#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
double d = 3.14;
double* pd = &d;
printf("%d\n", sizeof(pd));
*pd = 5.5;
printf("%lf\n", d);
printf("%lf\n", *pd);
return 0;
}
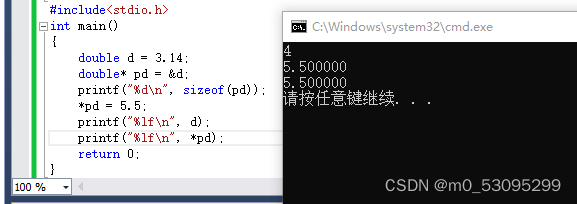
地址:32位地址-4个字节;64位地址-8个字节
结构体struct
构建一个结构体
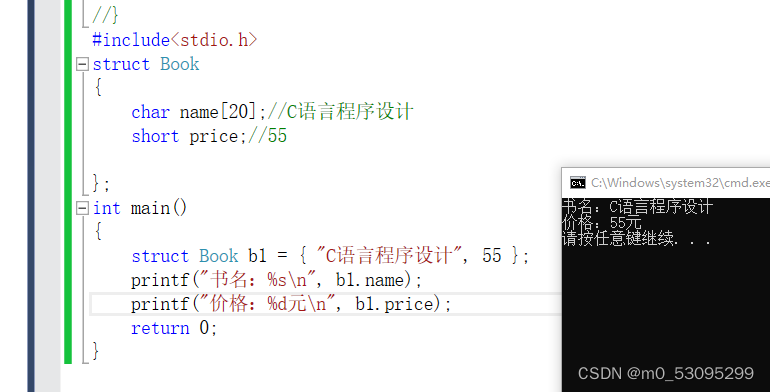
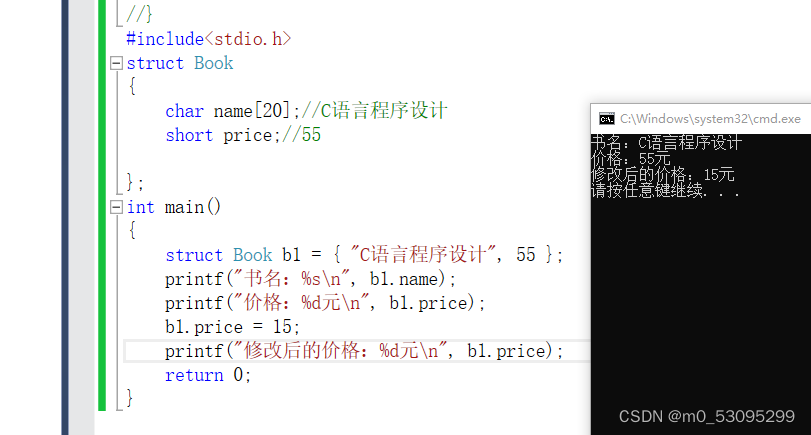
struct Book
{
char name[20];//C语言程序设计
short price;//55
};
int main()
{
struct Book b1 = { "C语言程序设计", 55 };
printf("书名:%s\n", b1.name);
printf("价格:%d元\n", b1.price);
b1.price = 15;
printf("修改后的价格:%d元\n", b1.price);
return 0;
}
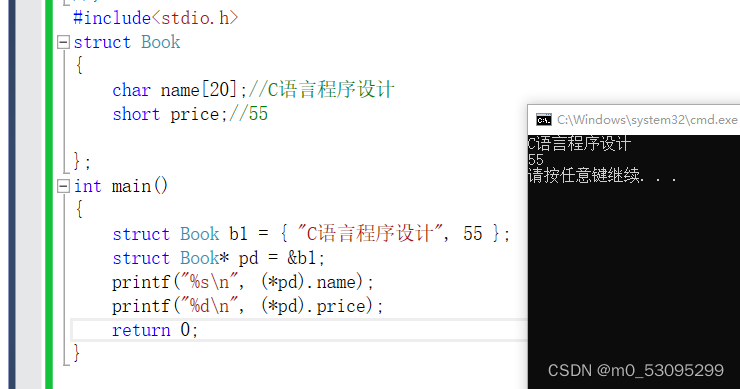
#include<stdio.h>
struct Book
{
char name[20];//C语言程序设计
short price;//55
};
int main()
{
struct Book b1 = { "C语言程序设计", 55 };
struct Book* pd = &b1;
printf("%s\n", (*pd).name);
printf("%d\n", (*pd).price);
return 0;
}
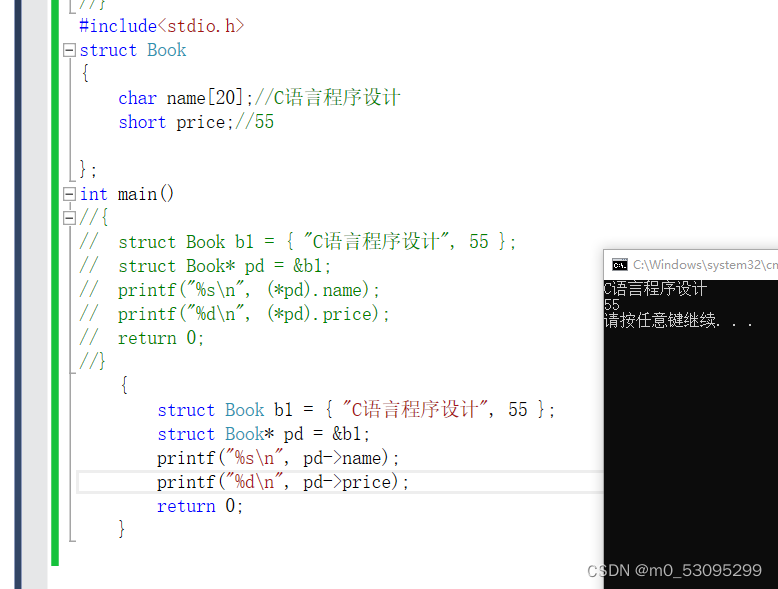
{
struct Book b1 = { "C语言程序设计", 55 };
struct Book* pd = &b1;
printf("%s\n", pd->name);
printf("%d\n", pd->price);
return 0;
}
//利用pd打印出我的书名和价格
//.结构体变量。成员
//->结构体指针->成员
#include<string.h>
struct Book
{
char name[20];//C语言程序设计
short price;//55
};
int main()
//{
// struct Book b1 = { "C语言程序设计", 55 };
// struct Book* pd = &b1;
// printf("%s\n", (*pd).name);
// printf("%d\n", (*pd).price);
// return 0;
//}
{
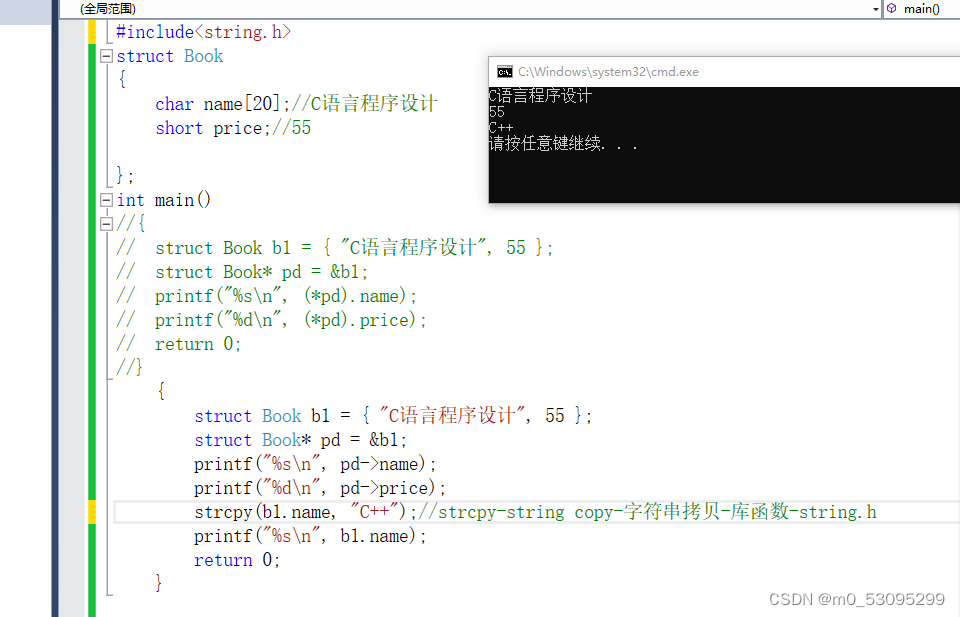
struct Book b1 = { "C语言程序设计", 55 };
struct Book* pd = &b1;
printf("%s\n", pd->name);
printf("%d\n", pd->price);
strcpy(b1.name, "C++");//strcpy-string copy-字符串拷贝-库函数-string.h
printf("%s\n", b1.name);
return 0;
}





















 318
318











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








