1、相交链表

本题思路就是定义两指针,指向两链表的同一起跑线,然后共同往前走,边走边判断两链表的节点是否相等, 代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
while(curA != null){
countA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curB != null){
countB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if(countA > countB){
int count = countA - countB;
while(count > 0){
curA = curA.next;
count--;
}
}
else if(countB > countA){
int count = countB - countA;
while(count > 0){
curB = curB.next;
count--;
}
}
while(curA != null){
if(curA == curB) return curA;
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}2、反转链表

经典题目,原地操作,需要定义一个pre节点, 具体代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while(cur != null && cur.next != null){
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
cur.next = pre;
return cur;
}
}3、回文链表

本题思路是将链表的节点值存入数组中,然后用左右指针分别判断数组的左右两边元素值是否相等, 代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
list.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
int left = 0;
int right = list.size()-1;
while(left < right){
if(list.get(left) != list.get(right)){
return false;
}
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}4、环形链表

定义快慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,如果有环的话他们就会相遇,代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null && fast.next.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}5、环形链表 II

本题先找到两节点相遇的地方,然后利用一点数学技巧可以得出在相遇的地方向前走a的距离,即可到达环的入口。(a为起点到环入口的距离)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(true){
if(fast==null || fast.next==null || fast.next.next==null) return null;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}6、合并两个有序链表

创建一个新链表,不断添加两个链表的节点即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null) return list2;
if(list2 == null) return list1;
ListNode head = new ListNode();
if(list1.val > list2.val){
head = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
else{
head = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while(list1!=null && list2!=null){
if(list1.val > list2.val){
cur.next = list2;
cur = cur.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
else{
cur.next = list1;
cur = cur.next;
list1 = list1.next;
}
}
if(list1 == null){
while(list2 != null){
cur.next = list2;
cur = cur.next;
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if(list2 == null){
while(list1 != null){
cur.next = list1;
cur = cur.next;
list1 = list1.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}7、两数相加
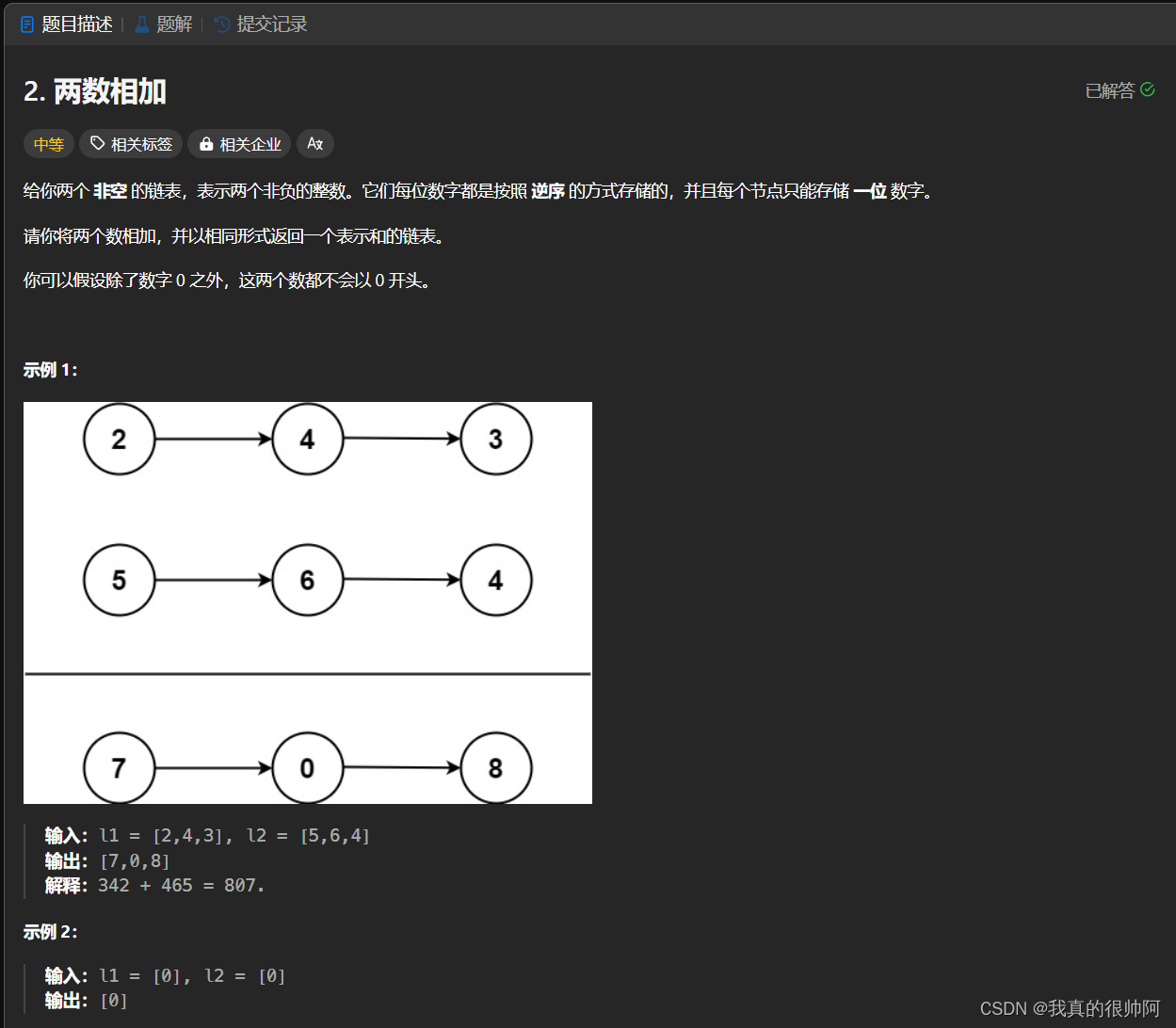
本题需要考虑2个情况:短的链表需要补0、需要考虑进位。 代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = dummy;
int next = 0; //进位
while(l1 != null || l2 != null){
int n1 = l1 == null? 0 : l1.val;
int n2 = l2 == null? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = n1 + n2 + next;
next = sum / 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
cur = cur.next;
if(l1 != null) l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null) l2 = l2.next;
}
if(next > 0){
cur.next = new ListNode(next);
}
return dummy.next;
}
}8、删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点

先找到要删除的那个节点的前驱节点,然后将其后继节点设为被删节点的后继节点即可。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
int sum = 0; //节点个数
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
sum++;
cur = cur.next;
}
int count = sum - n;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
cur = dummy;
//将节点移动至被删节点的前一个节点
while(count > 0){
cur = cur.next;
count--;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}9、LRU 缓存
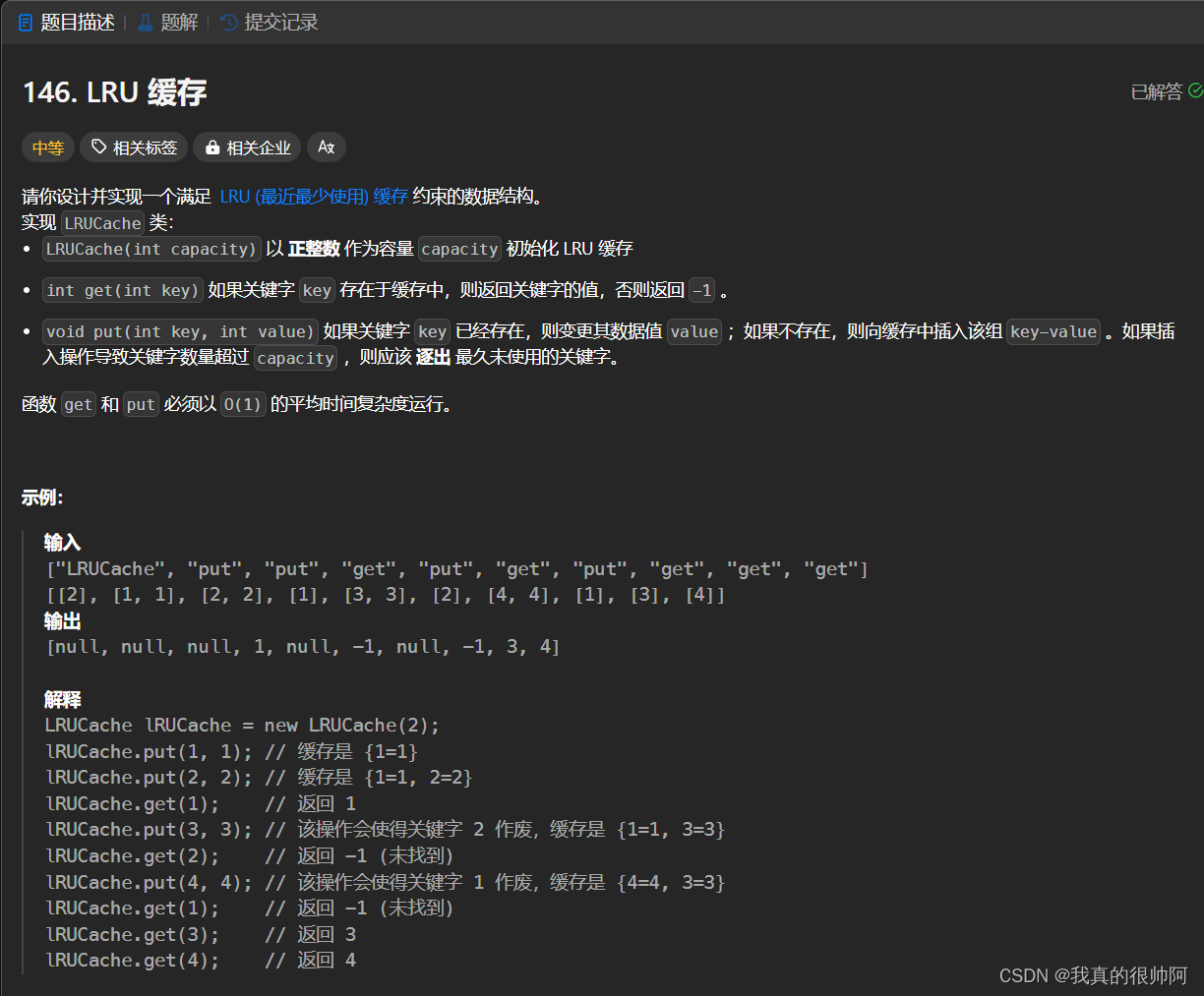
本题需要维护一个队列,队头元素即为最近使用的元素,队尾元素即为最近最久没使用过的元素。
class LRUCache {
private int capacity;
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
LinkedList<Integer> LRUlist = new LinkedList<>();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
int temp = map.getOrDefault(key,-1);
if(temp != -1){
//更新LRUlist
LRUlist.remove((Integer)key);
LRUlist.addFirst(key);
}
return temp;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
//已经存在该key
if(map.containsKey(key)){
LRUlist.remove((Integer)key);
LRUlist.addFirst(key);
map.put(key,value);
}
else{
//map未超出容量
if(map.size() < capacity){
map.put(key,value);
LRUlist.addFirst(key);
}
else{
int temp = LRUlist.removeLast(); //移除最近最久未使用的元素
map.remove(temp);
map.put(key,value);
LRUlist.addFirst(key);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/10、排序链表

本题先将链表的值保存至集合中,再将集合的元素排序,再重新构造出一个链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
while(cur != null){
nums.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
Collections.sort(nums);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
cur = dummy;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){
cur.next = new ListNode(nums.get(i));
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}





















 401
401











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








