1. 比较运算符
比较运算符用于比较运算,判断逻辑是否成立。
A operator B
常用的比较运算符有 =(等于) 、!=(不等于)、 <>(不等于)、<(小于)、<=(小于等于)、>(大于)、>=(大于等于),其中 != 和 <> 在特殊情况下用法是不同。
WHERE A operator B
查询学生人数超过 800 的课程
select * from `courses` where `student_count` > '800';

查询超过 20 岁的教师
select * from teachers where `age`>'20';

查询中国老师的姓名
select `name` from `teachers` where `country` = 'CN';
2.使用 AND 连接多条件
SELECT `column_name`
FROM `table_name`
WHERE condition1 AND condition2;condition 为设置的条件,最后返回的结果应为满足 condition1 和 condition2 的数据。
查询课程表 courses 中学生人数 student_count 在 800 (包括) 至 1000 (不包括) 之间的所有课程
select * from courses where student_count >=800 and student_count<1000;

查询课程表 courses 中课程创建时间 created_at 在 '2020-01-01' (包括) 到 '2020-05-01' (不包括) 之间的所有课程名称和课程创建时间
select name , created_at from `courses` where `created_at`>='2020-01-01' and `created_at`<'2020-05-01';
查询课程表 courses 中教师 id 为 4,且上课人数在 500 以上(不包括 500 人)的所有课程信息
select * from `courses` where `student_count`>'500'and `teacher_id`='4';
2. 使用 OR 连接多个条件
SQL 中的逻辑运算符 OR 与 AND 关键字不同,OR 关键字,只要记录满足任意一个条件,就会被查询出来。
SELECT `column_name`
FROM `table_name`
WHERE condition1 or condition2;其中:condition1 和 condition2 为设置的条件,最后返回的结果应满足 condition1 或 condition2 的数据
查询课程表 courses 中课程名为 'System Design' 或 'Django' 的课程信息
select * from `courses` where `name`='System Design' or `name` ='Django' ;
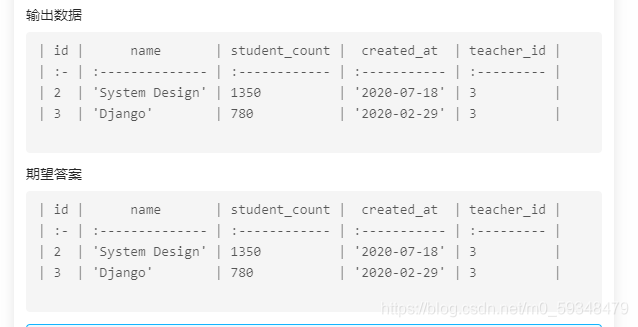
从 courses 表中,选取课程名为 'Web' 或者 'Big Data' 的课程信息
select * from courses where `name`='Web' or `name`='Big Data';
3. 使用 NOT 过滤不满足条件的数据
SELECT `column_name`
FROM `table_name`
WHERE NOT `condition`;其中:condition 为设置的条件,最后返回的结果应不满足 condition 。
查询教师表 teachers 中除了年龄 age 在 20 岁以上(不包括 20 岁)且来自于中国(CN)的以外所有教师信息
select * from `teachers` where not (`age`>'20' and `country`='CN');

查询课程表 courses 中,教师 id teacher_id 不为 3,且学生人数 student_count 超过 800 的所有课程
select * from `courses` where `teacher_id`!=3 and `student_count`>800;
3.使用 IN 查询多条件
SELECT *
FROM `table_name`
WHERE `column_name` IN `value`;查询教师表 teachers 中教师国籍为中国 (CN) 或英国 (UK) 的所有教师信息
select * from `teachers` where `country` in ('CN' , 'UK');

查询课程表 courses 中开课日期为 2021-01-01 或者 2021-01-03 的所有课程信息
select * from `courses` where `created_at`in ('2021-01-01','2021-01-03');
2. 使用 NOT IN 排除
SELECT *
FROM `table_name`
WHERE `column_name` NOT IN value;查询教师表 teachers 中国籍 "country" 不为日本 (JP) 和美国 (USA) 的所有教师信息
select * from teachers where country not in ('JP','USA');
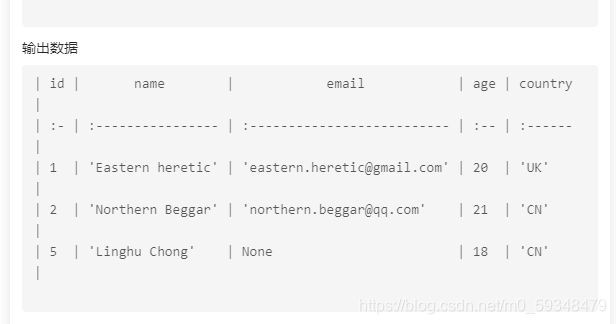
查询课程表 courses 中所有教师 id teacher_id 不为 1 或 3 的所有课程
select name from `courses` where teacher_id not in (1,3);
3. 使用 BETWEEN AND 查询两值间的数据范围
请注意,在不同的数据库中,BETWEEN 操作符会产生不同的结果!
在某些数据库中,BETWEEN 选取介于两个值之间但不包括两个测试值的字段。
在某些数据库中,BETWEEN 选取介于两个值之间且包括两个测试值的字段。
在某些数据库中,BETWEEN 选取介于两个值之间且包括第一个测试值但不包括最后一个测试值的字段。
SELECT *
FROM `table_name`
WHERE `column_name` BETWEEN `value` AND `value`;从 teachers 表中查询年龄在 20 到 25 岁之间( 包括 20 和 25 岁 )
select * from teachers where age between 20 and 25;

从 teachers 表中查询年龄在 20 到 25 岁之间( 包括 20 和 25 岁 ),但是国籍不为中国和英国的教师信息
select * from teachers where (`age` between 20 and 25) and (`country`not in ('UK', 'CN'));

查询课程表 courses 中学生数量在 50 到 55 之间的所有课程信息
select * from `courses` where `student_count` between 50 and 55;
4. 使用 IS NULL 查询空数据
NULL 值代表遗漏的未知数据。默认的,表的列可以存放 NULL 值。
注释:无法比较 NULL 和 0;它们是不等价的。
无法使用比较运算符来测试 NULL 值,比如 =、!= 或 <>。
我们必须使用 IS NULL 和 IS NOT NULL操作符。
SELECT *
FROM `table_name`
WHERE `column_name` IS NULL;教师表 teachers 中查询邮箱 email 为空的所有教师信息
select * from teachers where email is null;

查询教师表 teachers 中,国籍为 'CN' 或 'JP' 且 email 信息不为空的所有教师信息。
select * from `teachers` where (`country`='CN'or`country`='JP') and (`email` is not null);
08/07
5. 使用 LIKE 模糊查询
SELECT *
FROM `table_name`
WHERE `column_name` LIKE `value`;查询课程表 courses 中以字母 'D' 开头的所有课程
其中 'D%' 表示以 D 开头的所有单词,% 表示为通配符,可以替代 0 个或多个字
select * from courses where name like 'D%';

查询教师表 teachers 中,所有使用 qq 邮箱的教师名字和邮箱
select name,email from `teachers` where email like '%@qq.com';
6. 使用 ORDER BY 对数据进行排序
ASC :按升序排列,ORDER BY 默认按照升序对记录进行排序,因此升序的关键字 ASC 可以省去不写。
DESC:按降序排列,如果需要按照降序对记录进行排序,可以使用 DESC 关键字。
SELECT `column_name`, `column_name`
FROM `table_name`
ORDER BY `column_name`, `column_name` ASC|DESC;查询课程表 courses 中的所有内容,并按照学生人数 student_count 升序排序
select* from`courses` order by`student_count`;
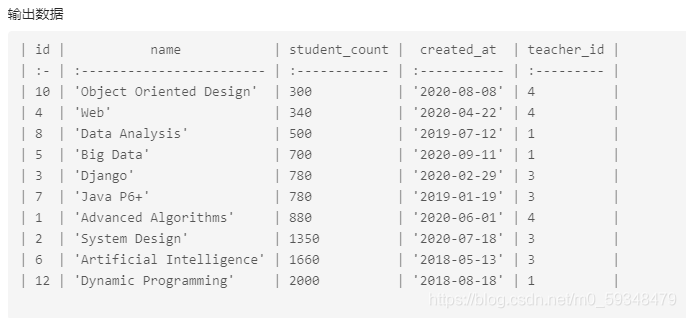
按学生人数从大到小排列
select* from`courses` order by`student_count`desc;

对多列进行排序
查询课程表 courses 中的课程信息中 teacher_id 为 1、2 或 3 的课程的名称、教师 id 和创建时间,并使结果按照教师 id 排序,如果教师 id 相同,则按照创建课程时间排序。
select name,teacher_id,created_at from courses where teacher_id in (1,2,3) order by teacher_id,created_at;
查询教师表 teachers 中教师年龄 age 的唯一值,并将结果进行升序排序
select distinct age from teachers order by age;
查询教师表 teachers 中的中国教师,并按照年龄降序排序
select * from teachers where country='CN' order by age desc;
2. 使用 LIMIT 限制输出行数
SELECT `column_name`, `column_name`
FROM `table_name`
LIMIT `offset` , `count`;LIMIT 子句用于 SELECT 中,对输出结果集的行数进行约束,LIMIT 接收2个参数 offset 和 count,两个参数都是整型数字,但通常只用一个
offset :是返回集的初始标注,起始点是0,不是1哦
count :制定返回的数量
查询课程表 course 中学生人数 student_count 最少的三门课程信息
select * from courses order by `student_count` limit 3;

从教师表(teachers)中查询一条年龄最大的中国教师的信息
select * from teachers where country='CN' order by age desc limit 1;







 本文详细介绍了SQL查询中的比较运算符、AND、OR、NOT及IN操作,展示了如何过滤和组合查询条件,例如如何查找学生人数在特定范围的课程,以及如何根据多个条件筛选教师信息。
本文详细介绍了SQL查询中的比较运算符、AND、OR、NOT及IN操作,展示了如何过滤和组合查询条件,例如如何查找学生人数在特定范围的课程,以及如何根据多个条件筛选教师信息。
















 6898
6898

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








