4.8. More on Defining Functions
It is also possible to define functions with a variable number of arguments. There are three forms, which can be combined.
4.8.1. Default Argument Values
The most useful form is to specify a default value for one or more arguments. This creates a function that can be called with fewer arguments than it is defined to allow. For example:
def ask_ok(prompt, retries=4, reminder='Please try again!'):
while True:
ok = input(prompt)
if ok in ('y', 'ye', 'yes'):
return True
if ok in ('n', 'no', 'nop', 'nope'):
return False
retries = retries - 1
if retries < 0:
raise ValueError('invalid user response')
print(reminder)
This function can be called in several ways:
-
giving only the mandatory argument:
ask_ok('Do you really want to quit?') -
giving one of the optional arguments:
ask_ok('OK to overwrite the file?', 2) -
or even giving all arguments:
ask_ok('OK to overwrite the file?', 2, 'Come on, only yes or no!')
This example also introduces the in keyword. This tests whether or not a sequence contains a certain value.
The default values are evaluated at the point of function definition in the defining scope, so that
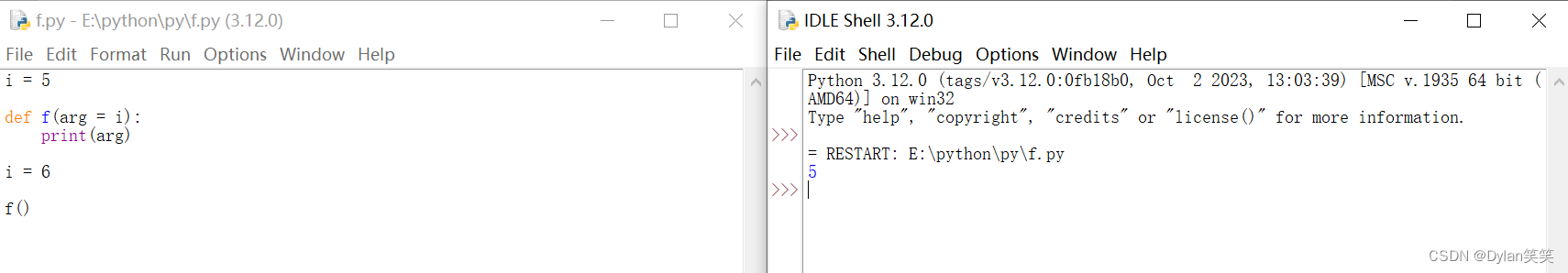
i = 5
def f(arg=i):
print(arg)
i = 6
f()
will print .5
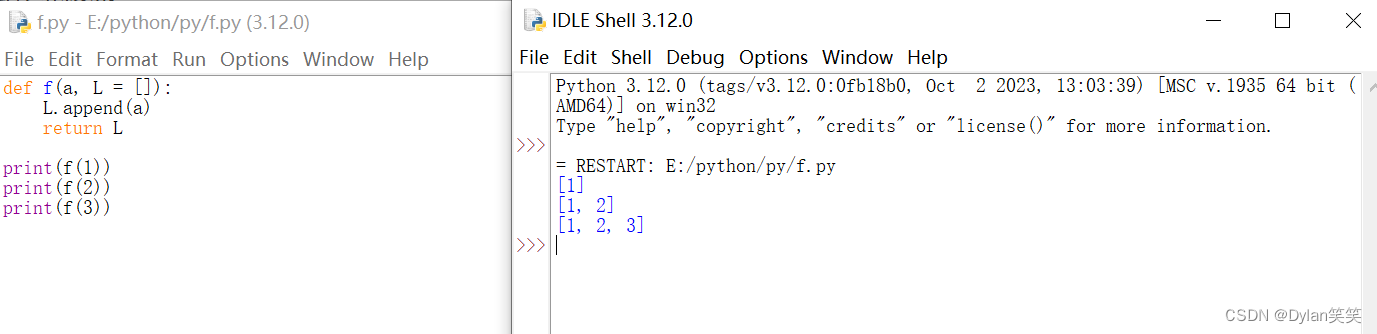
Important warning: The default value is evaluated only once. This makes a difference when the default is a mutable object such as a list, dictionary, or instances of most classes. For example, the following function accumulates the arguments passed to it on subsequent calls:
def f(a, L=[]):
L.append(a)
return L
print(f(1))
print(f(2))
print(f(3))
This will print
[1]
[1, 2]
[1, 2, 3]
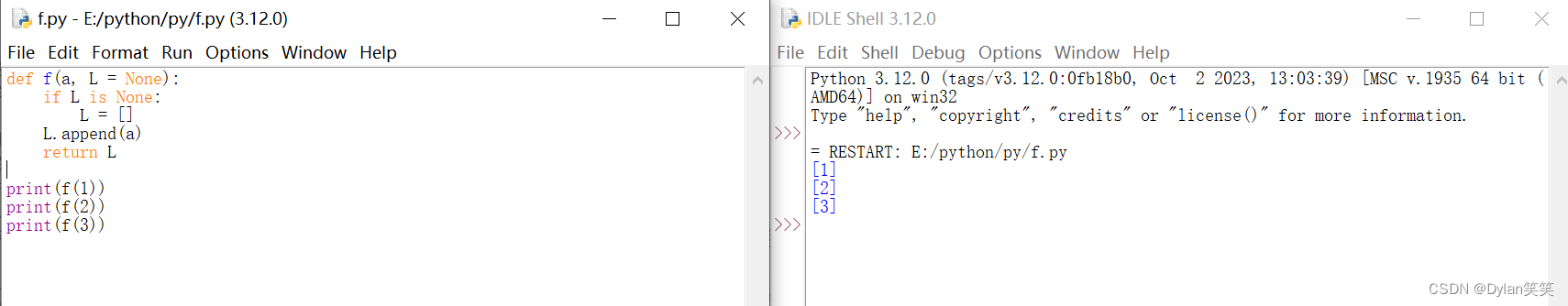
If you don’t want the default to be shared between subsequent calls, you can write the function like this instead:
def f(a, L=None):
if L is None:
L = []
L.append(a)
return L
4.8.详解函数定义
完全可以定义带有可变参数的函数。有三种形式,它们可以组合。
4.8.1.参数默认值
最有用的形式是指定一个或多个参数的默认值。现在建立一个函数,仅用被定义的少数参数就可以激活这个函数。例:
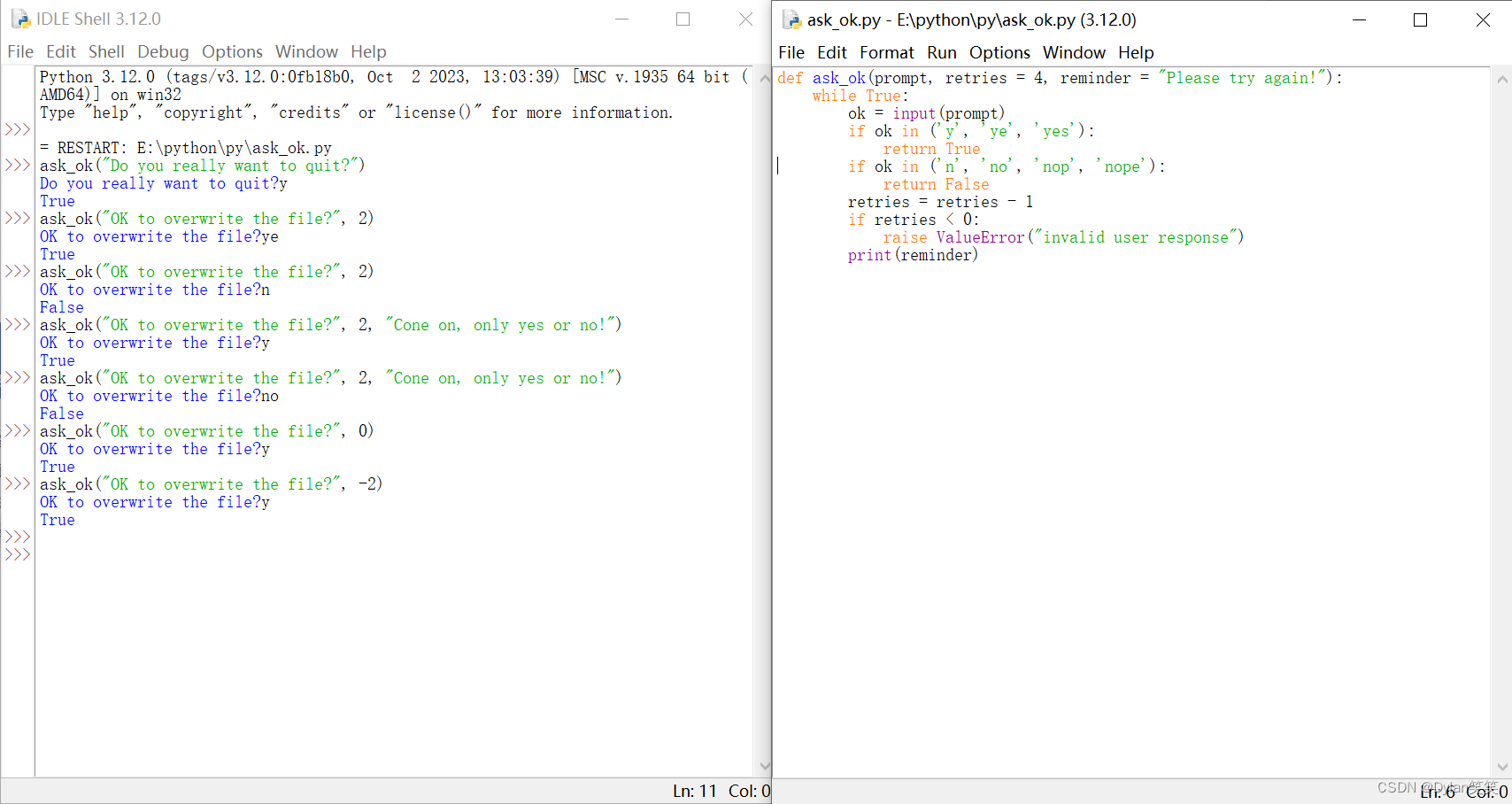
这个函数在这几种情况下可以被唤醒:
- 只给出强制性参数:ask_ok(“Do you really want to quit?”)
- 给出一个可选参数:ask_ok(“OK to overwrite the file?”, 2)
- 甚至给出所有的参数:ask_ok(“OK to overwrite the file?”, 2, “Come on, only yes or no!”)
实例中的关键字in,这是为了测试序列是不是包含特定值。
有效的默认值是在函数定义时定义的作用域内,例如。
重要提示:默认值仅计算一次。当默认值是可变对象,诸如列表,字典或大多数类的实例时,函数会在后续的调用中应用可变对象。例如:
如果不想在后续调用函数时引用可变对象默认值,程序可以这样写:





















 8669
8669

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








