PR curve
is plotted based on a set of precision-recall pairs. Given a predicted saliency probability map, its precision and recall scores are computed by comparing its thresholded binary mask against the ground truth mask. The precision and recall of a dataset are computed by averaging the precision and recall scores of those saliency maps. By varying the thresholds from 0 to 1, we can obtain a set of average precision-recall pairs of the dataset.
F-measure
Fβ is used to comprehensively evaluate both precision and recall as:![]()
We set the β2 to 0.3 and report the maximum Fβ (maxFβ) for each dataset similar to previous works
MAE
is the Mean Absolute Error which denotes the average per-pixel difference between a predicted saliency map and its ground truth mask. It is defined as:
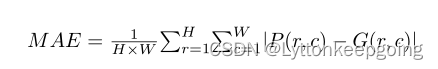
weighted F-measure
is utilized as a comple mentary measure to maxFβ for overcoming the possible unfair comparison caused by “interpolation flaw, dependency flaw and equal-importance flaw”It is defined as:

S-measure
is used to evaluate the structure similarity of the predicted non-binary saliency map and the ground truth. The S-measure is defined as the weighted sum of region-aware Sr and object-aware So structural similarity:
 where α is usually set to 0.5.
where α is usually set to 0.5.
codes:
class Evaluation_metrics():
def __init__(self):
self.beta2 = 0.3 # maxF measure
self.alpha = 0.5 # S measure
self.nb_grid_pr = 255 # pr score
def cal_total_metrics(self, pred, gt):
## pred and gt should have the same dimension: H * W
# MAE
mae = self.cal_mae(pred, gt)
# MaxF measure
prec, recall = self._eval_pr(pred, gt, 255)
f_score = (1 + self.beta2) * prec * recall / (self.beta2 * prec + recall)
f_score[f_score != f_score] = 0 # for Nan
max_f = f_score.max().item()
# AvgF measure
avg_f = f_score.mean().item()
# S measure
gt_mean = gt.mean()
if gt_mean == 0:
Q = 1.0 - pred.mean()
elif gt_mean == 1:
Q = pred.mean()
else:
gt[gt >= 0.5] = 1
gt[gt < 0.5] = 0
Q = self.alpha * self._S_object(pred, gt) + (1 - self.alpha) * self._S_region(pred, gt)
if Q.item() < 0:
Q = torch.FloatTensor([0.0])
s_score = Q.item()
return mae, max_f, avg_f, s_score
def _eval_pr(self, y_pred, y, num):
prec, recall = torch.zeros(self.nb_grid_pr), torch.zeros(self.nb_grid_pr)
thlist = torch.linspace(0, 1 - 1e-10, self.nb_grid_pr)
for i in range(self.nb_grid_pr):
y_temp = (y_pred >= thlist[i]).float()
tp = (y_temp * y).sum()
prec[i], recall[i] = tp / (y_temp.sum() + 1e-20), tp / (y.sum() + 1e-20)
return prec, recall
def _S_object(self, pred, gt):
fg = torch.where(gt == 0, torch.zeros_like(pred), pred)
bg = torch.where(gt == 1, torch.zeros_like(pred), 1 - pred)
o_fg = self._object(fg, gt)
o_bg = self._object(bg, 1 - gt)
u = gt.mean()
Q = u * o_fg + (1 - u) * o_bg
return Q
def _object(self, pred, gt):
x = pred[gt == 1]
mean_x = x.mean()
sigma_x = x.std()
score = 2.0 * mean_x / (mean_x * mean_x + 1.0 + sigma_x + 1e-20)
return score
def _S_region(self, pred, gt):
X, Y = self._centroid(gt)
gt1, gt2, gt3, gt4, w1, w2, w3, w4 = self._divideGT(gt, X, Y)
p1, p2, p3, p4 = self._dividePrediction(pred, X, Y)
Q1 = self._ssim(p1, gt1)
Q2 = self._ssim(p2, gt2)
Q3 = self._ssim(p3, gt3)
Q4 = self._ssim(p4, gt4)
Q = w1 * Q1 + w2 * Q2 + w3 * Q3 + w4 * Q4
return Q
def _centroid(self, gt):
h, w = gt.size()[-2:]
if gt.sum() == 0:
X = torch.eye(1) * round(w / 2)
Y = torch.eye(1) * round(h / 2)
else:
total = gt.sum()
i = torch.from_numpy(np.arange(0, w)).float()
j = torch.from_numpy(np.arange(0, h)).float()
X = torch.round((gt.sum(dim=0) * i).sum() / total)
Y = torch.round((gt.sum(dim=1) * j).sum() / total)
return X.long(), Y.long()
def _divideGT(self, gt, X, Y):
h, w = gt.size()
area = h * w
LT = gt[:Y, :X]
RT = gt[:Y, X:w]
LB = gt[Y:h, :X]
RB = gt[Y:h, X:w]
X = X.float()
Y = Y.float()
w1 = X * Y / area
w2 = (w - X) * Y / area
w3 = X * (h - Y) / area
w4 = 1 - w1 - w2 - w3
return LT, RT, LB, RB, w1, w2, w3, w4
def _dividePrediction(self, pred, X, Y):
h, w = pred.size()
LT = pred[:Y, :X]
RT = pred[:Y, X:w]
LB = pred[Y:h, :X]
RB = pred[Y:h, X:w]
return LT, RT, LB, RB
def _ssim(self, pred, gt):
gt = gt.float()
h, w = pred.size()
N = h * w
x = pred.mean()
y = gt.mean()
sigma_x2 = ((pred - x) * (pred - x)).sum() / (N - 1 + 1e-20)
sigma_y2 = ((gt - y) * (gt - y)).sum() / (N - 1 + 1e-20)
sigma_xy = ((pred - x) * (gt - y)).sum() / (N - 1 + 1e-20)
alpha = 4 * x * y * sigma_xy
beta = (x * x + y * y) * (sigma_x2 + sigma_y2)
if aplha != 0:
Q = alpha / (beta + 1e-20)
elif alpha == 0 and beta == 0:
Q = 1.0
else:
Q = 0
return Q






















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










