最后
Python崛起并且风靡,因为优点多、应用领域广、被大牛们认可。学习 Python 门槛很低,但它的晋级路线很多,通过它你能进入机器学习、数据挖掘、大数据,CS等更加高级的领域。Python可以做网络应用,可以做科学计算,数据分析,可以做网络爬虫,可以做机器学习、自然语言处理、可以写游戏、可以做桌面应用…Python可以做的很多,你需要学好基础,再选择明确的方向。这里给大家分享一份全套的 Python 学习资料,给那些想学习 Python 的小伙伴们一点帮助!
👉Python所有方向的学习路线👈
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。

👉Python必备开发工具👈
工欲善其事必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,给大家节省了很多时间。

👉Python全套学习视频👈
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。

👉实战案例👈
学python就与学数学一样,是不能只看书不做题的,直接看步骤和答案会让人误以为自己全都掌握了,但是碰到生题的时候还是会一筹莫展。
因此在学习python的过程中一定要记得多动手写代码,教程只需要看一两遍即可。

👉大厂面试真题👈
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。

一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
win_list = [[‘石头’, ‘剪刀’], [‘剪刀’, ‘布’], [‘布’, ‘石头’]]
prompt = “”“(0) 石头
(1) 剪刀
(2) 布
请选择(0/1/2): “””
computer = random.choice(all_choices)
ind = int(input(prompt))
player = all_choices[ind]
print(“Your choice: %s, Computer’s choice: %s” % (player, computer))
if player == computer:
print(‘\033[32;1m平局\033[0m’)
elif [player, computer] in win_list:
print(‘\033[31;1mYou WIN!!!\033[0m’)
else:
print(‘\033[31;1mYou LOSE!!!\033[0m’)
### 18-猜数,直到猜对
import random
num = random.randint(1, 10)
running = True
while running:
answer = int(input('guess the number: '))
if answer > num:
print(‘猜大了’)
elif answer < num:
print(‘猜小了’)
else:
print(‘猜对了’)
running = False
### 19-猜数,5次机会
import random
num = random.randint(1, 10)
counter = 0
while counter < 5:
answer = int(input('guess the number: '))
if answer > num:
print(‘猜大了’)
elif answer < num:
print(‘猜小了’)
else:
print(‘猜对了’)
break
counter += 1
else: # 循环被break就不执行了,没有被break才执行
print(‘the number is:’, num)
### 20-while循环,累加至100
因为循环次数是已知的,实际使用时,建议用for循环
sum100 = 0
counter = 1
while counter < 101:
sum100 += counter
counter += 1
print(sum100)
### 21-while-break
break是结束循环,break之后、循环体内代码不再执行。
while True:
yn = input('Continue(y/n): ')
if yn in [‘n’, ‘N’]:
break
print(‘running…’)
### 22-while-continue
计算100以内偶数之和。
continue是跳过本次循环剩余部分,回到循环条件处。
sum100 = 0
counter = 0
while counter < 100:
counter += 1
# if counter % 2:
if counter % 2 == 1:
continue
sum100 += counter
print(sum100)
### 23-for循环遍历数据对象
astr = ‘hello’
alist = [10, 20, 30]
atuple = (‘bob’, ‘tom’, ‘alice’)
adict = {‘name’: ‘john’, ‘age’: 23}
for ch in astr:
print(ch)
for i in alist:
print(i)
for name in atuple:
print(name)
for key in adict:
print(‘%s: %s’ % (key, adict[key]))
### 24-range用法及数字累加
range(10) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
# >>> list(range(10))
# range(6, 11) # [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
# range(1, 10, 2) # [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
# range(10, 0, -1) # [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
sum100 = 0
for i in range(1, 101):
sum100 += i
print(sum100)
### 25-列表实现斐波那契数列
列表中先给定两个数字,后面的数字总是前两个数字之和。
fib = [0, 1]
for i in range(8):
fib.append(fib[-1] + fib[-2])
print(fib)
### 26-九九乘法表
for i in range(1, 10):
for j in range(1, i + 1):
print(‘%s*%s=%s’ % (j, i, i * j), end=’ ')
print()
i=1 ->j: [1]
i=2 ->j: [1,2]
i=3 ->j: [1,2,3]
#由用户指定相乘到多少
n = int(input('number: '))
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, i + 1):
print(‘%s*%s=%s’ % (j, i, i * j), end=’ ')
print()
### 27-逐步实现列表解析
10+5的结果放到列表中
[10 + 5]
# 10+5这个表达式计算10次
[10 + 5 for i in range(10)]
# 10+i的i来自于循环
[10 + i for i in range(10)]
[10 + i for i in range(1, 11)]
# 通过if过滤,满足if条件的才参与10+i的运算
[10 + i for i in range(1, 11) if i % 2 == 1]
[10 + i for i in range(1, 11) if i % 2]
# 生成IP地址列表
['192.168.1.%s' % i for i in range(1, 255)]
### 28-三局两胜的石头剪刀布
import random
all_choices = [‘石头’, ‘剪刀’, ‘布’]
win_list = [[‘石头’, ‘剪刀’], [‘剪刀’, ‘布’], [‘布’, ‘石头’]]
prompt = “”“(0) 石头
(1) 剪刀
(2) 布
请选择(0/1/2): “””
cwin = 0
pwin = 0
while cwin < 2 and pwin < 2:
computer = random.choice(all_choices)
ind = int(input(prompt))
player = all_choices[ind]
print("Your choice: %s, Computer's choice: %s" % (player, computer))
if player == computer:
print('\033[32;1m平局\033[0m')
elif [player, computer] in win_list:
pwin += 1
print('\033[31;1mYou WIN!!!\033[0m')
else:
cwin += 1
print('\033[31;1mYou LOSE!!!\033[0m')
### 29-文件对象基础操作
文件操作的三个步骤:打开、读写、关闭
# cp /etc/passwd /tmp
f = open('/tmp/passwd') # 默认以r的方式打开纯文本文件
data = f.read() # read()把所有内容读取出来
print(data)
data = f.read() # 随着读写的进行,文件指针向后移动。
# 因为第一个f.read()已经把文件指针移动到结尾了,所以再读就没有数据了
# 所以data是空字符串
f.close()
f = open('/tmp/passwd')
data = f.read(4) # 读4字节
f.readline() # 读到换行符\n结束
f.readlines() # 把每一行数据读出来放到列表中
f.close()
################################
f = open('/tmp/passwd')
for line in f:
print(line, end='')
f.close()
##############################
f = open('图片地址', 'rb') # 打开非文本文件要加参数b
f.read(4096)
f.close()
##################################
f = open('/tmp/myfile', 'w') # 'w'打开文件,如果文件不存在则创建
f.write('hello world!\n')
f.flush() # 立即将缓存中的数据同步到磁盘
f.writelines(['2nd line.\n', 'new line.\n'])
f.close() # 关闭文件的时候,数据保存到磁盘
##############################
with open('/tmp/passwd') as f:
print(f.readline())
#########################
f = open('/tmp/passwd')
f.tell() # 查看文件指针的位置
f.readline()
f.tell()
f.seek(0, 0) # 第一个数字是偏移量,第2位是数字是相对位置。
# 相对位置0表示开头,1表示当前,2表示结尾
f.tell()
f.close()
### 30-拷贝文件
拷贝文件就是以r的方式打开源文件,以w的方式打开目标文件,将源文件数据读出后,写到目标文件。
以下是【不推荐】的方式,但是可以工作:
f1 = open(‘/bin/ls’, ‘rb’)
f2 = open(‘/root/ls’, ‘wb’)
data = f1.read()
f2.write(data)
f1.close()
f2.close()
### 31-拷贝文件
每次读取4K,读完为止:
src_fname = ‘/bin/ls’
dst_fname = ‘/root/ls’
src_fobj = open(src_fname, 'rb')
dst_fobj = open(dst_fname, 'wb')
while True:
data = src_fobj.read(4096)
if not data:
break
dst_fobj.write(data)
src_fobj.close()
dst_fobj.close()
### 32-位置参数
注意:位置参数中的数字是字符形式的
import sys
print(sys.argv) # sys.argv是sys模块里的argv列表
# python3 position_args.py
# python3 position_args.py 10
# python3 position_args.py 10 bob
### 33-函数应用-斐波那契数列
def gen_fib(l):
fib = [0, 1]
for i in range(l - len(fib)):
fib.append(fib[-1] + fib[-2])
return fib # 返回列表,不返回变量fib
a = gen_fib(10)
print(a)
print(‘-’ * 50)
n = int(input("length: "))
print(gen_fib(n)) # 不会把变量n传入,是把n代表的值赋值给形参
### 34-函数-拷贝文件
import sys
def copy(src_fname, dst_fname):
src_fobj = open(src_fname, 'rb')
dst_fobj = open(dst_fname, 'wb')
while True:
data = src_fobj.read(4096)
if not data:
break
dst_fobj.write(data)
src_fobj.close()
dst_fobj.close()
copy(sys.argv[1], sys.argv[2])
# 执行方式
# cp_func.py /etc/hosts /tmp/zhuji.txt
### 35-函数-九九乘法表
def mtable(n):
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(1, i + 1):
print(‘%s*%s=%s’ % (j, i, i * j), end=’ ')
print()
mtable(6)
mtable(9)
### 36-模块基础
每一个以py作为扩展名的文件都是一个模块。
star.py:
hi = 'hello world!'
def pstar(n=50):
print('*' * n)
if __name__ == '__main__':
pstar()
pstar(30)
在call_star.py中调用star模块:
import star
print(star.hi)
star.pstar()
star.pstar(30)
### 37-生成密码/验证码
此文件名为:randpass.py
思路:
1、设置一个用于随机取出字符的基础字符串,本例使用大小写字母加数字
2、循环n次,每次随机取出一个字符
3、将各个字符拼接起来,保存到变量result中
from random import choice
import string
all_chs = string.ascii_letters + string.digits # 大小写字母加数字
def gen_pass(n=8):
result = ''
for i in range(n):
ch = choice(all_chs)
result += ch
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(gen_pass())
print(gen_pass(4))
print(gen_pass(10))
### 38-序列对象方法
from random import randint
alist = list() # []
list(‘hello’) # [‘h’, ‘e’, ‘l’, ‘l’, ‘o’]
list((10, 20, 30)) # [10, 20, 30] 元组转列表
astr = str() # ‘’
str(10) # ‘10’
str([‘h’, ‘e’, ‘l’, ‘l’, ‘o’]) # 将列表转成字符串
atuple = tuple() # ()
tuple(‘hello’) # (‘h’, ‘e’, ‘l’, ‘l’, ‘o’)
num_list = [randint(1, 100) for i in range(10)]
max(num_list)
min(num_list)
### 39-序列对象方法2
alist = [10, ‘john’]
list(enumerate(alist)) # [(0, 10), (1, ‘john’)]
a, b = 0, 10 # a->0 ->10
for ind in range(len(alist)):
print(‘%s: %s’ % (ind, alist[ind]))
for item in enumerate(alist):
print(‘%s: %s’ % (item[0], item[1]))
for ind, val in enumerate(alist):
print(‘%s: %s’ % (ind, val))
atuple = (96, 97, 40, 75, 58, 34, 69, 29, 66, 90)
sorted(atuple)
sorted(‘hello’)
for i in reversed(atuple):
print(i, end=‘,’)
### 40-字符串方法
py_str = ‘hello world!’
py_str.capitalize()
py_str.title()
py_str.center(50)
py_str.center(50, ‘#’)
py_str.ljust(50, ‘')
py_str.rjust(50, '’)
py_str.count(‘l’) # 统计l出现的次数
py_str.count(‘lo’)
py_str.endswith(‘!’) # 以!结尾吗?
py_str.endswith(‘d!’)
py_str.startswith(‘a’) # 以a开头吗?
py_str.islower() # 字母都是小写的?其他字符不考虑
py_str.isupper() # 字母都是大写的?其他字符不考虑
‘Hao123’.isdigit() # 所有字符都是数字吗?
‘Hao123’.isalnum() # 所有字符都是字母数字?
’ hello\t '.strip() # 去除两端空白字符,常用
’ hello\t ‘.lstrip()
’ hello\t ‘.rstrip()
‘how are you?’.split()
‘hello.tar.gz’.split(’.’)
‘.’.join([‘hello’, ‘tar’, ‘gz’])
‘-’.join([‘hello’, ‘tar’, ‘gz’])
### 最后
**作为一个IT的过来人,我自己整理了一些python学习资料,都是别人分享给我的,希望对你们有帮助。**
**学好 Python 不论是就业还是做副业赚钱都不错,但要学会 Python 还是要有一个学习规划。**
**朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】**。

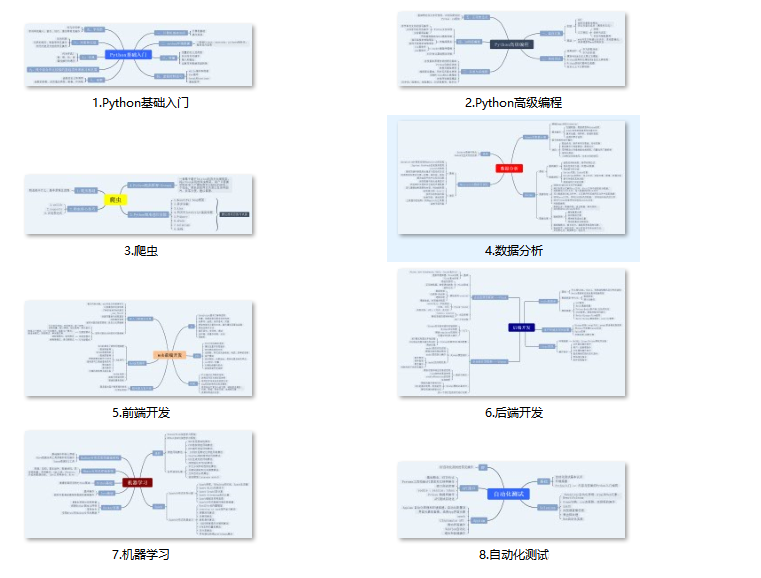
### 一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。

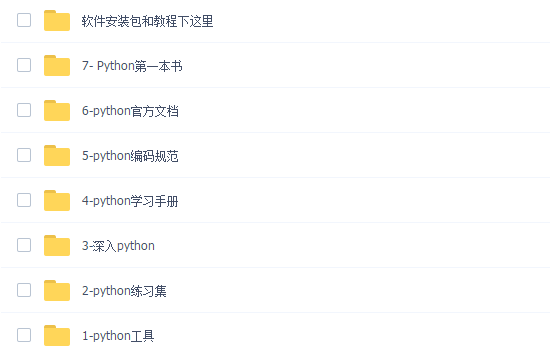
### 二、Python必备开发工具
### 一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向路线就是把Python常用的技术点做整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
### 二、学习软件
工欲善其事必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,给大家节省了很多时间。
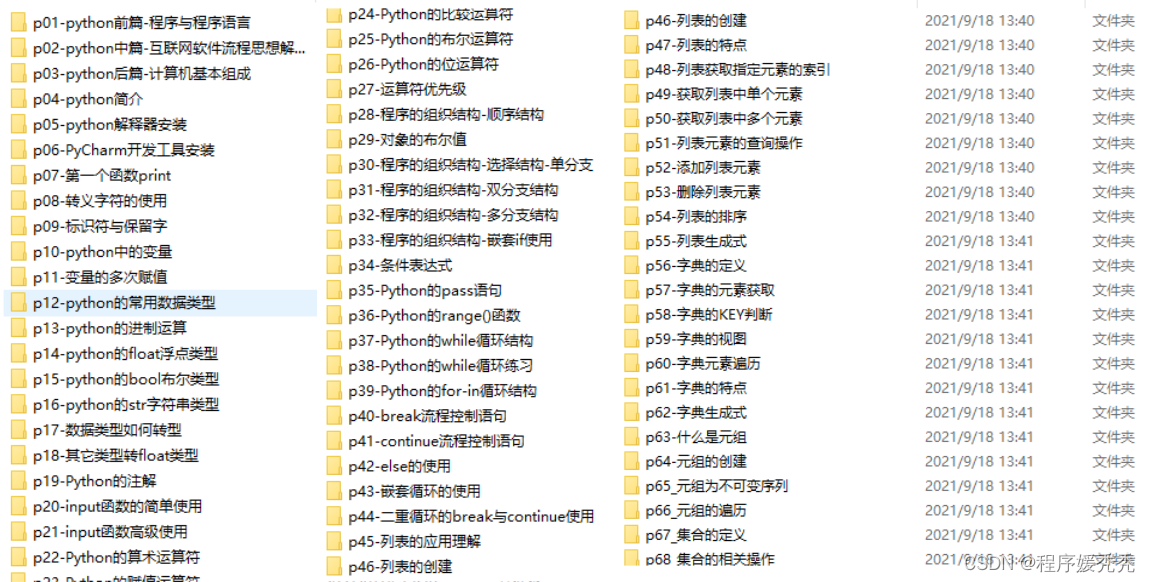
### 三、入门学习视频
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化学习资料的朋友,可以戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618317507)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**






















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








