1、java IO类的用法:
1.1、java中的io类就很好的运用了装饰者的设计模式,一般我们读取文件代码如下:
/**
*
* @author PengMvc
*
*/
public class ReadContent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
inputStream= new FileInputStream(new File("src/resources/template.properties"));
new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
System.out.println(properties.get("userName"));
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}我们能不能创建一个类快速的可以完成文件的读取而且还有缓存的作用?
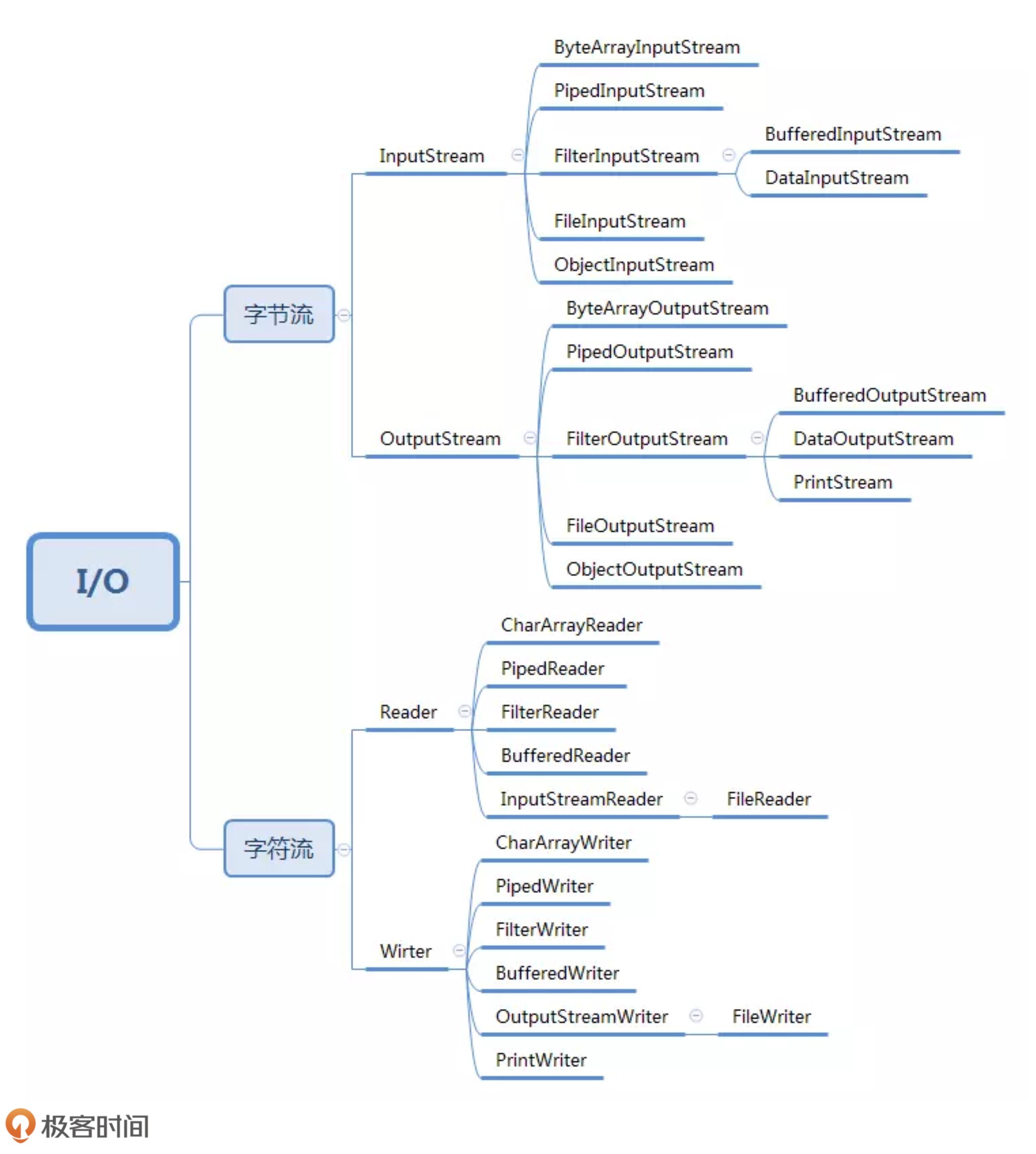
2、设计方案:
2.1、基于继承的设计方案:
如果 InputStream 只有一个子类 FileInputStream 的话,那我们在 FileInputStream 基础之上,再设计一个孙子类 BufferedFileInputStream,也算是可以接受的,毕竟继承结构还算简单。但实际上,继承 InputStream 的子类有很多。我们需要给每一个 InputStream 的子类,再继续派生支持缓存读取的子类。
如果我们继续按照继承的方式来实现的话,就需要再继续派生出 DataFileInputStream、DataPipedInputStream 等类。如果我们还需要既支持缓存、又支持按照基本类型读取数据的类,那就要再继续派生出 BufferedDataFileInputStream、BufferedDataPipedInputStream 等 n 多类。这还只是附加了两个增强功能,如果我们需要附加更多的增强功能,那就会导致组合爆炸,类继承结构变得无比复杂,代码既不好扩展,也不好维护。 (不是很好)
2.2、基于装饰器模式的设计方案:
“组合优于继承”,可以“使用组合来替代继承”,代码如下:
public abstract class InputStream {
//...
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
//...
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
//...
}
public int available() throws IOException {
return 0;
}
public void close() throws IOException {}
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {}
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
throw new IOException("mark/reset not supported");
}
public boolean markSupported() {
return false;
}
}
public class BufferedInputStream extends InputStream {
protected volatile InputStream in;
protected BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
//...实现基于缓存的读数据接口...
}
public class DataInputStream extends InputStream {
protected volatile InputStream in;
protected DataInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
//...实现读取基本类型数据的接口
}第一个比较特殊的地方是:装饰器类和原始类继承同样的父类,这样我们可以对原始类“嵌套”多个装饰器类。
第二个比较特殊的地方是:装饰器类是对功能的增强,这也是装饰器模式应用场景的一个重要特点。
实际上,符合“组合关系”这种代码结构的设计模式有很多,比如之前讲过的代理模式、桥接模式,还有现在的装饰器模式。尽管它们的代码结构很相似,但是每种设计模式的意图是不同的。就拿比较相似的代理模式和装饰器模式来说吧,代理模式中,代理类附加的是跟原始类无关的功能,而在装饰器模式中,装饰器类附加的是跟原始类相关的增强功能。
// 代理模式的代码结构(下面的接口也可以替换成抽象类)
public interface IA {
void f();
}
public class A impelements IA {
public void f() { //... }
}
public class AProxy implements IA {
private IA a;
public AProxy(IA a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void f() {
// 新添加的代理逻辑
a.f();
// 新添加的代理逻辑
}
}
// 装饰器模式的代码结构(下面的接口也可以替换成抽象类)
public interface IA {
void f();
}
public class A implements IA {
public void f() { //... }
}
public class ADecorator implements IA {
private IA a;
public ADecorator(IA a) {
this.a = a;
}
public void f() {
// 功能增强代码
a.f();
// 功能增强代码
}
}3、总结:
装饰器模式主要解决继承关系过于复杂的问题,通过组合来替代继承。它主要的作用是给原始类添加增强功能。这也是判断是否该用装饰器模式的一个重要的依据。除此之外,装饰器模式还有一个特点,那就是可以对原始类嵌套使用多个装饰器。为了满足这个应用场景,在设计的时候,装饰器类需要跟原始类继承相同的抽象类或者实现相同的接口。





















 347
347











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








