思维导图:
注意:
一维数组:数组名也是数组的首地址,是地址常量,不能为左值(=左边),不能被重新赋值。
指针运算:
算数运算:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
char a[]="hello";
char *p=a;
printf("%c\n",*p);
p++;//p=p+1;
printf("%c\n",*p);
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[5]={2,3,4,5,6};
int *p=a;
printf("%d\n",*p);
printf("%d\n",*p++);
printf("%d\n",*p+1);
return 0;
}
p++;//p=p+1 //指针向高地址方向移动一个数据单位(int 4字节;char 1字节),指针的指向发生改变
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[5]={2,3,4,5,6};
int *p=a;
printf("%p\n",p);
printf("%p\n",p++);
printf("%p\n",p);
return 0;
}
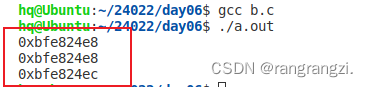
p+1只是暂时运用 //指针访问高地址方向第n个元素,指针的指向不发生改变
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[5]={2,3,4,5,6};
int *p=a;
printf("%p\n",p);
printf("%p\n",p+1);
printf("%p\n",p);
return 0;
}
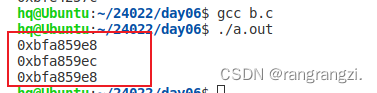
运用
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[5]={2,3,4,5,6};
int *p=&a[2];
printf("%d\n",*p);
printf("%d\n",*p++);
printf("%d\n",*p+2);
return 0;
}
验证:同一个数组,两个地址之间的差值=相差元素个数
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[5]={2,3,4,5,6};
int *p=&a[2];
int *q=a;
printf("%d\n",p-q);
return 0;
}

%p打印是十六进制格式,会把数字2转成十六进制格式
printf("%p\n",p-q); ![]()
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
double *q=NULL;
int m=100;
double n=200;
int *p=NULL;
p=&m;
q=&n;
printf("m=%d &m=%p\n",m,&m);
printf("p=%p p+2=%p\n",p,p+2);
printf("n=%lf & n=%p\n",n,&n);
printf("q=%p q+2=%p\n",q,q+2);
return 0;
}运行结果:
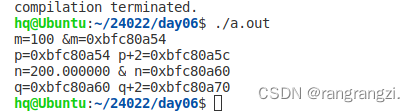
关系运算
< > ==
同一个数组下比较,才有意义
高地址>低地址
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[5]={2,3,4,5,6};
int *p=&a[2];
int *q=a;
printf("%d\n",p-q);
if(p>q){
printf("高地址大于低地址");
}
return 0;
}

练习:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
char *q=NULL;
char s[32]="hello";
char *p=s;
p++;
char y=*--p;
printf("%c\n",y);
return 0;
}

指针的大小
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a=3;
int *p1=&a;
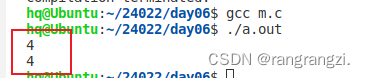
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p1));
char b='q';
char *p2=&b;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p2));
return 0;
}
getconf LONG_BIT 查看操作系统位数
32位操作系统
指针大小为4字节 1字节==8位
8位16进制 4*8=32位二进制 =4字节
64位操作系统
指针大小为8字节
练习1:
字符数字char a[]="1234"; ---》num=1234;
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
char a[]="1234";
char *p=a;
int num=0;
while(*p!='\0'){
num=10*num+*p-'0';
p++;
}
printf("%d\n",num);
return 0;
}
//字符数字char a[]="1234"; ---》num=1234;
练习2:
编写一个程序实现功能:将字符串“Computer Science”赋值给一个字符数组,然后从第一个字母开始间隔的输出该字符串,用指针完成。结果:Cmue cec
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
char a[33]="computer science";
char *p=a;
// while(*p!='\0'){
// printf("%c",*p);
// p+=2;
// }
for(;*p;p+=2){
printf("%c",*p);
}
return 0;
}段错误
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
https://www.cnblogs.com/linuxws/p/17227268.html
指针虽然灵活好用但是用不好会出现段错误。出现的原因有:访问不存在的内存地址、访问系统保护的内存地址 、访问只读的内存地址、空指针废弃 (eg:malloc与free释放后,继续使用) 、堆栈溢出、内存越界 (数组越界)
练习3:
字符串倒序输出,用指针hello--->olleh
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char a[33] = "hello";
int res = strlen(a);
for (int i = 0; i < res / 2; i++) {
char t = a[i];
a[i] = a[res - 1 - i];
a[res - 1 - i] = t;
}
puts(a);
return 0;
}
// while (p < q) {
// char t = *p;
// *p = *q;
// *q = t;
// p++;
// q--;
// }
练习4:
循环输入一个五位数,判断是否是回文数,当输入0时结束。12321
//回文数12321
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char a[33]={};
scanf("%s",a);
int res=strlen(a);
char *p=a;
char *q=a+res-1;
int test=1;
while(p<q){
if(*p!=*q)
test=0;
p++;
q--;
}
if(test==1)
printf("yes\n");
else
printf("no\n");
puts(a);
return 0;
}指针修饰
const void
const常量化 read-only
修饰普通变量,不能直接通过变量名进行修改
const int a=5; //int const a=5;
a+=6; //error
通过指针修改:
const int a=5;
int *p=&a;
*p=88;
printf("%d %d\n",a,*p);
修饰指针:
int const *p; //const修饰*p 指针指向的内容不能修改;但是指针的指向可以修改
int a=5;
const int *p=&a;
1)*p=33; //error
2)int b=33;
p=&b; //正确
修饰p
int * const p=&a; //const修饰p 指针的指向不能改,指针指向的内容可以改
int a=5;
int * const p=&a;
// p=&b;
*p=33;
printf("%d %d\n",a,*p);
课后作业:
1.

2.

3.

4.
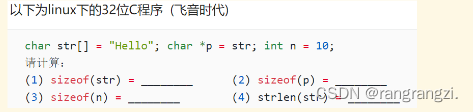
5.

6.
给定一串字符"I love china",实现以单词为单位的逆序,如:"china love i"
思路:可以先全部倒过来:anihc evol i,然后再把每个单词倒过来---- 根据空格确定单词--空格既是一个单词的开头又是一个单词的结尾
空格既是一个单词的开头又是一个单词的结尾,所以找到空格之后我们需要暂时记录以下当前空格的位置,方便我们从当前位置找下一个空格
然后进行交换,交换完成后再从空格的后面进行查找下一个空格






















 158
158











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








