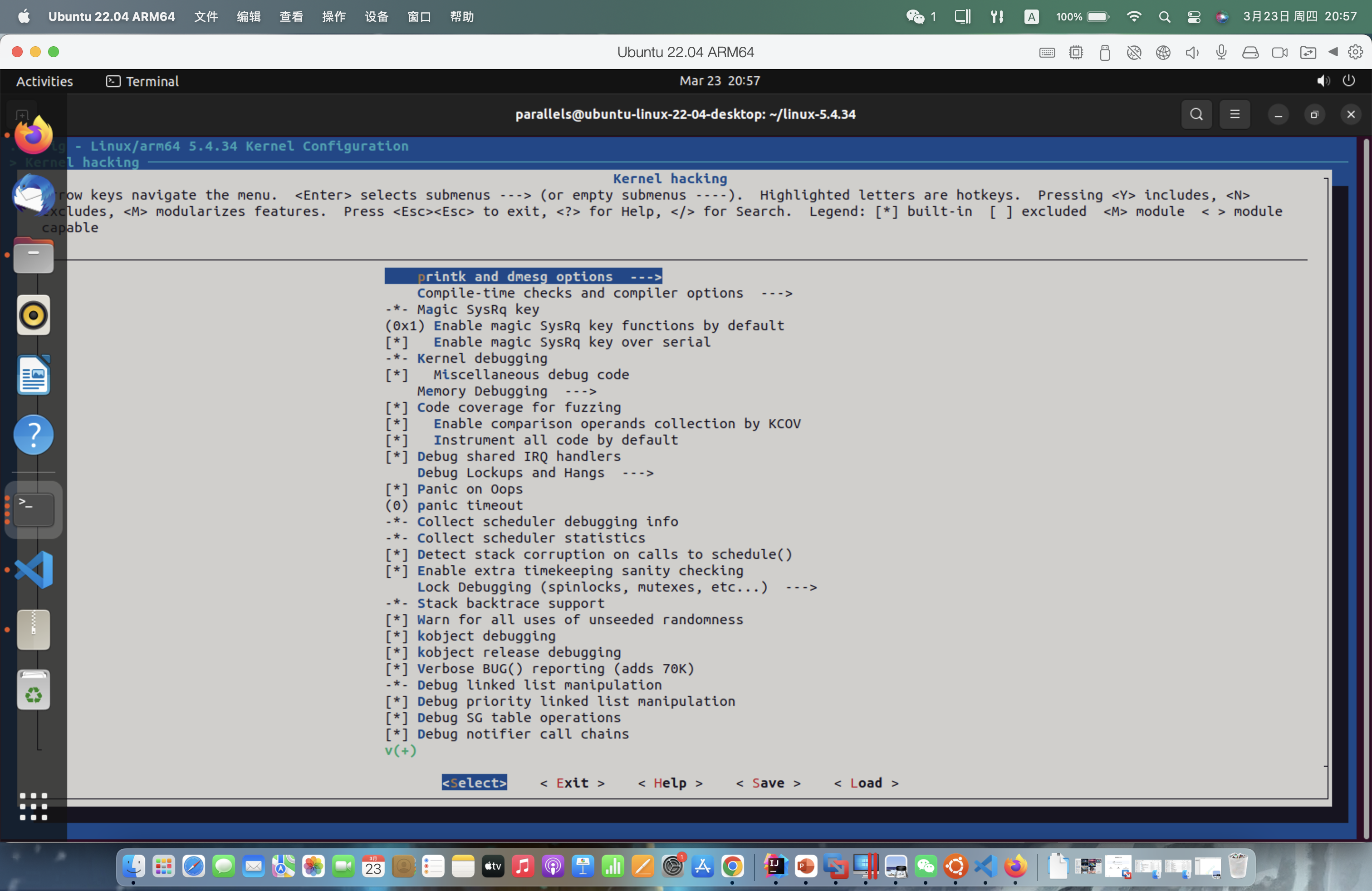
配置修改:
•# 打开debug相关选项
•Kernel hacking --->
• Compile-time checks andcompiler options --->
• [*] Compile the kernelwith debug info
• [*] Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging
• [*] Kernel debugging
•# 关闭KASLR,否则会导致打断点失败
•Processor type and features ---->
• [] Randomize the address ofthe kernel image (KASLR)
4.编译和运行内核
•make -j$(nproc) # nproc gives the number of CPU cores/threads available
•# 测试一下内核能不能正常加载运行,因为没有文件系统最终会kernel panic
•qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
5.制作根文件系统
•电脑加电启动首先由bootloader加载内核,内核紧接着需要挂载内存根文件系统,其中包含必要的设备驱动和工具,bootloader加载根文件系统到内存中,内核会将其挂载到根目录/下,然后运行根文件系统中init脚本执行一些启动任务,最后才挂载真正的磁盘根文件系统。
•我们这里为了简化实验环境,仅制作内存根文件系统。这里借助BusyBox 构建极简内存根文件系统,提供基本的用户态可执行程序。
步骤:
•首先从https://www.busybox.net下载 busybox源代码解压,解压完成后,跟内核一样先配置编译,并安装。
•axel -n 20 https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2
•tar -jxvf busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2
•cd busybox-1.31.1
•make menuconfig
•记得要编译成静态链接,不用动 xx态链接库。
•Settings --->
• [*] Build static binary (noshared libs)
•然后编译安装,默认会安装到源码目录下的_install 目录中。
•make -j$(nproc) && make install
•然后制作内存根文件系统镜像,大致过程如下:
•mkdir rootfs
•cd rootfs
•cp ../busybox-1.31.1/_install/* ./ -rf
•mkdir dev proc sys home
•sudo cp -a/dev/{null,console,tty,tty1,tty2,tty3,tty4} dev/
•准备init脚本文件放在根文件系统跟目录下(rootfs/init),添加如下内容到init文件。
•#!/bin/sh
•mount -t proc none /proc
•mount -t sysfs none /sys
•echo "Wellcome MengningOS!"
•echo "--------------------"
•cd home
•/bin/sh
•给init脚本添加可执行权限
chmod +x init
•打包成内存根文件系统镜像
•find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
•测试挂载根文件系统,看内核启动完成后是否执行init脚本
•qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz
6.配置vscode调试
•由于 Linux 内核高度定制化,所以没有办法直接通过配置 includePath 等让 Intellisense 正常提示,这里借助一个 Python 脚本来生成 compile_commands.json 文件帮助 Intellisense 正常提示(包括头文件和宏定义等)。在Linux源代码目录下直接运行如下命令就可以生成 compile_commands.json 了。
•python ./scripts/gen_compile_commands.py
•配置 VSCode 配置文件.vscode/c_cpp_properties.json

配置完进行调试
跟踪调试Linux内核的基本方法:下面具体看看如何使用gdb跟踪调试Linux内核。使用gdb跟踪调试内核,加两个参数,一个是-s,在TCP 1234端口上创建了一个gdb-server。可以另外打开一个窗口,用gdb把带有符号表的内核镜像vmlinux加载进来,然后连接gdbserver,设置断点跟踪内核。若不想使用1234端口,可以使用-gdb tcp:xxxx来替代-s选项),另一个是-S代表启动时暂停虚拟机,等待 gdb 执行 continue指令(可以简写为c)。
•qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz -S -s
•# 纯命令行下启动虚拟机
•qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz -S -s -nographic -append "console=ttyS0"
用以上命令先启动,然后可以看到虚拟机一启动就暂停了。加-nographic -append"console=ttyS0"参数启动不会弹出QEMU虚拟机窗口,可以在纯命令行下启动虚拟机,此时可以通过“killallqemu-system-x86_64”命令强行关闭虚拟机
•再打开一个窗口,启动gdb,把内核符号表加载进来,建立连接:
•cd linux-5.4.34/
•gdb vmlinux
•(gdb) target remote:1234
•(gdb) b start_kernel
•c、bt、list、next、step....





















 138
138

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








