5.1 一个简单的示例
先做一个简单的示例,演示if语句处理的特殊情形,代码示例如下:
cars = ["audi", "bmw", "subaru", "toyota"]
for car in cars:
if car == "bmw":
print(car.upper())
else:
print(car.title())执行结果:

5.2 条件测试
5.2.1 检查是否相等
使用相等运算符可以判断两个值是否相等,代码示例如下:
car = "bmw"
print(car == "bmw")
print(car == "audi")执行结果:

5.2.2 检查是否相等
检查相等时是否区分大小写,代码示例如下:
car = "Audi"
print(car == "audi")
print(car.lower() == "audi")执行结果:

5.2.3 检查是否不相等
要判断值的不相等可以使用(!=)来进行判断,代码示例如下:
requested_topping = "mushrooms"
if requested_topping != "anchovies":
print("Hold the anchovies!")代码示例如下:
![]()
5.2.4 数值比较
5.2.5 检查多个条件
1. 使用and检查多个条件
要检查两个条件是否都为true可以使用and,如果通过则返回true。代码示例如下:
age_0 = 22
age_1 = 18
print(age_0 >= 21 and age_1 >= 21)
age_1 = 22
print(age_0 >= 21 and age_1 >= 21)执行结果如下:

2.使用or检查多个条件
使用or检查条件,当只有一个条件通过则通过。代码示例如下:
age_0 = 22
age_1 = 18
print(age_0 >= 21 or age_1 >= 21)
age_0 = 18
print(age_0 >= 21 or age_1 >= 21)执行结果如下:

5.2.6 检查特定值是否包含在列表中
要判断值是否包含在列表当中可以使用关键字 in。代码示例如下:
requested_topping = ["mushrooms", "onions", "pineapple"]
print("mushrooms" in requested_topping)
print("pepperoni" in requested_topping)执行结果:

5.2.7 检查特定值是否不包含在列表中
查看特定值是否不包含在列表中,可以使用以下方法:
banned_users = ["andrew", "carolina", "david"]
user = "marie"
if user not in banned_users:
print(f'{user.title()}, you can post a response if you wish!')运行结果:

5.2.8 布尔表达式
布尔表达式通常用于记录条件。分别有True以及False代表真与假。
5.2.9 练习
练习 5-1:条件测试 编写一系列条件测试,将每条测试以及对其结果的预测和实际结果打印出来。
代码示例如下:
numbers = [1, 44, 5, 2, 7, 23, 7 ,3 , 34, 56,34 , 4 ,23, 13 ,6, 3, 34, 64, 21, 52]
for number in numbers:
print("该数是否是10以内的数", number<10)执行结果:

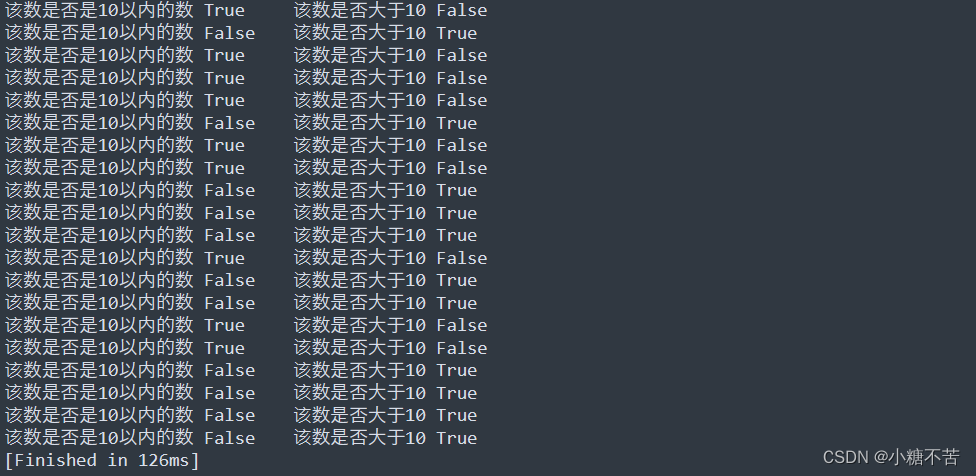
练习 5-2:更多条件测试 你并非只能创建10个测试。如果尝试做更多,可再编写一些测试,并将其加入conditional_tests.py中。
代码示例如下:
numbers = [1, 44, 5, 2, 7, 23, 7 ,3 , 34, 56,34 , 4 ,23, 13 ,6, 3, 34, 64, 21, 52]
for number in numbers:
print("该数是否是10以内的数", number<10, "\t该数是否大于10", number>10)执行结果:
5.3 if语句
5.3.1 简单的if语句
最简单的if语句示例:
age = 19
if age >=18:
print("You are old enough to vote!")执行结果:

5.3.2 if-else语句
if-else语句,当结果为真时,返回的是前一个结果,当条件与输入不符时返回结果为第二个结果代码示例:
age = 17
if age >=18:
print("You are old enough to vote!")
else:
print("Sorry,you are too young to vote!")执行结果

5.3.3 if-elif-else结构
if-elif-else依次检查每个条件测试,知道通过的示例才输出,代码示例如下:
age = 12
if age < 4:
print("You admission cost is $0.")
elif age < 18:
print("You admission cost is $25.")
else:
print("You admission cost is $40.")执行结果:

5.3.4 使用多个elif代码块
可根据需求,进行多个elif代码块的使用,代码示例如下:
age = 30
if age < 4:
price = 0
elif age < 18:
price = 25
elif age <65:
price = 40
else:
price = 20
print(f"You admission cost is ${price}.")执行结果:

5.3.5 省略else代码块
大部分情况使用else语句都是很有作用的,但是作用不大情况下,可以省略else语句:
age = 80
if age < 4:
price = 0
elif age < 18:
price = 25
elif age <65:
price = 40
elif age>=65:
price = 20
print(f"You admission cost is ${price}.")执行结果:
![]()
5.3.6 测试多个样例
如果需要判断多个情况是否符合条件的话,可以使用多个if语句进行测试,代码示例如下:
table = ["叉烧饭","烧鸭饭","鸡腿饭"]
if "叉烧饭" in table:
print("有叉烧饭")
if "烧鸭饭" in table:
print("有烧鸭饭")
if "鸡腿饭" in table:
print("有鸡腿饭")测试结果:

5.3.7 练习
练习 5-3:外星人颜色 假设游戏中刚射杀了一个外星人,请创建一个名为alien_color的变量,并将其赋值为‘green’、'yellow'或'red'。
· 编写一条if语句检查外星人的颜色是否为绿色,如果是则打印一条消息,指出玩家获得5分
· 编写两个版本,其中一个通过,另一个不通过。
代码示例:
alien_color = "green"
if alien_color == "green":
print("Player get 5 price")
alien_color = "red"
if alien_color == "green":
print("Player get 5 price")执行结果:

练习 5-4:外星人颜色2 在上一个练习改进,如果是绿色获得5分,不是获得10分
代码示例:
alien_color = "green"
if alien_color == "green":
print("Player get 5 price")
else:
print("Player get 10 price")
alien_color = "red"
if alien_color == "green":
print("Player get 5 price")
else:
print("Player get 10 price")执行结果:

练习5-5:外星人颜色3 使用if-elif-else语句,绿色5分,黄色10分,红色15分。
代码示例:
alien_color = "green"
if alien_color == "green":
print("Player get 5 price")
elif alien_color == "yellow":
print("Player get 10 price")
elif alien_color == "red":
print("Player get 15 price")
alien_color = "yellow"
if alien_color == "green":
print("Player get 5 price")
elif alien_color == "yellow":
print("Player get 10 price")
elif alien_color == "red":
print("Player get 15 price")
alien_color = "red"
if alien_color == "green":
print("Player get 5 price")
elif alien_color == "yellow":
print("Player get 10 price")
elif alien_color == "red":
print("Player get 15 price")执行结果:

练习 5-6:人生的不同阶段 设计变量age,编写一个if-elif-else语句
小于2岁:婴儿;2~4岁:幼儿;4~13岁:儿童;13~20:青少年;20~65:成年人;大于65:老年人
代码示例:
age = 23
if age < 2:
print("婴儿")
elif 2 <= age < 4:
print("幼儿")
elif 4 <= age < 13:
print("幼儿")
elif 13 <= age < 20:
print("青少年")
elif 20 <= age < 65:
print("成年")
elif age >= 65:
print("老年")执行结果:

练习 5-7 喜欢的水果 创建一个列表,如果喜欢的水果在列表里则打印出来
代码示例:
fruits = ["榴莲","香蕉","菠萝"]
fruit = "榴莲"
if fruit in fruit:
print(f"你最喜欢的水果是{fruit}")执行结果:

5.4 使用if语句处理列表
5.4.1 检查特殊列表
代码示例:
requsted_toppings = ["mushrooms","green peppers","extra cheese"]
for requsted_topping in requsted_toppings:
if requsted_topping == "green peppers":
print("Sorry ,we are out of green peppers right now!")
else:
print(f"Adding {requsted_topping}")
print("\nFinshed making your pizza!")执行结果:

5.4.2 确定列表不为空
判断列表是否为空的作用很多,其中之一就是判断for语句当中是否有元素用于循环。代码示例如下:
requsted_toppings = []
if requsted_toppings:
for requsted_topping in requsted_toppings:
if requsted_topping == "green peppers":
print("Sorry ,we are out of green peppers right now!")
else:
print(f"Adding {requsted_topping}")
else:
print("Are you sure you want a plain pizze")执行结果:

5.4.3 使用多个列表
代码示例:
requsted_toppings = ['mushrooms','olives','green peppers','pepperoni','pineapple','extra cheese']
available_toppings = ['mushrooms','french fries','extra cheese']
if requsted_toppings:
for requsted_topping in available_toppings:
if requsted_topping in requsted_toppings:
print(f"Adding {requsted_topping}")
else:
print(f"Sorry ,we are out of {requsted_topping} right now!")
else:
print("Are you sure you want a plain pizze")执行结果:

5.4.4 if语句的格式
比较运算符前后添加空格
5.4.5 练习
练习 5-8 以特殊的方式和管理员打招呼 创建一个5个用户的列表,其中一个为管理员用户。编写代码实现问候消息,代码示例如下:
user_names = ['lihua', 'zhangsan', 'lisi', 'wangwu', 'admin']
for user in user_names:
if user == 'admin':
print(f'你好,管理员{user}')
else:
print(f'你好,用户{user}')执行结果:

练习 5-9 处理用户情形 添加一个if语句判断用户列表是否为空:
user_names = []
if user_names != []:
for user in user_names:
if user == 'admin':
print(f'你好,管理员{user}')
else:
print(f'你好,用户{user}')
else:
print('当前无用户信息!')执行结果:

练习 5-10 检查用户名 确保每个用户名是独一无二的:
user_names = ['lihua', 'zhangsan', 'lisi', 'wangwu', 'admin']
new_user = ['luhua', 'zhangsan', 'lusi', 'wangwu', 'any']
if user_names == []:
print("当前用户表为空")
else:
for user in user_names:
if user in new_user:
print(f'{user}用户名重复!')
else:
print(f'{user}用户创建成功!')执行结果:

练习 5-11 序数 一个列表创建数字判断后以序数形式输出:
for i in range(1, 10):
if i == 1:
print(i , 'st')
elif i == 2:
print(i , 'nd')
elif i == 3:
print(i , 'rd')
else:
print(i , 'th')执行结果:


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








