.
文章目录
一、认识搜索引擎
像百度、搜狗这些搜索引擎,输入一个搜索词就会出现若干条结果,每条结果包含标题,内容描述,展示url,图片等相关内容。
搜索引擎的本质就是输入一个查询词,得到若干个结果标题、描述、点击url。
搜索的核心思路
我们把一个网页称为一个文档;每一次搜索就是在所有文档中查找搜索词,检查文档中是否有搜索词。但是这种搜索方法很直接很暴力,开销很巨大,随着文档的增多,每次搜索的时间都会很长,而我们对搜索引擎的效率要求很高,试想一下你要搜索一个单词,要1分多钟的时间你还会选择这个搜索引擎吗?
所以我们引入倒排索引,这是针对搜索引擎而设计的数据结构。
倒排索引
文档:我们只检索html页面
正排索引:按照文档进行索引,一个文档中有哪些词,描述一个文档中有哪些信息,将文档中的词进行分词并处理。
倒排索引:按照词语进行分类,一个词被那些文档引用,储存了这些词在那些文档,并在这些文档中占据的重要程度。
二、项目介绍
我们针对Java API文档实现一个搜索引擎。
我们将需要的Java API文档保存到本地。
我们要实现搜索引擎需要实现以下模块:
- 构建索引模块:扫码下载好的文档,分析数据内容使用正排索引和倒排索引,并保存到本地文件。
- 搜索模块:加载索引,根据输入的查询词,基于正排和倒排索引进行检索得到检索结果。
- web模块:编写一个简单的web页面,展示搜索结果。
三、索引构建具体实现
1、分词
正排索引和倒排索引都要对内容进行分词处理,我们使用ansj_seg分词技术来进行分词操作。
我们要在pom.xml文件中插入如下代码:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.ansj</groupId>
<artifactId>ansj_seg</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
2、文件检索
在配置文件中配置要进行检索文件的地址,代码如下:
searcher:
indexer:
doc-root-path: D:\搜索引擎\docs\api
url-prefix: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/
使用rootPath作为根目录,开始进行文件扫描,把所有符合要求的File对象作为结果,以List形式进行返回。首先通过@Service注解将该类注册为Spring Bean ,采用深度优先遍历,使用递归完成。
代码如下:
public List<File> scanFile(String rootPath, FileFilter filter) {
List<File> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
File rootFile = new File(rootPath);
traversal(rootFile, filter, resultList);
return resultList;
}
private void traversal(File directoryFile, FileFilter filter, List<File> resultList) {
// 1. 先通过目录,得到该目录下的孩子文件有哪些
File[] files = directoryFile.listFiles();
if (files == null) {
return;
}
// 2. 遍历每个文件,检查是否符合条件
for (File file : files) {
if (filter.accept(file)) {
resultList.add(file);
}
}
// 3. 遍历每个文件,针对是目录的情况,继续深度优先遍历(递归)
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
traversal(file, filter, resultList);
}
}
}
}
这样我们就完成文件的扫描。
3、库表的建立
我们使用MySQL储存我们要储存的文档。通过设计需要两个表来进行储存。一是储存正排索引的表,二是储存倒排索引的表。建表语句如下:
CREATE TABLE `searcher`.`weights` (
`wid` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`docId` int(11) NOT NULL,
`weight` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT
)COMMENT='倒排索引中的权重信息,包含 docId + weight
CREATE TABLE `searcher`.`documents` (
`docid` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT
`title` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`url` varchar(200) NOT NULL,
`content` longtext NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`docid`)
) COMMENT='文档表,也就是正排索引表';
正排索引表储存正排索引信息,倒排索引表储存倒排索引信息。同时在yml文件中配置关联MySQL。
4、对扫描的文件进行处理
第一步:扫描出来所有的html文件。代码如下:
List<File> htmlFileList = fileScanner.scanFile(properties.getDocRootPath(), file -> {
return file.isFile() && file.getName().endsWith(".html");
});
第二步:针对每个 html 文件,得到其 标题、URL、正文信息,把这些信息封装成一个对象(文档 Document)。代码如下:
File rootFile = new File(properties.getDocRootPath());
List<Document> documentList = htmlFileList.stream()
.parallel() // 【注意】由于我们使用了 Stream 用法,所以,可以通过添加 .parallel(),使得整个操作变成并行,利用多核增加运行速度
.map(file -> new Document(file, properties.getUrlPrefix(), rootFile))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
1、分词处理
因为读取的文件都会带有.html的后缀,不能算作文件的标题,所以在计算分词之前首先要把获取文档的后缀去掉;代码如下:
private String parseTitle(File file) {
// 从文件名中,将 .html 后缀去掉,剩余的看作标题,进行简单的拼接即可。
String name = file.getName();
String suffix = ".html";
return name.substring(0, name.length() - suffix.length());
}
针对文档进行分词,并计算权重值(我们这里将在标题中出现的词权重10,在文档正文中出现的词权重1)。
标题分词处理
代码如下:
public Map<String, Integer> segWordAndCalcWeight() {
// 统计标题中的每个词出现次数 | 分词:标题有哪些词
List<String> wordInTitle = ToAnalysis.parse(title)
.getTerms()
.stream()
.parallel()
.map(Term::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 统计标题中,每个词的出现次数 | 统计次数
Map<String, Integer> titleWordCount = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : wordInTitle) {
int count = titleWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
titleWordCount.put(word, count + 1);
}
内容分词处理
代码如下:
// 统计内容中的词,以及词的出现次数
List<String> wordInContent = ToAnalysis.parse(content)
.getTerms()
.stream()
.parallel()
.map(Term::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Map<String, Integer> contentWordCount = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : wordInContent) {
int count = contentWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
contentWordCount.put(word, count + 1);
}
2、权重计算
权重的计算因为是不同的单词所以要进行去重 ,这里采用Set来去重。然后通过遍历然后计算获得该词的权重并放入List中。
// 计算权重值
Map<String, Integer> wordToWeight = new HashMap<>();
// 先计算出有哪些词,不重复
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordInTitle);
wordSet.addAll(wordInContent);
for (String word : wordSet) {
int titleCount = titleWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
int contentCount = contentWordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0);
int weight = titleCount * 10 + contentCount;
wordToWeight.put(word, weight);
}
return wordToWeight;
}
3、url及文件中Js的处理
因为在yml文件中配置了前缀url为:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/
所以要获得完整的url就要从文件路径中获取,又因为文件路径为"\“而url中为”/"所以要进行替换并把前缀url和绝对路径进行拼接,就是完整的url了
代码如下:
// 需要得到一个相对路径,file 相对于 rootFile 的相对路径
// 比如:rootFile 是 D:\docs\api
// file 是 D:\docs\api\javax\sql\DataSource.html
// 则相对路径就是:javax\sql\DataSource.html
// 把所有反斜杠(\) 变成正斜杠(/)
// 最终得到 java/sql/DataSource.html
private String parseUrl(File file, String urlPrefix, File rootFile) {
String rootPath = rootFile.getCanonicalPath();
rootPath = rootPath.replace("/", "\\");
if (!rootPath.endsWith("\\")) {
rootPath = rootPath + "\\";
}
String filePath = file.getCanonicalPath();
String relativePath = filePath.substring(rootPath.length());
relativePath = relativePath.replace("\\", "/");
return urlPrefix + relativePath;
}
Js处理
因为是html会带有JS代码,所以搜索的时候关键字中会由JS代码所以要把代码去除掉,这里采用正则表达式去除。
代码如下:
@SneakyThrows
private String parseContent(File file) {
StringBuilder contentBuilder = new StringBuilder();
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file)) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is, "ISO-8859-1")) {
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
contentBuilder.append(line).append(" ");
}
return contentBuilder.toString()
// 首先去掉 <script ...>...</script>
.replaceAll("<script[^>]*>[^<]*</script>", " ")
// 去掉标签
.replaceAll("<[^>]*>", " ")
// 多带的空格的意思是,把 换行符 也视为空格了
.replaceAll("\\s+", " ")
//再去掉两边的空格
.trim();
}
}
}
5、索引的构建
索引的构建需要对数据库进行操作这里我用MyBatis进行操作,我们生成一个接口将其注册为Spring Bean并与xml文件关联,通过java对象中sql的动态参数进行映射生产最终执行的sql语句,最后再由Mybatis框架执行sql并将结果映射为java对象并返回。
这里我还做了一些优化,使用线程池来进行操作可以减少插入索引所需的时间。代码如下:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public ExecutorService executorService() {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
8, 20, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5000),
(Runnable task) -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(task);
thread.setName("批量插入线程");
return thread;
},
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
return executor;
}
}
1、正排索引
其xml中的配置语句为:
<insert id="batchInsertForwardIndexes" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="docId" keyColumn="docid">
insert into forward_indexes (title, url, content) values
<!-- 一共有多少条记录,得根据用户传入的参数来决定,所以这里采用动态 SQL 特性 -->
<foreach collection="list" item="doc" separator=", ">
(#{doc.title}, #{doc.url}, #{doc.content})
</foreach>
</insert>
在插入过程中我们采取批量插入来进行操作,减少操作所需的时间。因为正排索引插入的是文档,MySQL每次插入数据的大小有限制,所以我们每次插入数据的大小为10条。
代码如下:
@SneakyThrows
public void saveForwardIndexesConcurrent(List<Document> documentList) {
// 1. 批量插入时,每次插入多少条记录(由于每条记录比较大,所以这里使用 10 条就够了)
int batchSize = 10;
// 2. 一共需要执行多少次 SQL? 向上取整(documentList.size() / batchSize)
int listSize = documentList.size();
int times = (int) Math.ceil(1.0 * listSize / batchSize); // ceil(天花板): 向上取整
log.debug("一共需要 {} 批任务。", times);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(times); // 统计每个线程的完全情况,初始值是 times(一共多少批)
// 3. 开始分批次插入
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i += batchSize) {
// 从 documentList 中截取这批要插入的 文档列表(使用 List.subList(int from, int to)
int from = i;
int to = Integer.min(from + batchSize, listSize);
Runnable task = () -> { // 内部类 / lambda 表达式里如果用到了外部变量,外部变量必须的 final(或者隐式 final 的变量)
List<Document> subList = documentList.subList(from, to);
// 针对这个 subList 做批量插入
mapper.batchInsertForwardIndexes(subList);
latch.countDown(); // 每次任务完成之后,countDown(),让 latch 的个数减一
};
executorService.submit(task); // 主线程只负责把一批批的任务提交到线程池,具体的插入工作,由线程池中的线程完成
}
// 4. 循环结束,只意味着主线程把任务提交完成了,但任务有没有做完是不知道的
// 主线程等在 latch 上,只到 latch 的个数变成 0,也就是所有任务都已经执行完了
latch.await();
}
这样正排索引就插入方法就完成了。
2、倒排索引
其xml文件中配置语句为:
<insert id="batchInsertInvertedIndexes">
insert into inverted_indexes (word, docid, weight) values
<foreach collection="list" item="record" separator=", ">
(#{record.word}, #{record.docId}, #{record.weight})
</foreach>
</insert>
在插入过程中我们采取批量插入来进行操作,减少操作所需的时间。倒排索引每次插入数据大小较小,所以我们每次插入10,000条,在这里我创建一个单独的方法来处理插入。代码如下:
static class InvertedInsertTask implements Runnable {
private final CountDownLatch latch;
private final int batchSize;
private final List<Document> documentList;
private final IndexDatabaseMapper mapper;
InvertedInsertTask(CountDownLatch latch, int batchSize, List<Document> documentList, IndexDatabaseMapper mapper) {
this.latch = latch;
this.batchSize = batchSize;
this.documentList = documentList;
this.mapper = mapper;
}
@Override
public void run() {
List<InvertedRecord> recordList = new ArrayList<>(); // 放这批要插入的数据
for (Document document : documentList) {
Map<String, Integer> wordToWeight = document.segWordAndCalcWeight();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : wordToWeight.entrySet()) {
String word = entry.getKey();
int docId = document.getDocId();
int weight = entry.getValue();
InvertedRecord record = new InvertedRecord(word, docId, weight);
recordList.add(record);
// 如果 recordList.size() == batchSize,说明够一次插入了
if (recordList.size() == batchSize) {
mapper.batchInsertInvertedIndexes(recordList); // 批量插入
recordList.clear(); // 清空 list,视为让 list.size() = 0
}
}
}
// recordList 还剩一些,之前放进来,但还不够 batchSize 个的,所以最后再批量插入一次
mapper.batchInsertInvertedIndexes(recordList); // 批量插入
recordList.clear();
latch.countDown();
}
}
@Timing("构建 + 保存倒排索引 —— 多线程版本")
@SneakyThrows
public void saveInvertedIndexesConcurrent(List<Document> documentList) {
int batchSize = 10000; // 批量插入时,最多 10000 条
int groupSize = 50;
int listSize = documentList.size();
int times = (int) Math.ceil(listSize * 1.0 / groupSize);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(times);
for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i += groupSize) {
int from = i;
int to = Integer.min(from + groupSize, listSize);
List<Document> subList = documentList.subList(from, to);
Runnable task = new InvertedInsertTask(latch, batchSize, subList, mapper);
executorService.submit(task);
}
latch.await();
}
这样倒排索引插入的方法就完成了。
6、索引的保存
使用创建好的正排索引和倒排索引的方法再将文件传入传入即可。代码如下:
// 3. 进行正排索引的保存
indexManager.saveForwardIndexesConcurrent(documentList);
log.debug("正排索引保存成功。");
// 4. 进行倒排索引的生成核保存
indexManager.saveInvertedIndexesConcurrent(documentList);
log.debug("倒排索引保存成功。");
四、Web界面的构建
Web界面的构建是使用搜索引擎的关键,通过Web界面所构建的html文件来通过后端文件来进行搜索,简单来说就是根据用户所提交的搜索词通过Mybatis操作数据库并将搜索出来的数据传给前端来展示给用户。
1、前端与数据库的交互
1、注册SearchMapper接口通过@Repository和@Mapper共同作用于dao
层,获取数据库中的信息。
代码如下:
public class DocumentWightWeight {
private int docId;
private String title;
private String url;
private String content;
public int weight;
public DocumentWightWeight() {}
public DocumentWightWeight(DocumentWightWeight documentWightWeight) {
this.docId = documentWightWeight.docId;
this.title = documentWightWeight.title;
this.url = documentWightWeight.url;
this.content = documentWightWeight.content;
this.weight = documentWightWeight.weight;
}
public Document toDocument() {
Document document = new Document();
document.setDocId(this.docId);
document.setTitle(this.title);
document.setUrl(this.url);
document.setContent(this.content);
return document;
}
}
这些是想要从数据库中拿到的信息。
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface SearchMapper {
List<DocumentWightWeight> queryWithWeight(
@Param("word") String word,
@Param("limit") int limit,
@Param("offset") int offset
);
}
这是对数据库进行操作。这段代码所在的类会与xml文件关联。xml中代码如下:
<resultMap id="DocumentWithWeightResultMap" type="com.searcher.web.DocumentWightWeight">
<id property="docId" column="docid" />
<result property="title" column="title" />
<result property="url" column="url" />
<result property="content" column="content" />
<result property="weight" column="weight" />
</resultMap>
<select id="queryWithWeight" resultMap="DocumentWithWeightResultMap">
select ii.docid, title, url, content, weight
from inverted_indexes ii
join forward_indexes fi
on ii.docid = fi.docid
where word = #{word}
order by weight desc
limit ${limit}
offset ${offset}
</select>
sql语句中使用连表查询将正排索引和倒排索引关联起来。
2、对数据进行处理
通过传入的query来对数据库进行搜索,并进行分页操作。如果是多词查找就先分词然后对词语分别查找并进行聚合操作。
具体操作代码如下:
public String search(String query, @RequestParam(value = "page", required = false) String pageString, Model model) {
//进行分词操作
List<String> queryList = ToAnalysis.parse(query)
.getTerms()
.stream()
.map(Term::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
重新聚合每个词在不同文件中的权重,然后按照权重大小进行排序。
代码如下:
List<DocumentWightWeight> totalList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : queryList) {
List<DocumentWightWeight> documentList = mapper.queryWithWeight(s, limit, offset);
totalList.addAll(documentList);
}
// 针对所有文档列表,做权重聚合工作
// 维护:
// docId -> document 的 map
Map<Integer, DocumentWightWeight> documentMap = new HashMap<>();
for (DocumentWightWeight documentWightWeight : totalList) {
int docId = documentWightWeight.getDocId();
if (documentMap.containsKey(docId)) {
DocumentWightWeight item = documentMap.get(docId);
item.weight += documentWightWeight.weight;
continue;
}
DocumentWightWeight item = new DocumentWightWeight(documentWightWeight);
documentMap.put(docId, item);
}
Collection<DocumentWightWeight> values = documentMap.values();
// Collection 没有排序这个概念(只有线性结构才有排序的概念),所以我们需要一个 List
List<DocumentWightWeight> list = new ArrayList<>(values);
// 按照 weight 的从大到小排序了
Collections.sort(list, (item1, item2) -> {
return item2.weight - item1.weight;
});
int from = (page - 1) * 20;
int to = from + 20;
// 从 list 中把分页区间取出来
List<DocumentWightWeight> subList = list.subList(from, to);
List<Document> documentList = subList.stream()
.map(DocumentWightWeight::toDocument)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// lambda 中无法使用非 final 变量
List<String> wordList = queryList;
documentList = documentList.stream()
.map(doc -> descBuilder.build(wordList, doc))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 这里将数据添加到 model 中,是为了在 渲染模板的时候用到
model.addAttribute("query", query);
model.addAttribute("docList", documentList);
model.addAttribute("page", page);
}
这样之后就把多词查找分别单词的权重重新聚合并进行分页。
3、展示页
这里采用了thymeleaf语法来对展示页就行操作
代码如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-hans" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title th:text="${query} + ' - 学习搜索'"></title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/query.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<div class="brand"><a href="/">学习搜索</a></div>
<form class="input-shell" method="get" action="/web">
<input type="text" name="query" th:value="${query}">
<button>搜索一下</button>
</form>
</div>
<div class="result">
<div class="result-item" th:each="doc : ${docList}">
<a th:href="${doc.url}" th:text="${doc.title}"></a>
<div class="desc" th:utext="${doc.desc}"></div>
<div class="url" th:text="${doc.url}"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="pagination">
<a th:href="'/web?query=' + ${query} + '&page=' + ${page - 1}">上一页</a>
<a th:href="'/web?query=' + ${query} + '&page=' + ${page + 1}">下一页</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
使用thymeleaf语法可以使展示页中展示出从数据库拿到的信息不如url,titile,简介等信息,使得查询界面更加丰富。
4、其他
还可以对搜索首页进行优化,网上有什么CSS样式,可以在B站上进行学习。
五、测试
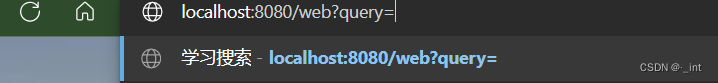
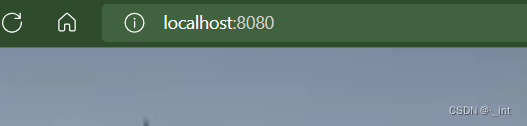
1、当输入为空时,跳转到首页
2、当输入符号
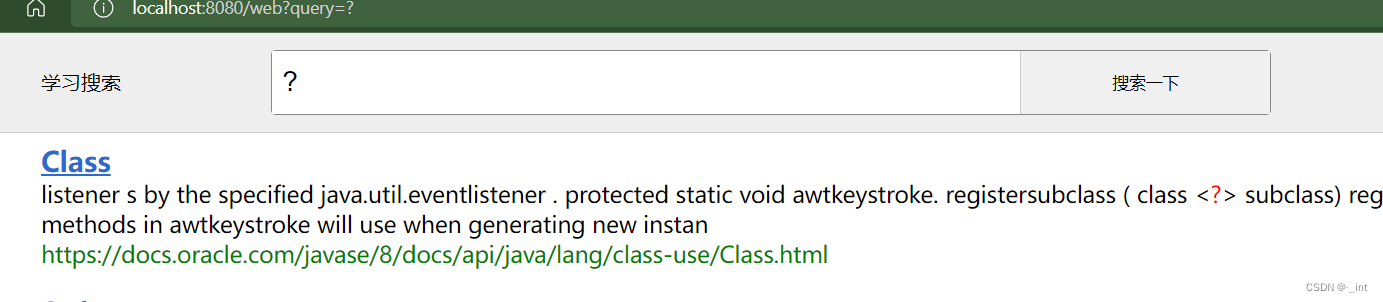
可以进行查找。
3、任意检索词
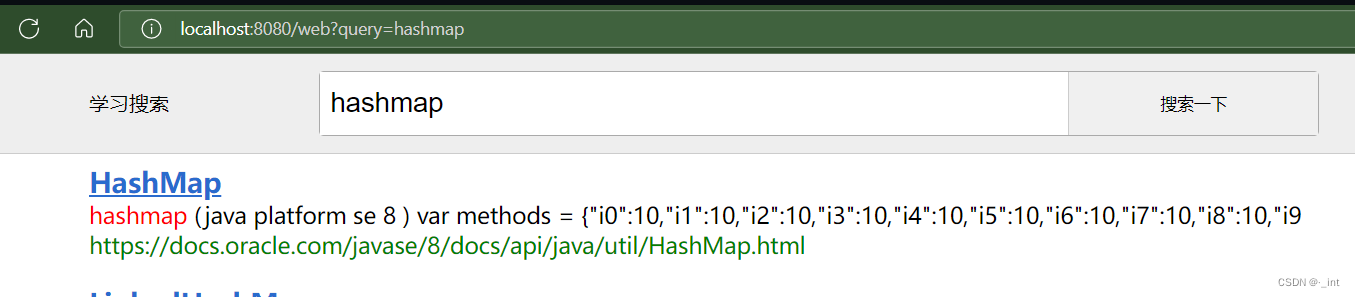
4、输入汉字

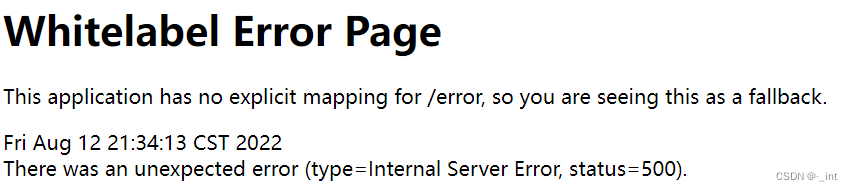
无法进行查询。






















 1076
1076











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








