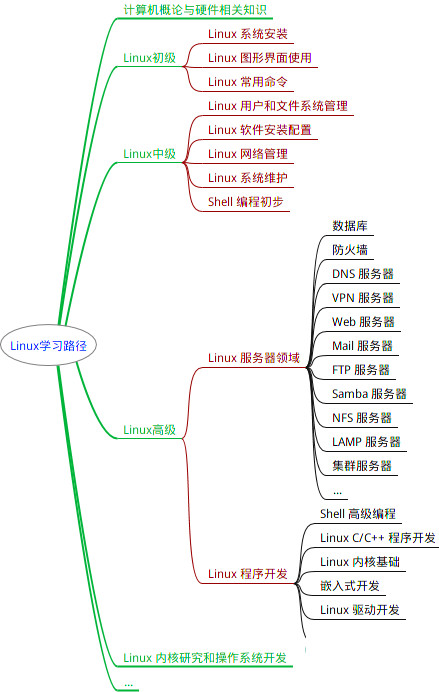
最全的Linux教程,Linux从入门到精通
======================
-
linux从入门到精通(第2版)
-
Linux系统移植
-
Linux驱动开发入门与实战
-
LINUX 系统移植 第2版
-
Linux开源网络全栈详解 从DPDK到OpenFlow

第一份《Linux从入门到精通》466页
====================
内容简介
====
本书是获得了很多读者好评的Linux经典畅销书**《Linux从入门到精通》的第2版**。本书第1版出版后曾经多次印刷,并被51CTO读书频道评为“最受读者喜爱的原创IT技术图书奖”。本书第﹖版以最新的Ubuntu 12.04为版本,循序渐进地向读者介绍了Linux 的基础应用、系统管理、网络应用、娱乐和办公、程序开发、服务器配置、系统安全等。本书附带1张光盘,内容为本书配套多媒体教学视频。另外,本书还为读者提供了大量的Linux学习资料和Ubuntu安装镜像文件,供读者免费下载。

本书适合广大Linux初中级用户、开源软件爱好者和大专院校的学生阅读,同时也非常适合准备从事Linux平台开发的各类人员。
需要《Linux入门到精通》、《linux系统移植》、《Linux驱动开发入门实战》、《Linux开源网络全栈》电子书籍及教程的工程师朋友们劳烦您转发+评论
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
而使用netty来进行文件传输也是利用netty天然的优势:零拷贝功能。很多同学都听说过netty的”零拷贝”功能,但是具体体现在哪里又不知道,下面我们就简要介绍下:
Netty的“零拷贝”主要体现在如下三个方面:
-
Netty的接收和发送ByteBuffer采用DIRECT BUFFERS,使用堆外直接内存进行Socket读写,不需要进行字节缓冲区的二次拷贝。如果使用传统的堆内存(HEAP BUFFERS)进行Socket读写,JVM会将堆内存Buffer拷贝一份到直接内存中,然后才写入Socket中。相比于堆外直接内存,消息在发送过程中多了一次缓冲区的内存拷贝。
-
Netty提供了组合Buffer对象,可以聚合多个ByteBuffer对象,用户可以像操作一个Buffer那样方便的对组合Buffer进行操作,避免了传统通过内存拷贝的方式将几个小Buffer合并成一个大的Buffer。
-
Netty的文件传输采用了transferTo方法,它可以直接将文件缓冲区的数据发送到目标Channel,避免了传统通过循环write方式导致的内存拷贝问题。
具体的分析在此就不多做介绍,有兴趣的可以查阅相关文档。我们还是把重点放在文件传输上。Netty作为高性能的服务器端异步IO框架必然也离不开文件读写功能,我们可以使用netty模拟http的形式通过网页上传文件写入服务器,当然要使用http的形式那你也用不着netty!大材小用。netty4中如果想使用http形式上传文件你还得借助第三方jar包:okhttp。使用该jar完成http请求的发送。但是在netty5 中已经为我们写好了,我们可以直接调用netty5的API就可以实现。所以netty4和5的差别还是挺大的,至于使用哪个,那就看你们公司选择哪一个了!本文目前使用netty4来实现文件上传功能。下面我们上代码:
pom文件:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.5.Final</version>
</dependency>
server端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ClassResolvers;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectEncoder;
public class FileUploadServer {
public void bind(int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, ClassResolvers.weakCachingConcurrentResolver(null))); // 最大长度
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FileUploadServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
new FileUploadServer().bind(port);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
server端handler:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class FileUploadServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private int byteRead;
private volatile int start = 0;
private String file_dir = "D:";
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof FileUploadFile) {
FileUploadFile ef = (FileUploadFile) msg;
byte[] bytes = ef.getBytes();
byteRead = ef.getEndPos();
String md5 = ef.getFile_md5();//文件名
String path = file_dir + File.separator + md5;
File file = new File(path);
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
randomAccessFile.seek(start);
randomAccessFile.write(bytes);
start = start + byteRead;
if (byteRead > 0) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(start);
} else {
randomAccessFile.close();
ctx.close();
}
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
client端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ClassResolvers;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.serialization.ObjectEncoder;
import java.io.File;
public class FileUploadClient {
public void connect(int port, String host, final FileUploadFile fileUploadFile) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true).handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ObjectDecoder(ClassResolvers.weakCachingConcurrentResolver(null)));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FileUploadClientHandler(fileUploadFile));
}
});
ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8080;
if (args != null && args.length > 0) {
try {
port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
FileUploadFile uploadFile = new FileUploadFile();
File file = new File("c:/1.txt");
String fileMd5 = file.getName();// 文件名
uploadFile.setFile(file);
uploadFile.setFile_md5(fileMd5);
uploadFile.setStarPos(0);// 文件开始位置
new FileUploadClient().connect(port, "127.0.0.1", uploadFile);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
client端handler:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class FileUploadClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
private int byteRead;
private volatile int start = 0;
private volatile int lastLength = 0;
public RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile;
private FileUploadFile fileUploadFile;
public FileUploadClientHandler(FileUploadFile ef) {
if (ef.getFile().exists()) {
if (!ef.getFile().isFile()) {
System.out.println("Not a file :" + ef.getFile());
return;
}
}
this.fileUploadFile = ef;
}
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
try {
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileUploadFile.getFile(), "r");
randomAccessFile.seek(fileUploadFile.getStarPos());
lastLength = (int) randomAccessFile.length() / 10;
byte[] bytes = new byte[lastLength];
if ((byteRead = randomAccessFile.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fileUploadFile.setEndPos(byteRead);
fileUploadFile.setBytes(bytes);
ctx.writeAndFlush(fileUploadFile);
} else {
System.out.println("文件已经读完");
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException i) {
i.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof Integer) {
start = (Integer) msg;
if (start != -1) {
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileUploadFile.getFile(), "r");
randomAccessFile.seek(start);
System.out.println("块儿长度:" + (randomAccessFile.length() / 10));
System.out.println("长度:" + (randomAccessFile.length() - start));
int a = (int) (randomAccessFile.length() - start);
int b = (int) (randomAccessFile.length() / 10);
if (a < b) {
lastLength = a;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[lastLength];
System.out.println("-----------------------------" + bytes.length);
if ((byteRead = randomAccessFile.read(bytes)) != -1 && (randomAccessFile.length() - start) > 0) {
System.out.println("byte 长度:" + bytes.length);
fileUploadFile.setEndPos(byteRead);
fileUploadFile.setBytes(bytes);
try {
ctx.writeAndFlush(fileUploadFile);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
randomAccessFile.close();
ctx.close();
System.out.println("文件已经读完--------" + byteRead);
}
}
}
}
// @Override
// public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws
// Exception {
// System.out.println("Server is speek :"+msg.toString());
// FileRegion filer = (FileRegion) msg;
// String path = "E://Apk//APKMD5.txt";
// File fl = new File(path);
// fl.createNewFile();
// RandomAccessFile rdafile = new RandomAccessFile(path, "rw");
// FileRegion f = new DefaultFileRegion(rdafile.getChannel(), 0,
// rdafile.length());
//
// System.out.println("This is" + ++counter + "times receive server:["
// + msg + "]");
// }
// @Override
// public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws
// Exception {
// ctx.flush();
// }
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
// @Override
// protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg)
// throws Exception {
// String a = msg;
// System.out.println("This is"+
// ++counter+"times receive server:["+msg+"]");
// }
}
我们还自定义了一个对象,用于统计文件上传进度的:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class FileUploadFile implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private File file;// 文件
private String file_md5;// 文件名
private int starPos;// 开始位置
private byte[] bytes;// 文件字节数组
private int endPos;// 结尾位置
public int getStarPos() {
return starPos;
}
public void setStarPos(int starPos) {
this.starPos = starPos;
}
public int getEndPos() {
return endPos;
}
public void setEndPos(int endPos) {
this.endPos = endPos;
}
public byte[] getBytes() {
return bytes;
}
public void setBytes(byte[] bytes) {
this.bytes = bytes;
}
public File getFile() {
return file;
}
public void setFile(File file) {
this.file = file;
}
public String getFile\_md5() {
return file_md5;
}
public void setFile\_md5(String file_md5) {
this.file_md5 = file_md5;
}
}
输出为:
块儿长度:894
长度:8052
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:7158
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:6264
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:5370
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:4476
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:3582
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:2688
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:1794
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:900
-----------------------------894
byte 长度:894
块儿长度:894
长度:6
-----------------------------6
byte 长度:6
块儿长度:894
长度:0
-----------------------------0
文件已经读完--------0
Process finished with exit code 0
这样就实现了服务器端文件的上传,当然我们也可以使用http的形式。
server端:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class HttpFileServer implements Runnable {
private int port;
public HttpFileServer(int port) {
super();
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void run() {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
//serverBootstrap.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new HttpChannelInitlalizer());
try {
ChannelFuture f = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpFileServer b = new HttpFileServer(9003);
new Thread(b).start();
}
}
Server端initializer:
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler;
public class HttpChannelInitlalizer extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpChannelHandler());
}
}
server端hadler:
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus.FORBIDDEN;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus.NOT_FOUND;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelProgressiveFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelProgressiveFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultFullHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpRequest;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpChunkedInput;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.LastHttpContent;
import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedFile;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;
import io.netty.util.internal.SystemPropertyUtil;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import javax.activation.MimetypesFileTypeMap;
public class HttpChannelHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> {
public static final String HTTP_DATE_FORMAT = "EEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss zzz";
public static final String HTTP_DATE_GMT_TIMEZONE = "GMT";
public static final int HTTP_CACHE_SECONDS = 60;
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception {
// 监测解码情况
if (!request.getDecoderResult().isSuccess()) {
sendError(ctx, BAD_REQUEST);
return;
}
final String uri = request.getUri();
final String path = sanitizeUri(uri);
System.out.println("get file:"+path);
if (path == null) {
sendError(ctx, FORBIDDEN);
return;
}
//读取要下载的文件
File file = new File(path);
if (file.isHidden() || !file.exists()) {
sendError(ctx, NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
if (!file.isFile()) {
sendError(ctx, FORBIDDEN);
return;
}
RandomAccessFile raf;
try {
raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
} catch (FileNotFoundException ignore) {
sendError(ctx, NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
long fileLength = raf.length();
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK);
HttpHeaders.setContentLength(response, fileLength);
setContentTypeHeader(response, file);
//setDateAndCacheHeaders(response, file);
if (HttpHeaders.isKeepAlive(request)) {
response.headers().set("CONNECTION", HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE);
}
// Write the initial line and the header.
ctx.write(response);
// Write the content.
ChannelFuture sendFileFuture =
ctx.write(new HttpChunkedInput(new ChunkedFile(raf, 0, fileLength, 8192)), ctx.newProgressivePromise());
//sendFuture用于监视发送数据的状态
sendFileFuture.addListener(new ChannelProgressiveFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationProgressed(ChannelProgressiveFuture future, long progress, long total) {
if (total < 0) { // total unknown
System.err.println(future.channel() + " Transfer progress: " + progress);
} else {
System.err.println(future.channel() + " Transfer progress: " + progress + " / " + total);
}
}
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelProgressiveFuture future) {
System.err.println(future.channel() + " Transfer complete.");
}
});
// Write the end marker
ChannelFuture lastContentFuture = ctx.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT);
// Decide whether to close the connection or not.
if (!HttpHeaders.isKeepAlive(request)) {
// Close the connection when the whole content is written out.
lastContentFuture.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
if (ctx.channel().isActive()) {
sendError(ctx, INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
ctx.close();
}
private static final Pattern INSECURE_URI = Pattern.compile(".\*[<>&\"].\*");
为了做好运维面试路上的助攻手,特整理了上百道 **【运维技术栈面试题集锦】** ,让你面试不慌心不跳,高薪offer怀里抱!
这次整理的面试题,**小到shell、MySQL,大到K8s等云原生技术栈,不仅适合运维新人入行面试需要,还适用于想提升进阶跳槽加薪的运维朋友。**

本份面试集锦涵盖了
* **174 道运维工程师面试题**
* **128道k8s面试题**
* **108道shell脚本面试题**
* **200道Linux面试题**
* **51道docker面试题**
* **35道Jenkis面试题**
* **78道MongoDB面试题**
* **17道ansible面试题**
* **60道dubbo面试题**
* **53道kafka面试**
* **18道mysql面试题**
* **40道nginx面试题**
* **77道redis面试题**
* **28道zookeeper**
**总计 1000+ 道面试题, 内容 又全含金量又高**
* **174道运维工程师面试题**
> 1、什么是运维?
> 2、在工作中,运维人员经常需要跟运营人员打交道,请问运营人员是做什么工作的?
> 3、现在给你三百台服务器,你怎么对他们进行管理?
> 4、简述raid0 raid1raid5二种工作模式的工作原理及特点
> 5、LVS、Nginx、HAproxy有什么区别?工作中你怎么选择?
> 6、Squid、Varinsh和Nginx有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 7、Tomcat和Resin有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 8、什么是中间件?什么是jdk?
> 9、讲述一下Tomcat8005、8009、8080三个端口的含义?
> 10、什么叫CDN?
> 11、什么叫网站灰度发布?
> 12、简述DNS进行域名解析的过程?
> 13、RabbitMQ是什么东西?
> 14、讲一下Keepalived的工作原理?
> 15、讲述一下LVS三种模式的工作过程?
> 16、mysql的innodb如何定位锁问题,mysql如何减少主从复制延迟?
> 17、如何重置mysql root密码?
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取!](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618635766)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**
> 1、什么是运维?
> 2、在工作中,运维人员经常需要跟运营人员打交道,请问运营人员是做什么工作的?
> 3、现在给你三百台服务器,你怎么对他们进行管理?
> 4、简述raid0 raid1raid5二种工作模式的工作原理及特点
> 5、LVS、Nginx、HAproxy有什么区别?工作中你怎么选择?
> 6、Squid、Varinsh和Nginx有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 7、Tomcat和Resin有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 8、什么是中间件?什么是jdk?
> 9、讲述一下Tomcat8005、8009、8080三个端口的含义?
> 10、什么叫CDN?
> 11、什么叫网站灰度发布?
> 12、简述DNS进行域名解析的过程?
> 13、RabbitMQ是什么东西?
> 14、讲一下Keepalived的工作原理?
> 15、讲述一下LVS三种模式的工作过程?
> 16、mysql的innodb如何定位锁问题,mysql如何减少主从复制延迟?
> 17、如何重置mysql root密码?
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取!](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618635766)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








