1、前言
在后端接口开发中,通常为了避免恶意的参数请求,通常需要我们对接口的参数进行校验,以此来保证程序的健壮性、正确性,在JAVAEE中采用JSR-303的接口校验规范,官方参考实现是Hibernate Validator
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>5.2.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
2、如何使用?
在jsr-303中定义了许多校验注解
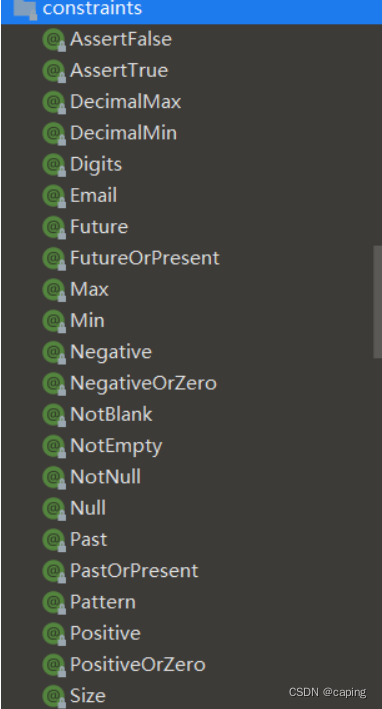
| @NotNull | 注解元素必须是非空 |
| @Null | 注解元素必须是空 |
| @Digits | 验证数字构成是否合法 |
| @Future | 验证是否在当前系统时间之后 |
| @Past | 验证是否在当前系统时间之前 |
| @Max | 验证值是否小于等于最大指定整数值 |
| @Min | 验证值是否大于等于最小指定整数值 |
| @Pattern | 验证字符串是否匹配指定的正则表达式 |
| @Size | 验证元素大小是否在指定范围内 |
| @DecimalMax | 验证值是否小于等于最大指定小数值 |
| @DecimalMin | 验证值是否大于等于最小指定小数值 |
| @AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为true |
| @AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为false |
将这些注解添加在需要检验的字段上
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
public class Person {
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄(要求1-100)
*/
@Max(value = 100,message = "年龄不能超过100岁")
@Min(value = 1,message = "年龄不能小于1岁")
private Integer age;
/**
* 邮箱
*/
@Email
private String email;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
import com.example.demo.entity.Person;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController {
/**
* 简单检验测试
*/
@PostMapping("/test01")
public Object test01(@Validated @RequestBody Person person){
return person;
}
}
正常情况下
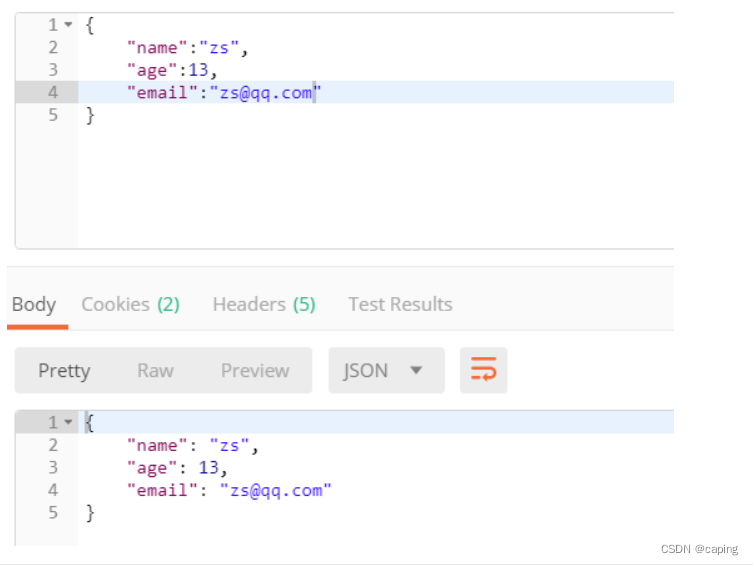
将年龄改为异常情况,后台就会抛出异常
 2、如果特殊情况下,需要对某一个字段进行不同约束如何实现?(使用group选项进行分组)
2、如果特殊情况下,需要对某一个字段进行不同约束如何实现?(使用group选项进行分组)
//定义两个用于分组的接口
public interface GroupA {
}
public interface GroupB {
}
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
public class Person {
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄(要求1-100)
*/
@Max(value = 100,message = "年龄不能超过100岁")
@Min(value = 1,message = "年龄不能小于1岁",groups = GroupA.class) //年龄大于1,在对GroupA的组,进行校验时有效
@Min(value = 18,message = "年龄不能小于18岁",groups = GroupB.class) //年龄大于18,在对GroupB的组,进行校验时有效
private Integer age;
/**
* 邮箱
*/
@Email
private String email;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
import com.example.demo.entity.GroupB;
import com.example.demo.entity.Person;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class TestController {
/**
* 简单检验测试
*/
@PostMapping("/test01")
public Object test01(@Validated @RequestBody Person person){
return person;
}
/**
* 分组校验,对B组进行校验,即大于18的生效,大于1的限制不会生效
*/
@PostMapping("/test02")
public Object test02(@Validated({GroupB.class}) @RequestBody Person person){
return person;
}
}
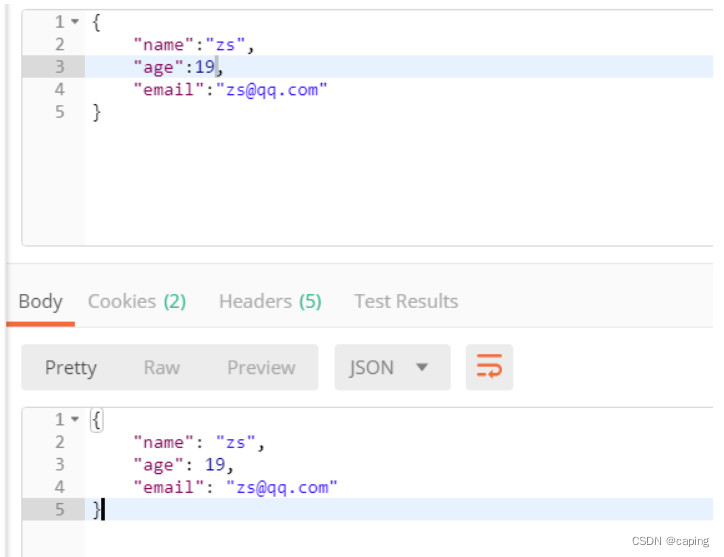
验证通过
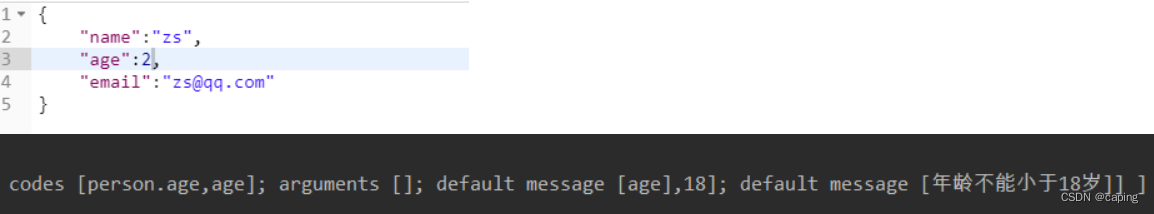
在输入age为2时,抛出不能小于18的生效
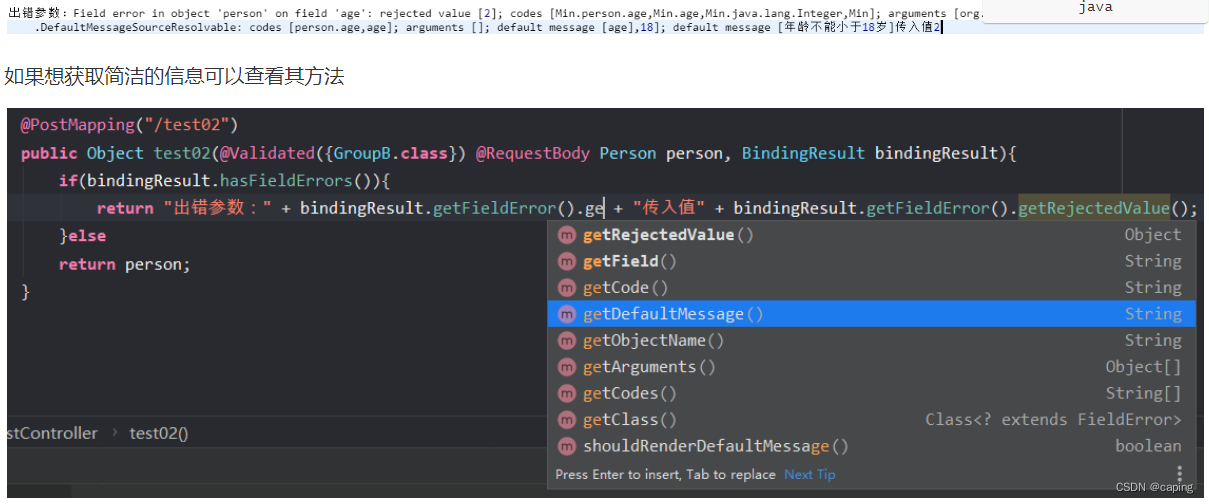
如果想在出现参数异常时,能进行处理怎么实现?
@PostMapping("/test02")
public Object test02(@Validated({GroupB.class}) @RequestBody Person person, BindingResult bindingResult){
if(bindingResult.hasFieldErrors()){
return "出错参数:" + bindingResult.getFieldError() + "传入值" + bindingResult.getFieldError().getRejectedValue();
}else
return person;
}
最后如果需要多层校验,如何实现呢?
//定义一个实体类
public class Student {
@Length(max = 8,message = "长度不能大于8")
private String number;
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
}
在Person中
public class Person {
@Valid //这个和@Validated差不多也是进行校验的注解,但是@Validated不能写在字段上
private Student student;
}
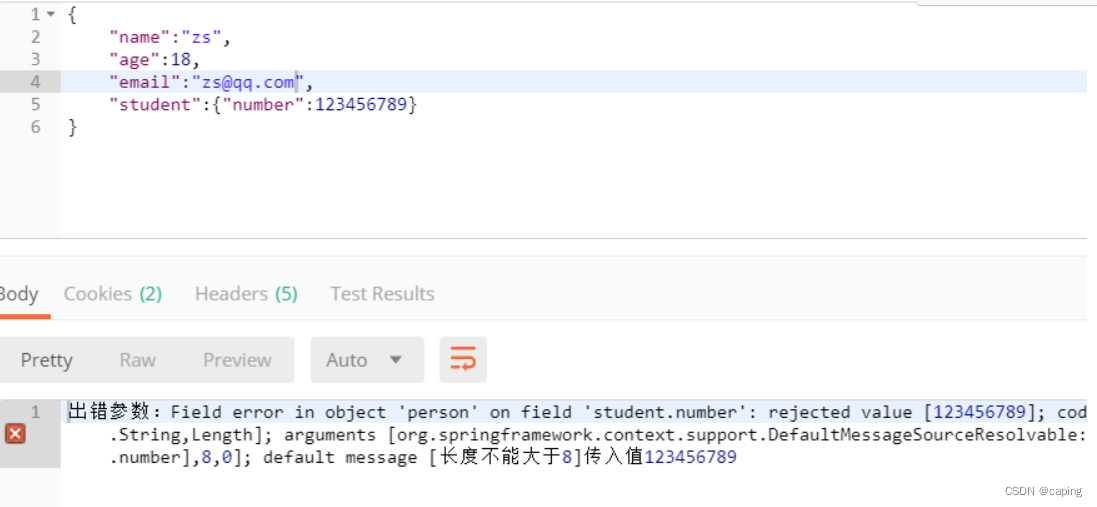
注意:在使用分组校验后,没有分组的字段不会校验,因为不分组属于默认分组,通过如果开启了多个分组,可以采用@GroupSequence({GroupA.class,GroupB.class})来进行排序




















 1286
1286

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








