1.1链表是个好东西
链表的概念:
1.什么是链表——>数据结构——>数据存放(集合)的思想
链表的每一项都是一个结构体 链表存放数据a->b的地址 b->c的地址
数组:元素的地址连续
缺点:增加元素,删,改,查 不灵活
1.2链表和数组区别及实现
1.普通的数组遍历输出
#include "stdio.h"
int main()
{
int i;
int len;
int arry[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
len = sizeof(arry)/sizeof(arry[0]);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arry[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}2. 利用链表的方式输出
![]()
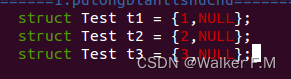
这是定义的3个结构体和数组在结构体中的内存对比如下图 :

#include "stdio.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
int i;
int len;
int arry[] = {1,2,3};
len = sizeof(arry)/sizeof(arry[0]);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arry[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
t1.next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
return 0;
}1.3链表静态添加和动态遍历
#include "stdio.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
int i;
int len;
int arry[] = {1,2,3};
len = sizeof(arry)/sizeof(arry[0]);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arry[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};
struct Test t6 = {6,NULL};
t1.next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
t3.next = &t4;
t4.next = &t5;
t5.next = &t6;
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
return 0;
}
1.4链表遍历中的point=point-next

1.5统计链表节点个数及链表查找
1.链表的个数计算
#include "stdio.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
int getLinkTotalNodeNum(struct Test *head)
{
int cnt = 0;
while(head != NULL)
{
cnt++;
head = head->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
int i;
int len;
int arry[] = {1,2,3};
len = sizeof(arry)/sizeof(arry[0]);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arry[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};
struct Test t6 = {6,NULL};
t1.next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
t3.next = &t4;
t4.next = &t5;
t5.next = &t6;
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
int ret = getLinkTotalNodeNum(&t1);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
return 0;
}
2.链表的查找
#include "stdio.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
int getLinkTotalNodeNum(struct Test *head)
{
int cnt = 0;
while(head != NULL)
{
cnt++;
head = head->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int searchLink(struct Test *head,int data)
{
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head->data == data)
{
return 1;
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
int i;
int len;
int arry[] = {1,2,3};
len = sizeof(arry)/sizeof(arry[0]);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arry[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};
struct Test t6 = {6,NULL};
t1.next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
t3.next = &t4;
t4.next = &t5;
t5.next = &t6;
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
int ret = getLinkTotalNodeNum(&t1);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
//==============5.lianbiaochazhao============
ret = searchLink(&t1,1);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 1\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 1\n");
}
ret = searchLink(&t1,8);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 8\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 8\n");
}
return 0;
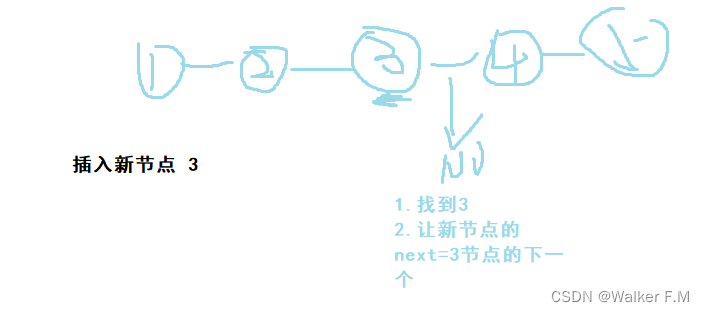
}1.6 链表从指定节点后方插入新节点
插入新节点:
节点后:
节点前:
#include "stdio.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
int inserFromBehind(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
int getLinkTotalNodeNum(struct Test *head)
{
int cnt = 0;
struct Test *p;
while(p != NULL)
{
cnt++;
p = p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int searchLink(struct Test *head,int data)
{
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head->data == data)
{
return 1;
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
int i;
int len;
int arry[] = {1,2,3};
len = sizeof(arry)/sizeof(arry[0]);
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arry[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};
struct Test t6 = {6,NULL};
t1.next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
t3.next = &t4;
t4.next = &t5;
t5.next = &t6;
struct Test new = {100,NULL};
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
puts("after insert behind:\n");
inserFromBehind(&t1,5,&new);
printLink(&t1);
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
/* int ret = getLinkTotalNodeNum(&t1);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
//==============5.lianbiaochazhao============
ret = searchLink(&t1,1);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 1\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 1\n");
}
ret = searchLink(&t1,8);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 8\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 8\n");
}*/
return 0;
}1.7链表从指定节点前方插入新节点
前方插入:
1.第1个节点是目标节点——>修改链表头(链头)
2.第一个节点是中间节点添加链表元素
1. 第一个节点是目标节点修改链表头
#include "stdio.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
//1.第一个节点是链表头
struct Test* inserFromfor(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = head;
return new;
}
}
int charubenhind(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == data){
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL){
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int getshu(struct Test *d)
{
int cnt = 0;
while(d != NULL)
{
cnt++;
d=d->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int findshu(struct Test *d,int data)
{
while(d != NULL)
{
if(d->data == data){
return 1;
}
d = d->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i;
int ret;
int array[] = {1,2,3};
struct Test *head = NULL;
for(i=0;i<sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);i++)
{
printf("%d ",array[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};
struct Test new = {100,NULL};
t1.next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
t3.next = &t4;
head = &t1;
printf("====================\n");
printf("%d %d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data,t1.next->next->next->data);
printLink(head);
charubenhind(head,1,&new);
printLink(head);
struct Test new2 = {101,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new2);
printLink(head);
}2.第一个节点是中间节点添加链表元素
#include "stdio.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
struct Test* inserFromfor(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = head;
return new;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
printf("no this data%d",data);
return head;
}
int charubenhind(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == data){
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL){
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int getshu(struct Test *d)
{
int cnt = 0;
while(d != NULL)
{
cnt++;
d=d->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int findshu(struct Test *d,int data)
{
while(d != NULL)
{
if(d->data == data){
return 1;
}
d = d->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i;
int ret;
int array[] = {1,2,3};
struct Test *head = NULL;
for(i=0;i<sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]);i++)
{
printf("%d ",array[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};
struct Test new = {100,NULL};
t1.next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
t3.next = &t4;
head = &t1;
printf("====================\n");
printf("%d %d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data,t1.next->next->next->data);
printLink(head);
charubenhind(head,1,&new);
printLink(head);
struct Test new2 = {101,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new2);
printLink(head);
struct Test new3 = {103,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new3);
printLink(head);
/* ret = getshu(&t1);
printf("sum = %d\n",ret);
charubehind(&t1,3,new);
ret = findshu(&t1,1);
if(ret == 0)
{
printf("no 1\n");
}
else
{
nserFromfor printf("have 1\n");
}
ret = findshu(&t1,8);
if(ret == 0)
{
printf("no 8\n");
}
else
{
printf("have 8\n");
}
*/ return 0;
}1.8链表删除指定节点
一样的删除节点要考虑2种情况:头节点、中间节点
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
int inserFromBehind(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
//================6.xiugaitoujiedian====================
struct Test* inserFromfor(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = head;
return new;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
printf("insert ok\n");
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
printf("no this data%d",data);
return head;
}
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
int getLinkTotalNodeNum(struct Test *head)
{
int cnt = 0;
struct Test *p;
while(p != NULL)
{
cnt++;
p = p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int searchLink(struct Test *head,int data)
{
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head->data == data)
{
return 1;
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct Test *deletNode(struct Test *head,int data)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
head = head->next;
free(p);
return head;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
// struct Test *tmp = p;
p->next = p->next->next;
// free(p);
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test *head = NULL;
struct Test *p = (struct Test*)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test t1 = {1,NULL};
struct Test t2 = {2,NULL};
struct Test t3 = {3,NULL};
struct Test t4 = {4,NULL};
struct Test t5 = {5,NULL};
p->data = 1;
// t1.next = &t2;
p->next = &t2;
t2.next = &t3;
t3.next = &t4;
t4.next = &t5;
// head = &t1;
head = p;
printLink(head);
head = deletNode(head,5);
printLink(head);
/* struct Test new = {100,NULL};
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
puts("after insert behind:\n");
inserFromBehind(&t1,5,&new);
printLink(&t1);
struct Test new2 = {101,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new2);
puts("after insert head:\n");
printLink(head);
struct Test new3 = {103,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new3);
puts("after insert for:\n");
printLink(head);
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
/* int ret = getLinkTotalNodeNum(&t1);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
//==============5.lianbiaochazhao============
ret = searchLink(&t1,1);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 1\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 1\n");
}
ret = searchLink(&t1,8);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 8\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 8\n");
}*/
return 0;
}1.9链表动态创建之头插法
前面几节课讲述了链表的:遍历、节点个数统计、查找、插入(头、尾)、删除
这节课:动态创建(头、尾插入)
头->是最新的节点
补充查找:
int gaiLink(struct Test *head,int data,int newdata)
{
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head->data == data)
{
head->data = newdata;
return 1;
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
动态创建 :
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
int inserFromBehind(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
//================6.xiugaitoujiedian====================
struct Test* inserFromfor(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = head;
return new;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
printf("insert ok\n");
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
printf("no this data%d",data);
return head;
}
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
int getLinkTotalNodeNum(struct Test *head)
{
int cnt = 0;
struct Test *p;
while(p != NULL)
{
cnt++;
p = p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int searchLink(struct Test *head,int data)
{
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head->data == data)
{
return 1;
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct Test *deletNode(struct Test *head,int data)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
head = head->next;
free(p);
return head;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
// struct Test *tmp = p;
p->next = p->next->next;
// free(p);
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
return head;
}
struct Test* inserFromHead(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *new;
while(1){
new =(struct Test *)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
printf("input your new node data:\n");
scanf("%d",&(new->data));
if(new->data == 0)
{
printf("0 quit\n");
return head;
}
if(head == NULL)
{
head = new;
}
else
{
new->next = head;
head = new;
}
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test *head = NULL;
head = inserFromHead(head);
printLink(head);
/* struct Test new = {100,NULL};
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
puts("after insert behind:\n");
inserFromBehind(&t1,5,&new);
printLink(&t1);
struct Test new2 = {101,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new2);
puts("after insert head:\n");
printLink(head);
struct Test new3 = {103,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new3);
puts("after insert for:\n");
printLink(head);
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
/* int ret = getLinkTotalNodeNum(&t1);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
//==============5.lianbiaochazhao============
ret = searchLink(&t1,1);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 1\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 1\n");
}
ret = searchLink(&t1,8);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 8\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 8\n");
}*/
return 0;
}1.10头插法优化补充
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
int inserFromBehind(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
//================6.xiugaitoujiedian====================
struct Test* inserFromfor(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = head;
return new;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
printf("insert ok\n");
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
printf("no this data%d",data);
return head;
}
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
int getLinkTotalNodeNum(struct Test *head)
{
int cnt = 0;
struct Test *p;
while(p != NULL)
{
cnt++;
p = p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int searchLink(struct Test *head,int data)
{
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head->data == data)
{
return 1;
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct Test *deletNode(struct Test *head,int data)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
head = head->next;
free(p);
return head;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
// struct Test *tmp = p;
p->next = p->next->next;
// free(p);
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
return head;
}
struct Test* inserFromHead(struct Test *head,struct Test *new)
{
if(head == NULL)
{
head = new;
}
else
{
new->next = head;
head = new;
}
return head;
}
struct Test* createLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *new;
while(1){
new =(struct Test *)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
printf("input your new node data:\n");
scanf("%d",&(new->data));
if(new->data == 0)
{
printf("0 quit\n");
free(new);
return head;
}
head = inserFromHead(head,new);
}
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test *head = NULL;
head = createLink(head);
printLink(head);
struct Test t1 = {1000,NULL};
head = inserFromHead(head,&t1);
printLink(head);
/* struct Test new = {100,NULL};
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
puts("after insert behind:\n");
inserFromBehind(&t1,5,&new);
printLink(&t1);
struct Test new2 = {101,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new2);
puts("after insert head:\n");
printLink(head);
struct Test new3 = {103,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new3);
puts("after insert for:\n");
printLink(head);
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
/* int ret = getLinkTotalNodeNum(&t1);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
//==============5.lianbiaochazhao============
ret = searchLink(&t1,1);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 1\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 1\n");
}
ret = searchLink(&t1,8);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 8\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 8\n");
}*/
return 0;
}1.11尾插法创建链表
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct Test
{
int data;
struct Test *next;
};
int inserFromBehind(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
return 1;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 0;
}
//================6.xiugaitoujiedian====================
struct Test* inserFromfor(struct Test *head,int data,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
new->next = head;
return new;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
new->next = p->next;
p->next = new;
printf("insert ok\n");
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
printf("no this data%d",data);
return head;
}
void printLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *point;
point = head;
while(point != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",point->data);
point = point->next;
}
putchar('\n');
}
int getLinkTotalNodeNum(struct Test *head)
{
int cnt = 0;
struct Test *p;
while(p != NULL)
{
cnt++;
p = p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int searchLink(struct Test *head,int data)
{
while(head != NULL)
{
if(head->data == data)
{
return 1;
}
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct Test *deletNode(struct Test *head,int data)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p->data == data)
{
head = head->next;
free(p);
return head;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
if(p->next->data == data)
{
// struct Test *tmp = p;
p->next = p->next->next;
// free(p);
return head;
}
p = p->next;
}
return head;
}
struct Test* inserFromHead(struct Test *head,struct Test *new)
{
if(head == NULL)
{
head = new;
}
else
{
new->next = head;
head = new;
}
return head;
}
struct Test* createLink(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *new;
while(1){
new =(struct Test *)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
printf("input your new node data:\n");
scanf("%d",&(new->data));
if(new->data == 0)
{
printf("0 quit\n");
free(new);
return head;
}
head = inserFromHead(head,new);
}
}
struct Test* insertBehind(struct Test *head,struct Test *new)
{
struct Test *p = head;
if(p == NULL)
{
head = new;
return head;
}
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = new;
return head;
}
struct Test* createLink2(struct Test *head)
{
struct Test *new;
while(1){
new =(struct Test *)malloc(sizeof(struct Test));
printf("input your new node data:\n");
scanf("%d",&(new->data));
if(new->data == 0)
{
printf("0 quit\n");
free(new);
return head;
}
head = insertBehind(head,new);
}
}
int main()
{
//==========1.putongbianlishuchu===============
struct Test *head = NULL;
head = createLink2(head);
printLink(head);
struct Test t1 = {1000,NULL};
head = inserFromHead(head,&t1);
printLink(head);
struct Test t2 = {2000,NULL};
head = insertBehind(head,&t2);
printLink(head);
/* struct Test new = {100,NULL};
printf("use t1 to printf three nums\n");
// printf("%d %d %d\n",t1.data,t1.next->data,t1.next->next->data);
printLink(&t1);
puts("after insert behind:\n");
inserFromBehind(&t1,5,&new);
printLink(&t1);
struct Test new2 = {101,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new2);
puts("after insert head:\n");
printLink(head);
struct Test new3 = {103,NULL};
head = inserFromfor(head,1,&new3);
puts("after insert for:\n");
printLink(head);
//===============5.jisuanlianbiaogeshu==========
/* int ret = getLinkTotalNodeNum(&t1);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
//==============5.lianbiaochazhao============
ret = searchLink(&t1,1);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 1\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 1\n");
}
ret = searchLink(&t1,8);
if(ret = 1)
{
printf("have you 8\n");
}
else
{
printf("no 8\n");
}*/
return 0;
}






















 14万+
14万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








