进程是程序(静态概念)的一次运行(动态概念),每一次运行都需要操作系统为之分配必要的资源(内存、CPU、PCB编号等)而构成进程实体。进程的并发性(Concurrency)是指一组进程的执行在时间上是重叠的。所谓执行在时间上是重叠的,是指一个进程执行的第一条指令是在另一个进程执行的最后一条指令完成之前开始的。
第一关:进程启动与查看
期望树结构: test-+-sh---pstree `-2*[test---2*[test---2*[test]]]
check.sh:
#/bin/bash
#在begin和end中间输入查看进程和结束进程的命令
#------------begin--------------
ps j|grep helloloop
killall helloloop
#------------end----------------hello-loop.c
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
printf("Hello World!\n");
while(1){
printf("running\n");
}
return 0;
}run.sh
#/bin/bash
#在begin和end中间输入编译和运行程序的命令
#------------begin--------------
gcc hello-loop.c -o helloloop
./helloloop
#------------end----------------第三关:创建两层父子进程树
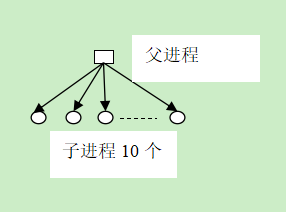
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
pid_t pid;
char cmd[100];
//---------begin---------------
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
pid=fork();
if(pid==0){
return 0;
}
}
//-----------End--------------
sprintf(cmd, "pstree %d > temp", getpid());
system(cmd);
}第四关:创建多层父子进程树
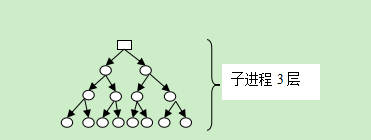
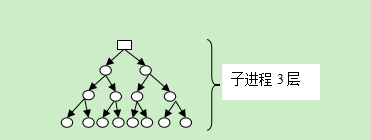
在最后一个子进程创建完成的时候,去获得整个树结构。最上面的进程也没有退出。
期望父子进程树 demo3---demo3---demo3---demo3---demo3---demo3---demo3---demo3---demo3---demo3---sh---pstree
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
pid_t pid,top_pid;
int i = 1;
char cmd[100];
top_pid=getpid();
//*************Begin*******************
for(i=0;i<9;i++){
pid=fork();
if(pid==0){
if(i==8){
sprintf(cmd, "pstree %d > temp", top_pid);
system(cmd);
}
continue;
}
else{
sleep(10);
return 0;
}
}
//在创建最后一层子进程时,获取整个父子进程树结构
//*************End*********************
}第五关:创建父子进程树
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <math.h>
void CheckProcessTree(pid_t top_pid);
void GenerateChildProcess(); //补充完整
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
pid_t top_pid;
int level = 3;
char cmd[100];
top_pid = getpid();
GenerateChildProcess(level,top_pid);//补充完整
}
void CheckProcessTree(pid_t top_pid)
{
char cmd[100];
sprintf(cmd, "pstree %d >temp", top_pid);
system(cmd);
}
void GenerateChildProcess(int level,pid_t top_pid)//参数自己定义
{
//在该函数内实现生成进程树结构,注意在每个子进程中停留10s
//整个进程树建成后,调用CheckProcessTree()
for(int i=0;i<level;i++){
pid_t pida,pidb;
pida=fork();
if(pida>0){
pidb=fork();
if(pidb>0){
break;
}
}
}
if(top_pid==getpid()){
CheckProcessTree(top_pid);
sleep(5);
}
else{
sleep(5);
}
}






















 350
350











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










