概述
计算机科学中,queue 是以顺序的方式维护的一组数据集合,在一端添加数据,从另一端移除数据。习惯来说,添加的一端称为尾,移除的一端称为头,就如同生活中的排队买商品
先定义一个简化的队列接口
public interface Queue<E> {
/**
* 向队列尾插入值
* @param value 待插入值
* @return 插入成功返回 true, 插入失败返回 false
*/
boolean offer(E value);
/**
* 从对列头获取值, 并移除
* @return 如果队列非空返回对头值, 否则返回 null
*/
E poll();
/**
* 从对列头获取值, 不移除
* @return 如果队列非空返回对头值, 否则返回 null
*/
E peek();
/**
* 检查队列是否为空
* @return 空返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 检查队列是否已满
* @return 满返回 true, 否则返回 false
*/
boolean isFull();
}链表实现
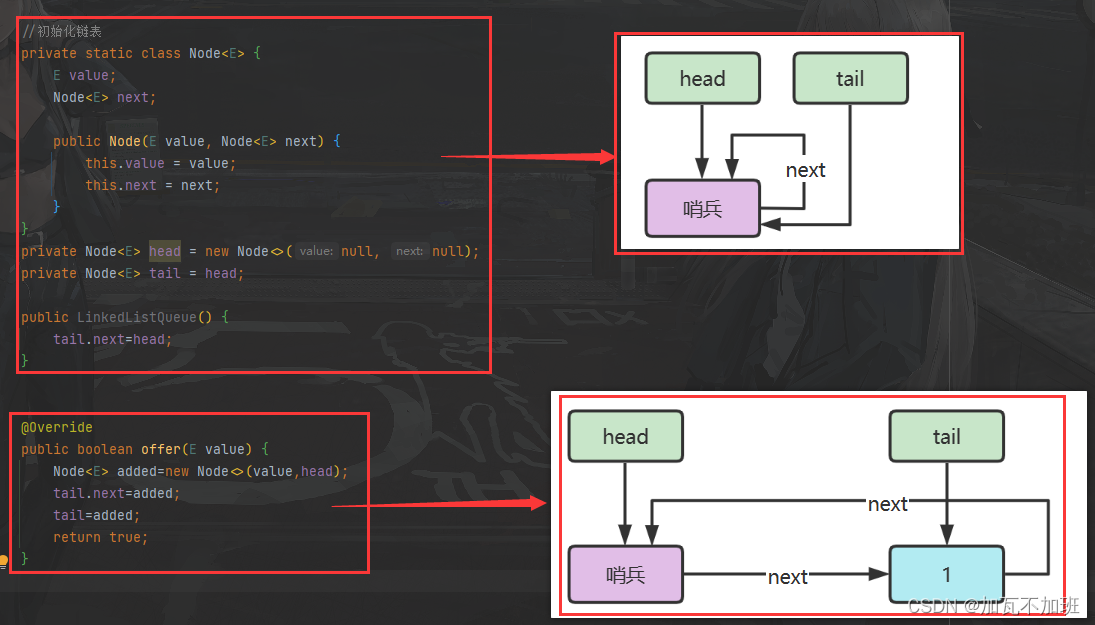
下面以单向环形带哨兵链表方式来实现队列

代码:
public class LinkedListQueue<E>
implements Queue<E>, Iterable<E> {
private static class Node<E> {
E value;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E value, Node<E> next) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node<E> head = new Node<>(null, null);
private Node<E> tail = head;
private int size = 0;//节点数
private int capacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//容量 默认初始容量:Integer.MAX_VALUE
//在java里,如果构造方法里有重复的代码,可以写在初始化语句块中
{
tail.next = head;
}
public LinkedListQueue() {
//tail.next = head;
}
//如果调用了有参构造,可以设置容量
public LinkedListQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
//tail.next = head;
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E value) {
//如果容量满了,就停止添加操作
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
Node<E> added = new Node<>(value, head);
tail.next = added;
tail = added;
size++;
return true;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node<E> first = head.next;
head.next = first.next;
//当链表中只有一个节点
if (first == tail) {
tail = head;
}
size--;
return first.value;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return head.next.value;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
//当头指向尾,就是没有节点
return head == tail;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Iterator<E>() {
Node<E> p = head.next;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
//当我最后一个节点的下一个节点不是头节点
return p != head;
}
@Override
public E next() {
E value = p.value;
p = p.next;
return value;
}
};
}
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








