目录
前言:
闭散列线性探测缺点:一旦发生哈希冲突,所有的产生哈希冲突的数据连续存储在一块区域,容易产生数据"堆积",即:不同关键码占据了可利用的空位置,使得寻找某关键码的位置需要许多次比较,导致搜索效率降低,并且闭散列导致空间利用率低,因此本文探索采用开散列(哈希桶)的数据结构从而避免数据 "堆积" ;
开散列(哈希桶)
开散列的概念
开散列法又叫链地址法(拉链法),首先对关键码集合用哈希函数计算哈希地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链
接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中;
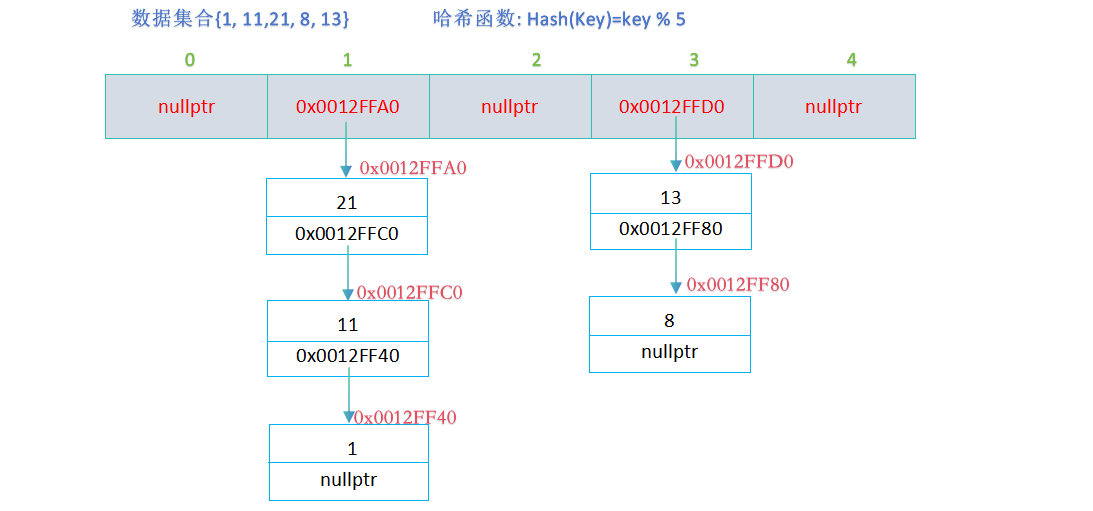
哈希桶的模拟实现
整体框架
template<class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
pair<K, V> _kv;
//开辟结点时需要结点的构造函数
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
_kv = kv;
_next = nullptr;
}
};
template<class K, class V>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//...
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;//记录哈希表中实际存放的数据个数
};查找
思路:
首先根据键值key使用哈希函数计算哈希地址,确定待查找的数据的位置;
其次遍历桶中数据,查找到返回数据所在结点的指针,查找不到返回空指针;
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if ((cur->_kv).first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}插入
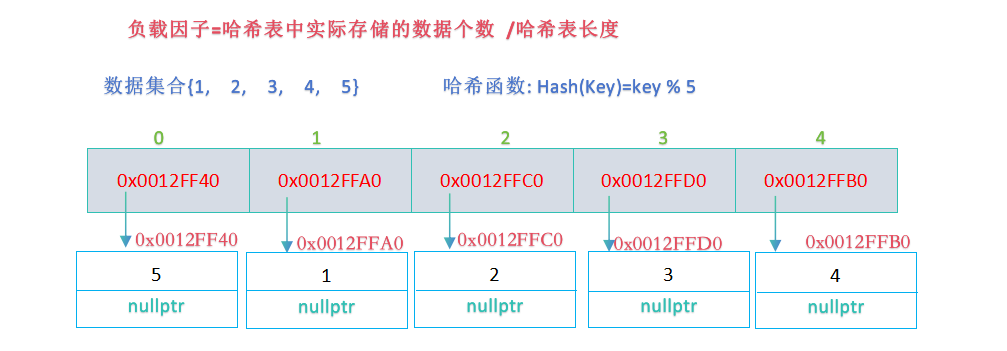
开散列最优情形:每个哈希桶中刚好挂一个节点,再继续插入元素时,每一次都会发生哈希冲突,因此,在元素个数刚好等于桶的个数时,考虑哈希表扩容;
- 查看哈希表中是否存在该键值的键值对,若已存在则插入失败;
- 当负载因子增加到1时,进行扩容操作(即创建一个新的哈希表,该哈希表的大小为原哈希表的两倍,然后遍历原哈希表,将原哈希表中的结点插入到新哈希表,最后将原哈希表与新哈希表交换即可);
- 将结点插入哈希桶(头插);
- 哈希表中的记录实际存储的数据个数自增1;
//构造函数
HashTable(size_t n = 10)
{
_tables.resize(n, nullptr);
_n = 0;
}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
//若键值对中的键值key已存在,则插入失败
Node* ret = Find(kv.first);
if (ret != nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//控制负载因子为1,即哈希表中实际存放的数据个数与哈希表长度长度相等
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
//新表扩容到旧表的两倍
vector<Node*> _newtables(_tables.size() * 2);
//遍历旧表,取旧表结点头插到新表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* nextnode = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % _newtables.size();
cur->_next = _newtables[hashi];
_newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = nextnode;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
//交换新表与旧表
_tables.swap(_newtables);
}
//插入
//计算插入位置
size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
//单链表头插
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}删除
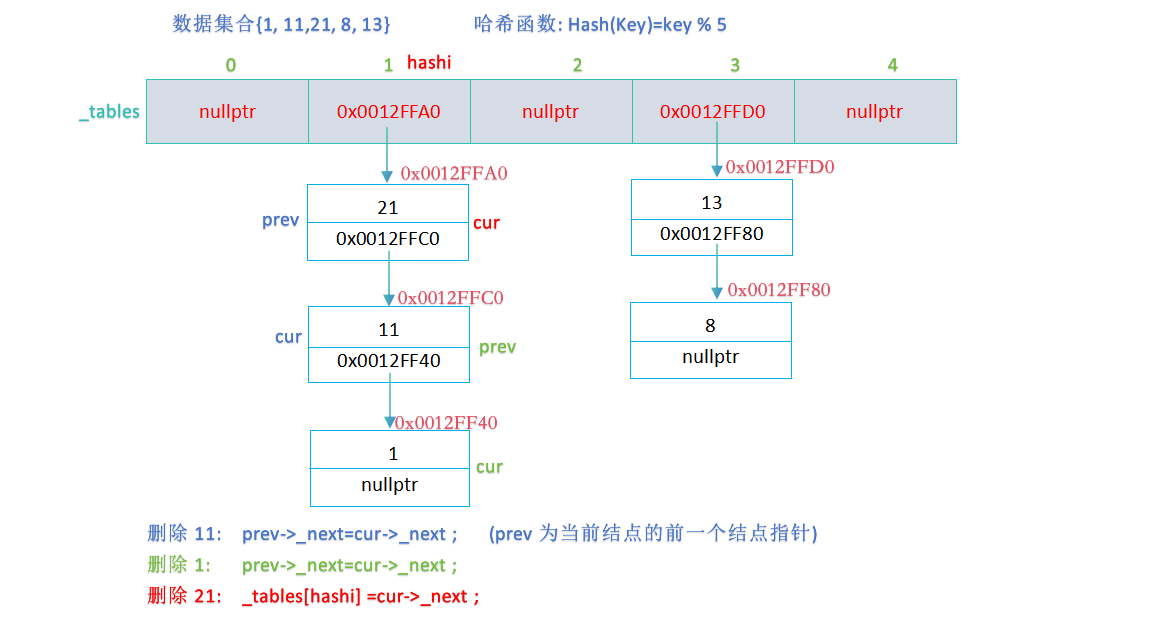
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//确定待删除数据的位置
size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if ((cur->_kv).first == key)
{
//删除
if (prev != nullptr)
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
else
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}析构函数
//析构函数
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}当哈希表中的HashNode存储string时,string类型的数据不支持取模运算,若采用运算符重载,需要更改库中的string,除留余数法如何建立string类型数据与存储位置的映射关系吗?
解决方案:
- 首先将string类型转换为整型,建立string类型与整型的映射关系(采用仿函数实现);
- 其次转换后的整型值与存储位置建立映射关系(模版参数增加1个接收仿函数);
思考:任意类型的值如何转换为整型值 ?
- 本身为整型家族的成员,则可以通过强制类型转换可以转化为整型;
- 对于string类型,可以取每个字符的ASCII码值,逐个相加且每相加一次乘以权重31;
- 对于其他类型,按数据类型各自的特征自定义仿函数实现转换为整型;
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//string类型使用模版的特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto e : key)
{
hash += e;
hash *= 31;//BKDR字符串哈希算法,累乘因子为31
}
return hash;
}
};template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//...
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;//记录哈希表中实际存放的数据个数
};拷贝构造函数
//拷贝构造函数 ht2(ht1)
HashTable(const HashTable& ht)
{
Hash hs;
//开辟相同大小的空间
_tables.resize(ht._tables.size());
//遍历旧表,头插到新表
for (size_t i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._tables[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
//计算新表的插入位置
size_t hashi = hs(cur->_kv.first) % _tables.size();
cur->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_n = ht._n;
}
赋值运算符重载
//赋值运算符重载 ht2=ht1
HashTable& operator=(HashTable ht)
{
_tables.swap(ht._tables);
swap(_n, ht._n);
return *this;
}哈希桶模拟实现源码
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
// 特化
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto e : s)
{
hash += e;
hash *= 31;
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
_kv = kv;
_next = nullptr;
}
};
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//构造函数
HashTable(size_t n = 10)
{
_tables.resize(n, nullptr);
_n = 0;
}
//析构函数
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
//拷贝构造函数 ht2(ht1)
HashTable(const HashTable& ht)
{
Hash hs;
//开辟相同大小的空间
_tables.resize(ht._tables.size());
//遍历旧表,头插到新表
for (size_t i = 0; i < ht._tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = ht._tables[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
//计算新表的插入位置
size_t hashi = hs(cur->_kv.first) % _tables.size();
cur->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_n = ht._n;
}
//ht2=ht1
HashTable& operator=(HashTable ht)
{
_tables.swap(ht._tables);
swap(_n, ht._n);
return *this;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if ((cur->_kv).first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
//若键值对中的键值key已存在,则插入失败
Node* ret = Find(kv.first);
if (ret != nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//控制负载因子为1,即哈希表中实际存放的数据个数与哈希表长度长度相等
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
//新表扩容到旧表的两倍
vector<Node*> _newtables(_tables.size() * 2);
//遍历旧表,取旧表结点头插到新表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur != nullptr)
{
Node* nextnode = cur->_next;
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(cur->_kv.first) % _newtables.size();
cur->_next = _newtables[hashi];
_newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = nextnode;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
//交换新表与旧表
_tables.swap(_newtables);
}
//插入
//计算插入位置
Hash hs;
size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
//单链表头插
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
//确定待删除数据的位置
size_t hashi = hs(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if ((cur->_kv).first == key)
{
//删除
if (prev != nullptr)
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
else
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;//记录哈希表中实际存放的数据个数
};欢迎大家批评指正,博主会持续输出优质内容,谢谢各位观众老爷观看,码字画图不易,希望大家给个一键三连支持~ 你的支持是我创作的不竭动力~























 933
933











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










