1.switch 和 if 的区别
switch后只能跟等值判断
比如:
int num = 2;
switch (num) {
case 1:
// 当num的值等于1时,执行这里的代码
break;
case 2:
// 当num的值等于2时,执行这里的代码
break;
case 3:
// 当num的值等于3时,执行这里的代码
break;
default:
// 如果没有匹配的值,则执行这里的代码
}
因此switch中可以使用字符串类型的判断
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = sc.nextInt();
double b = sc.nextInt();
String c = sc.next();
switch (c){
case "+"-> System.out.println(a+b);
case "-"-> System.out.println(a-b);
case "*"-> System.out.println(a*b);
case "/"-> System.out.println(a/b);
default -> System.out.println("无效");
};
这里的运算符可以通过switch来进行等值判断
if更适合连续区间的判断
没有switch选择结构的限制,适合某个变量处于某个连续区间时的情况。
比如:
if
int num = 5;
if (num >= 1 && num <= 5) {
// num在范围[1, 5]内,执行这里的代码
} else if (num >= 6 && num <= 10) {
// num在范围[6, 10]内,执行这里的代码
} else {
// 不在以上范围内,执行这里的代码
}
switch
int num = 5;
switch (num) {
case 1 to 5: // 错误,不能直接使用范围
// 执行这里的代码
break;
case 6 to 10: // 错误,同样不能使用范围
// 执行这里的代码
break;
default:
// 执行这里的代码
}
2.IDE配置
1.常用配置
字体,自动导包,代码提示大小写区分,代码模板,编码集
2.DEBUG的使用
该功能可以详细了解代码的每一步实现步骤,更适合开发人员调试
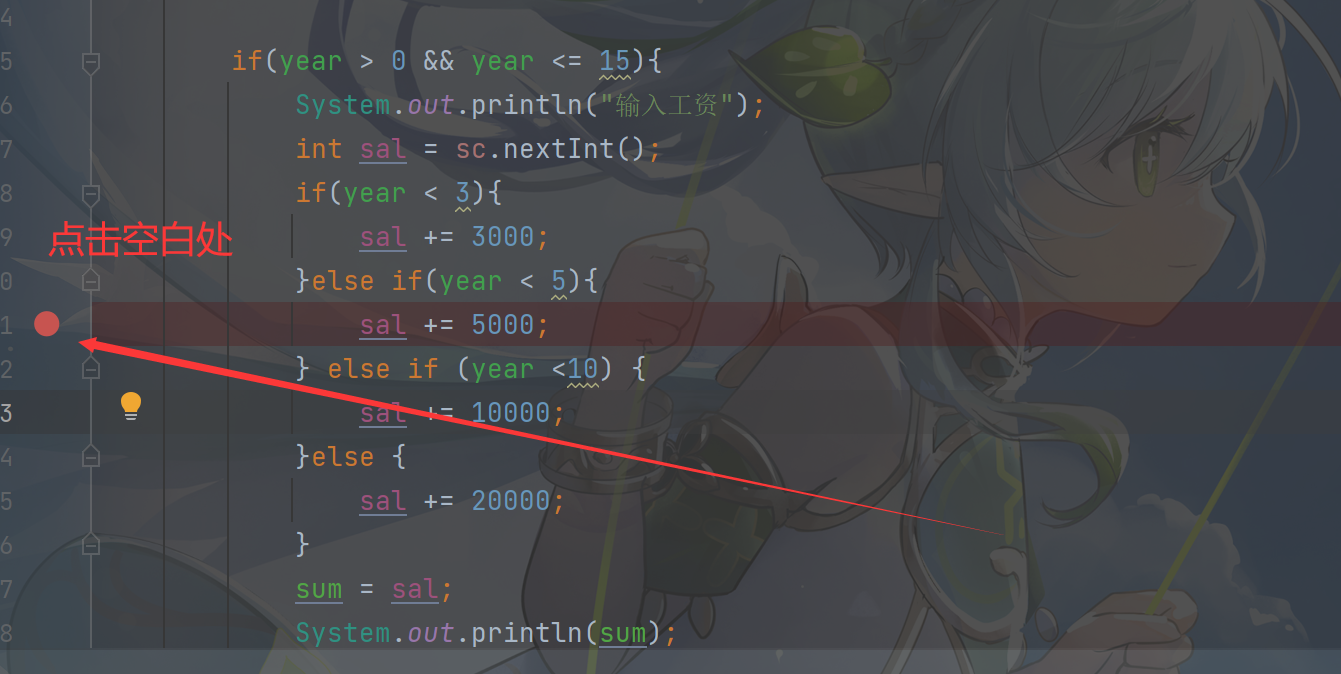
1.设置/取消断点
在代码行按快捷键 Ctrl +F8 或者点击代码行数与编辑区的中间区域,可以在为该行设置或取消断点,断点处可以暂停运行
2.调试运行
调试运行有如下几种方式
点击工具栏的 debug 按钮
使用 Shift + F9 快捷键
选择类或在代码编辑区,右键 >Debug 'xxxxxx'

3.DEBUG的基本用法(调试)
Show Execution Point (Alt + F10):如果你的光标在其它行或其它页面,点击这个按钮可跳转到当前代码执行的行。
Step Over (F8):步过,一行一行地往下走,如果这一行上有方法不会进入方法。
Step Into (F7):步入,如果当前行有方法,可以进入方法内部,一般用于进入自定义方法内,不会进入官方类库的方法,如第25行的put方法。
Force Step Into (Alt + Shift + F7):强制步入,能进入任何方法,查看底层源码的时候可以用这个进入官方类库的方法。
Step Out (Shift + F8):步出,从步入的方法内退出到方法调用处,此时方法已执行完毕,只是还没有完成赋值。
Drop Frame (默认无):回退断点,后面章节详细说明。
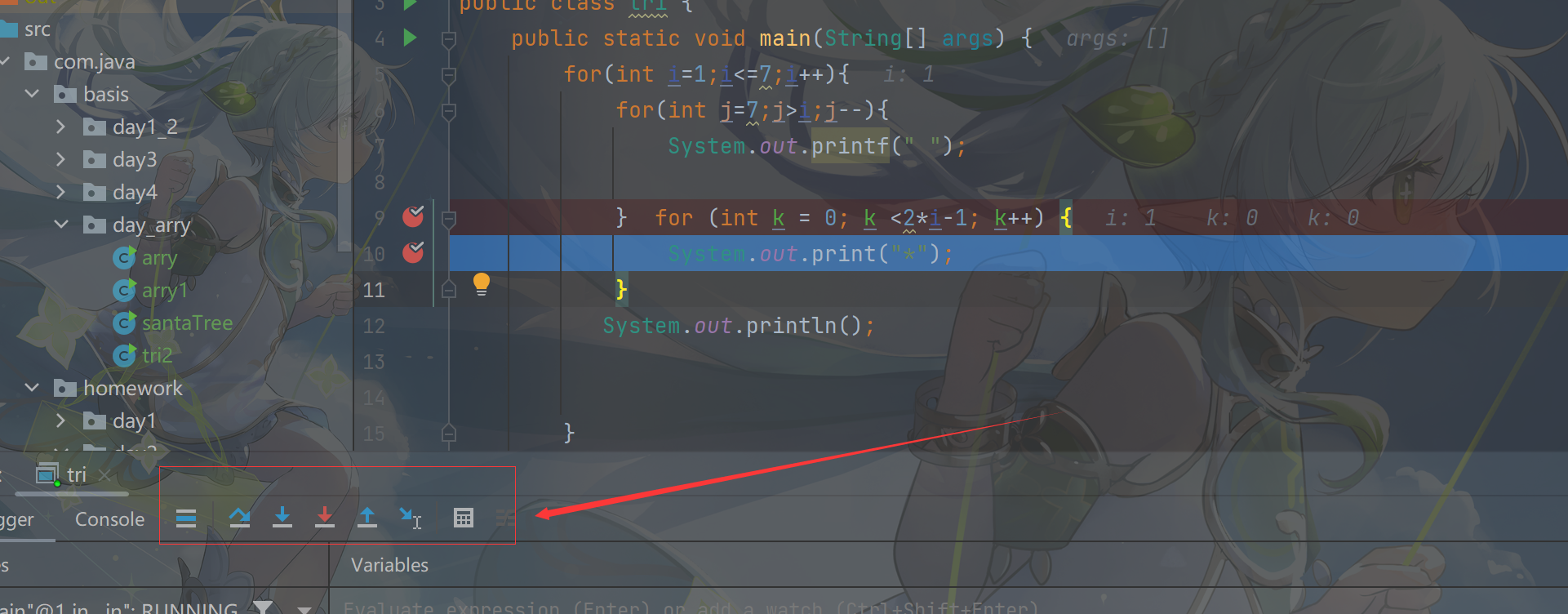
Run to Cursor (Alt + F9):运行到光标处,你可以将光标定位到你需要查看的那一行,然后使用这个功能,代码会运行至光标行,而不需要打断点。
找不到这排按钮可以选择箭头处重置一下就重新恢复了

4.DEBUG的基本用法(启动终止)
Rerun 'xxxx':重新运行程序,会关闭服务后重新启动程序。
Update 'tech' application (Ctrl + F5):更新程序,一般在你的代码有改动后可执行这个功能。而这个功能对应的操作则是在服务配置里,如图2.3。
Resume Program (F9):恢复程序,比如,你在第20行和25行有两个断点,当前运行至第20行,按F9,则运行到下一个断点(即第25行),再按F9,则运行完整个流程,因为后面已经没有断点了。
Pause Program:暂停程序,启用Debug。目前没发现具体用法。
Stop 'xxx' (Ctrl + F2):连续按两下,关闭程序。有时候你会发现关闭服务再启动时,报端口被占用,这是因为没完全关闭服务的原因,你就需要查杀所有JVM进程了。
View Breakpoints (Ctrl + Shift + F8):查看所有断点,后面章节会涉及到。
Mute Breakpoints:哑的断点,选择这个后,所有断点变为灰色,断点失效,按F9则可以直接运行完程序。再次点击,断点变为红色,有效。如果只想使某一个断点失效,可以在断点上右键取消Enabled,如图2.4,则该行断点失效。
当没有这一列按键时,可以勾选show toolbar 开启窗口
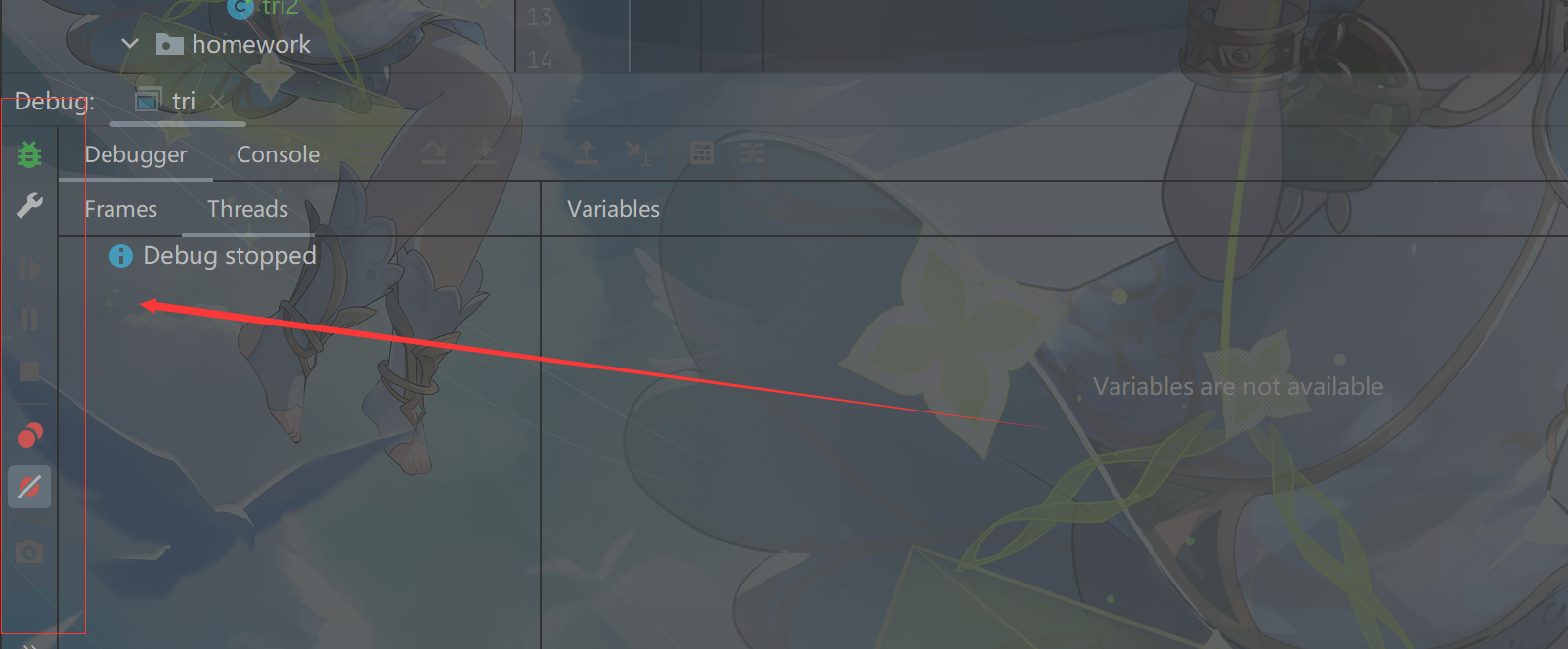
5.DEBUG的基本用法(表达式切换值)


在箭头处可以填写变量值,查看变量值
3.常用插件
在 settings -> plugins 选项中下载。目前推荐安装以下插件: Translation 一款翻译插件 Alibaba Java Coding Guidelines 阿里编码规约检查插件 jclasslib bytecode viewer 查看字节码文件的插件
不建议安装太多插件会导致ide启动速度的降低
4.快捷键(常用)
默认快捷键 Ctrl + F 在当前文件进行文本查找 (必备) Ctrl + R 在当前文件进行文本替换 (必备) Ctrl + Z 撤销 (必备) Ctrl + X 剪切光标所在行 或 剪切选择内容 Ctrl + C 复制光标所在行 或 复制选择内容 Ctrl + D 复制光标所在行 或 复制选择内容,并把复制内容插入光标位置下面 (必备) Ctrl + E 显示最近打开的文件记录列表 (必备) Ctrl + / 注释光标所在行代码,会根据当前不同文件类型使用不同的注释符号 (必备) Ctrl + Alt + L 格式化代码,可以对当前文件和整个包目录使用 (必备) Ctrl + Alt + O 优化导入的类,可以对当前文件和整个包目录使用 (必备) 连按两次 Shift
弹出 Search Everywhere 弹出层
3.IF与SWITCH题目练习
计算器
-
编写一个简单的计算器程序,要求用户输入两个数和操作符(+、-、*、/),然后根据操作符进行相应的运算,并输出结果。如果输入的运算符不是有效的运算符,则输出"无效的运算符"。
import javax.xml.transform.Result;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Author:Yinan
* @DATE:
*/
/*
编写一个简单的计算器程序,要求用户输入两个数和操作符(+、-、*、/),然后根据操作符进行相应的运算,并输出结果。
如果输入的运算符不是有效的运算符,则输出"无效的运算符"。
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个值:");
double a = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入第二个值:");
double b = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入需要执行的计算(+、-、*、/):");
String c = sc.next();
switch (c) {
case "+" -> {
double result = a+b;
System.out.printf("计算的结果为:%f F \n", result);
}
case "-" -> {
double result = a-b;
System.out.printf("计算的结果为:%f F \n", result);
}
case "*" -> {
double result = a*b;
System.out.printf("计算的结果为:%f \n", result);
}
case "/" -> {
double result = a/b;
System.out.printf("计算的结果为:%f \n", result);
}
}
}
}
季节
-
编写一个程序,根据用户输入的月份(1 到 12),输出该月份所属的季节。假设春季是 3到 5 月,夏季是 6 到 8 月,秋季是 9 到 11 月,冬季是 12、1 和 2月。如果输入的月份超出了范围,输出"输入错误"。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.zip.Deflater;
/**
* @Author:Yinan
* @DATE:
*/
/*
编写一个程序,根据用户输入的月份(1 到 12),输出该月份所属的季节。假设春季是 3到 5 月,夏季是 6 到 8 月,
秋季是 9 到 11 月,冬季是 12、1 和 2月。如果输入的月份超出了范围,输出"输入错误"。
*/
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个月份:");
int month = sc.nextInt();
/*方法一
switch (month){
case 3,4,5 -> System.out.println("这个月份是春季!!");
case 6,7,8 -> System.out.println("这个月份是夏季!!");
case 9,10,11 -> System.out.println("这个月份是秋季!!");
case 12,1,2 -> System.out.println("这个月份是冬季!!");
default -> System.out.println("您输入的月份无效");
}
*/
//方法二
if (month == 3 || month == 4 || month == 5 ){
System.out.println("这个月份是春季!!");
}else if (month == 6 || month == 7 || month == 8 ){
System.out.println("这个月份是夏季!!");
}else if (month == 9 || month == 10 || month == 11 ){
System.out.println("这个月份是秋季!!");
}else if (month == 12 || month == 1 || month == 2 ){
System.out.println("这个月份是冬季!!");
}else {
System.out.println("您输入的月份无效");
}
}
}
星座
-
编写一个程序,根据用户输入的月份和日期,输出该日期所在的星座。以下是一个简单的星座日期范围参考:
| 水瓶座(1月20日到2月18日) | 双鱼座(2月19日到3月20日) |
|---|---|
| 白羊座(3月21日到4月19日) | 金牛座(4月20日到5月20日) |
| 双子座(5月21日到6月20日) | 巨蟹座(6月21日到7月22日) |
| 狮子座(7月23日到8月22日) | 处女座(8月23日到9月22日) |
| 天秤座(9月23日到10月22日) | 天蝎座(10月23日到11月21日) |
| 射手座(11月22日到12月21日) | 魔羯座(12月22日到1月19日) |
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Author:Yinan
* @DATE:
*/
/*
编写一个程序,根据用户输入的月份和日期,输出该日期所在的星座。
*/
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入月份:");
int month = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入日期:");
int day = sc.nextInt();
switch (month) {
case 1 -> {
if (day >= 20 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为水瓶座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为摩羯座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 2 -> {
if (day >= 19 && day < 29) {
System.out.println("您的星座为双鱼座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 29) {
System.out.println("您的星座为水瓶座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 3 -> {
if (day >= 21 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为白羊座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为双鱼座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 4 -> {
if (day >= 20 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为金牛座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为白羊座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 5 -> {
if (day >= 21 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为双子座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为金牛座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 6 -> {
if (day >= 21 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为巨蟹座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为双子座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 7 -> {
if (day >= 23 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为狮子座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为巨蟹座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 8 -> {
if (day >= 23 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为处女座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为狮子座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 9 -> {
if (day >= 23 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为天秤座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为处女座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 10 -> {
if (day >= 23 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为天蝎座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为天秤座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 11 -> {
if (day >= 22 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为射手座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 31) {
System.out.println("您的星座为天蝎座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
case 12 -> {
if (day >= 22 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为摩羯座!");
} else if (day > 0 && day < 32) {
System.out.println("您的星座为射手座!");
} else {
System.out.println("您输入的日期无效!");
}
}
default -> System.out.println("您输入的月份无效");
}
}
}
奖金
-
编写一个程序,根据员工的工龄来计算年终奖金。奖金计算规则如下:
-
工龄小于等于5年,奖金为工资的5%
-
工龄大于5年且小于等于10年,奖金为工资的10%
-
工龄大于10年,奖金为工资的15%
-
(工资和工龄输入)
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Author:Yinan
* @DATE:
*/
/*
编写一个程序,根据员工的工龄来计算年终奖金。奖金计算规则如下:
工龄小于等于5年,奖金为工资的5%
工龄大于5年且小于等于10年,奖金为工资的10%
工龄大于10年,奖金为工资的15%
*/
public class Test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您的工资:");
double salary = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("请输入您的工龄:");
int year = sc.nextInt();
salary *=12;
if (year <= 5 & year > 0) {
salary *=0.05;
} else if (year>5&year<=10) {
salary *=0.1;
}else if (year>10){
salary *=0.15;
}
System.out.printf("您的奖金为:%f 元",salary);
}
}
循环的练习
1.洪乞丐干10天,收入是多少?
天朝有一个乞丐姓洪,去天桥要钱 第一天要了1块钱 第二天要了2块钱 第三天要了4块钱 第四天要了8块钱 以此类推
// 天朝有一个乞丐姓洪,去天桥要钱
// 第一天要了1块钱
// 第二天要了2块钱
// 第三天要了4块钱
// 第四天要了8块钱
// 以此类推a天一共多少钱
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int sal =1;
int daysal=1;
for (int i = 1; i <a; i++) {
if(a==1){
System.out.println(1);
continue;
} else if (a==0) {
System.out.println(0);
} else {
daysal *= 2;
}
sal += daysal;
}
System.out.println(sal);
}
2.李四跑步
李四每天跑步
第一周周一跑 100 米,周二到周天每天比前一天多 100 米。
往后每周以比前一周周一多 100 米。
请问 李四 n(控制台输入) 天后跑了多少米
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int day = sc.nextInt();
int week = day / 7;
int extraday = day % 7;
int running = 0;
int run = 0;
int extrarun=0;
extrarun=(week+1)*100;
for (int i = 1; i <= week; i++) {
run = 100 * i ;
for (int j = 7; j > 0; j--) {
running += run;
run += 100;
}
} for(int k=1;k<=extraday;k++){
running += extrarun;
extrarun += 100;
}
System.out.println(running);
}
3.输入一个数字,和位数,判断是否回文数字
eg:1221 就是回文数字
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
// int wei = sc.nextInt();
int ge =0;
int tem=num;
int n=0;
while(num!=0){
//从右到左依次获得数字
ge = num%10;
num = num/10;
n = n*10 +ge;
}
String flag = n==tem?"是":"不是";
System.out.println(flag);
}
4.打印输出一个由字符构成的正方形图案
其中边 长 由 用 户 输 入 确 定 。 要 求 字 符 按 照 以 下 顺 序 循 环 使 用:'#', '@', '*'。例如,当边长为 5 时,输出如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //行
if( i==1||i==n) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (j == 1 || j == n) {
System.out.print("#");
} else {
System.out.print("@");
}
} System.out.println();
//中间
}else {
for (int j = 1; j <=n; j++) {
if (j==1||j==n) {
System.out.print("@");
}else {
System.out.print("*");
}
} System.out.println();
}
}
}





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








