02-数组模拟队列
1、思路
举个例子我们人排队过安检,这就是一个队列,先排队的人先过完安检,后排队的人后过完安检,假设有5个人过安检,从头到尾排队顺序为12345,那么过安检的顺序就为12345,用一句话来形容队列的特点就是先进先出,后进后出。
数组模拟队列的图解如下:

添加数据到队列图解:
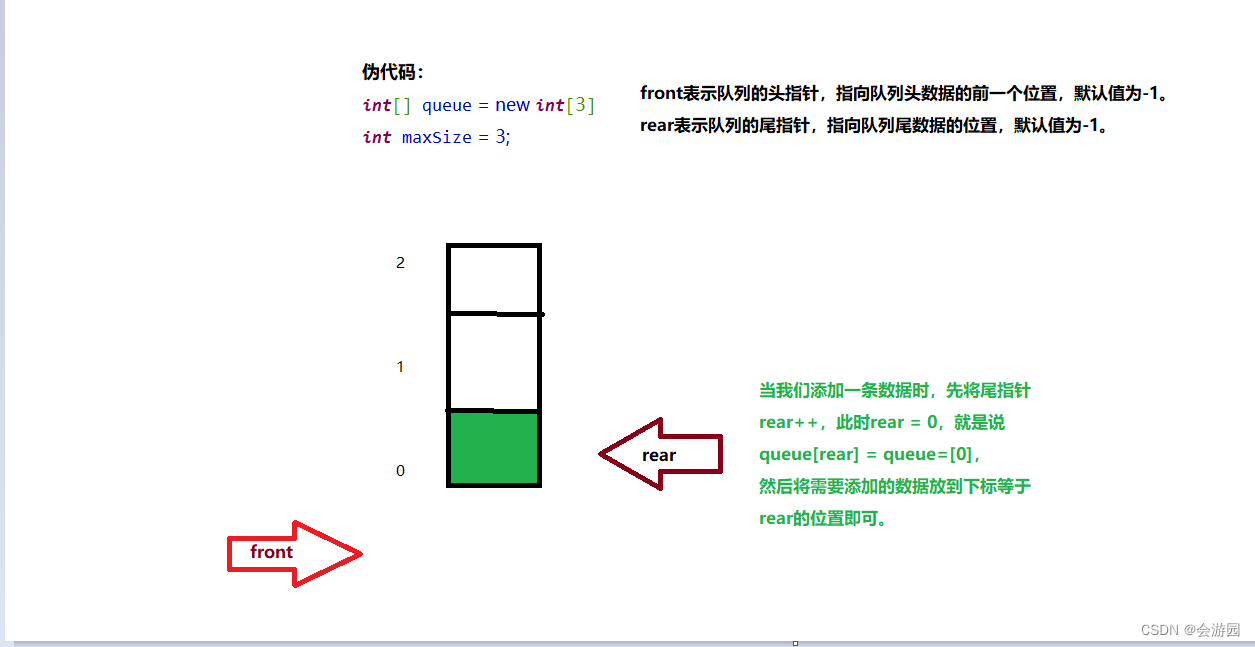
以此类推……
取出队列的头数据图解:

以此类推……
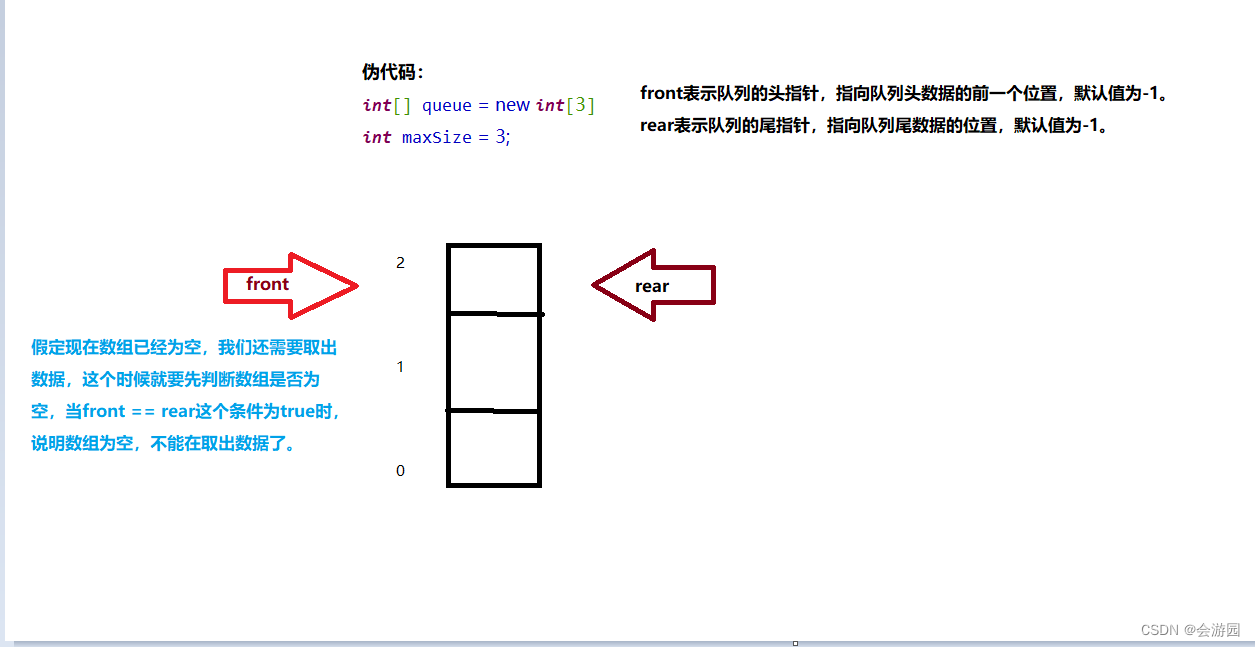
以上就是数组模拟队列的图解。
这种数据结构的设置存在数组空间不能重复利用的问题,我们不难发现,当头指针front和尾指针rear都等于maxSize - 1也就是说都指向数组的最后一个位置时,我们就不能添加数据了,虽然真正的意义上数组是空的,但是我们操作数组用的是front和rear指针,所以我们已经访问不到数组为空的地方。
也就是说,我们创建一个大小为3的数组模拟出来的队列,我们往里面添加3条数据,然后在取出3条数据,此时这个队列已经用不了了,这个问题就导致不能循环利用数组空间的问题。
2、代码实现
package com.ljkj.codetest;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 数组模拟环形队列
*
* @author zd
*/
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(3);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("[a]添加,[g]取出头数据,[p]查看头数据,[s]展示队列,[e]退出程序");
System.out.println("请输入指令:");
// 接受控制台输入的内容
char input = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (input) {
case 'a':
System.out.println("请输入需要添加的数据:");
queue.addData(scanner.nextInt());
break;
case 'g':
try {
System.out.println(queue.getData());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'p':
try {
System.out.println(queue.peekData());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'e':
System.out.println("程序退出");
return;
default:
System.out.println("无效指令");
break;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 用数组模拟队列
*/
class ArrayQueue {
/**
* 用来模拟队列的数组
*/
private int[] queue;
/**
* 队列的容量长度
*/
private int maxSize;
/**
* 队列的头指针,指向队列头数据的前一个位置,默认=-1
*/
private int front;
/**
* 队列的尾指针,指向队列尾数据的位置,默认=-1
*/
private int rear;
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize > 0) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
// 初始化队列
this.queue = new int[maxSize];
// 默认为-1
this.front = -1;
this.rear = -1;
return;
}
throw new RuntimeException("队列容量长度不能小于1");
}
/**
* 判断队列是否为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
// 头指针和尾指针相等说明为空
return this.front == this.rear;
}
/**
* 判断队列是否已满
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isFull() {
// 如果尾指针等于队列长度减一,说明队列已满
return this.rear == this.maxSize - 1;
}
/**
* 添加数据到队列
*
* @param data
*/
public void addData(int data) {
if (this.isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列已满");
return;
}
// 尾指针自加一
this.rear++;
// 添加到队列中
queue[this.rear] = data;
}
/**
* 取出队列的头数据
*
* @return
*/
public int getData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
}
// 头指针自加一
this.front++;
// 取出头数据
return this.queue[this.front];
}
/**
* 查看队列的头数据
*
* @return
*/
public int peekData() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空");
}
// 将头指针加一,查看队列的数据
return this.queue[this.front + 1];
}
/**
* 展示队列数据
*/
public void showQueue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空");
return;
}
for (int i = this.front; i < this.rear; i++) {
System.out.printf("queue[%d] = %d\n", i + 1, this.queue[i + 1]);
}
}
}
对于以上提到的空间不能循环利用的问题,下一章节我们通过数组模拟出来的环形队列来解决。






















 1055
1055











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








