void test_string1()
{
string s1; //无参构造函数初始化
string s2("hello");//带参构造函数初始化
string s2="hello";构造+拷贝构造+优化,本质就是隐式类型转换,单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换
cin >> s1;//流插入
cout << s1<<endl;//流提取
cout << s2 << endl;
//字符串的拼接
string ret = s1 + s2; 重载operator+
cout << ret << endl;
string ret1 = s1 + "我喜欢";
}1.遍历string的三种方式
方法1

string s1("hello world");
方法1:
for(size_t i=0;i<s1.size();i++)
{
//读
cout<<s1[i]<<“ ”;//调用operator[],返回第i个位置的字符,并且还能修改
}
for(size_t i=0;i<s1.size();i++)
{
//写
s1[i]++;
}
cout<<s1<<endl;方法2
迭代器(遍历数据结构的一种方式),可以想象成一个指针,string就和顺序表一样
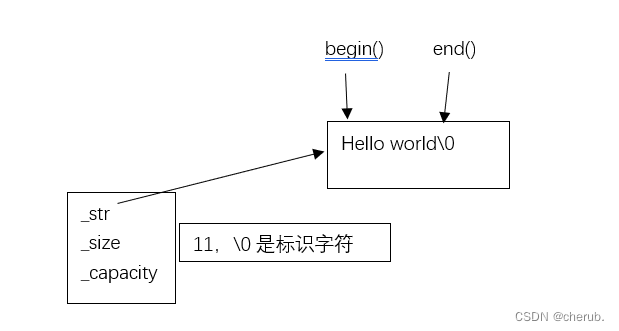
为什么要放\0?因为C++有时要调用C的接口

void test_string2()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello world");
string::iterator it = s1.begin();//begin()返回它开始的指针,正向迭代器
while (it != s1.end())//end()是最后一个元素的下一个位置,最后一个有效字符是d
{
//读
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
输出:hello world
it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
//写
*it='a';
++it;
}
}void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
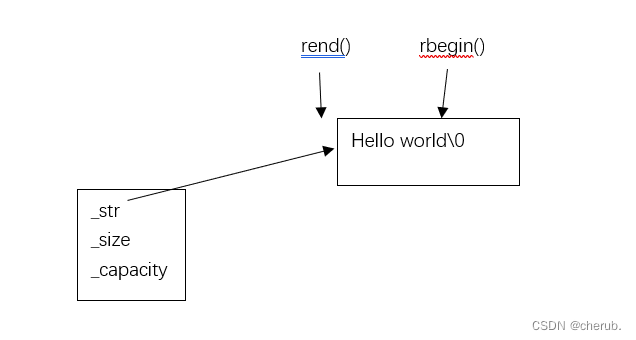
//string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); //反向迭代器
上一行简化为:auto rit=s1.rbegin(); //因为rbegin的返回值就是一个反向迭代器,自动推导左边类型
while (rit != s1.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit; //++是倒着走的,反向迭代器
}
cout << endl;
输出:d l r o w o l l e h
}
方式3
范围for,会取s1中的字符赋值给ch,自动判断结束,自动++,原理:编译器替换成迭代器。*it赋值给ch,ch是*it的拷贝,所以不支持修改。但是取别名可以修改,并且范围for不支持倒着遍历。
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
//读
for (auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//写
for (auto& ch : s1)
{
ch++;
cout << ch << " ";
}
}const迭代器,只能读,不能写
void func(const string& s)//不能用传值传参,会调用拷贝构造,并且是深拷贝,_str,所以加引用,为了防止改变,加const
{
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
//不支持写
//*it = 'a';
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
}
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
func(s1);
}
int main()
{
test_string3();
return 0;
}总结:4种迭代器(两两组合)
正向迭代器 const
反向迭代器 非const
2.string的构造函数

应用:其中1,2,4用的多
第三个
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2(s1);//拷贝构造
//我只想要world
string s3(s1, 6, 5);
cout << s3<<endl; //world
}
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world*******************************************");
string s3(s1, 6); 不写第三个参数,就是有多少取多少
cout << s3<<endl; //world
}
第五个
void test()
{
string s7(10,'a'); aaaaaaaaa
迭代器区间
string s8(s7.begin(),s7.end()); aaaaaaaaa
}3.其他函数
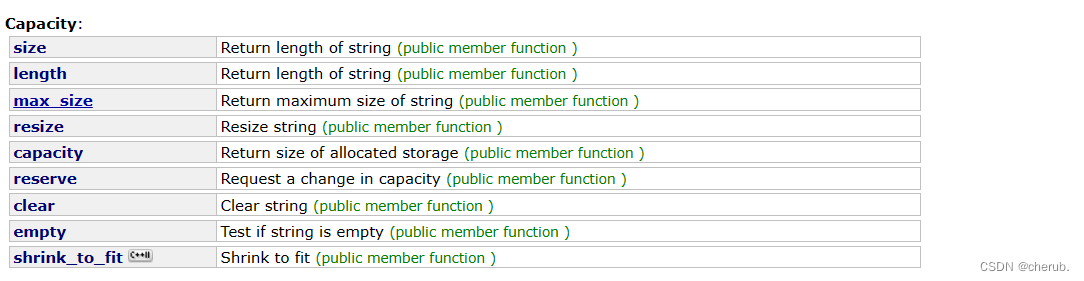
1.size不算\0,\0是用来标识结束的
2.length,不具有通用性,所以就用size
3.clear清理数据,不释放空间。
4.max_size不用管,无用






















 30万+
30万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








