第1关:迷宫求解
任务描述
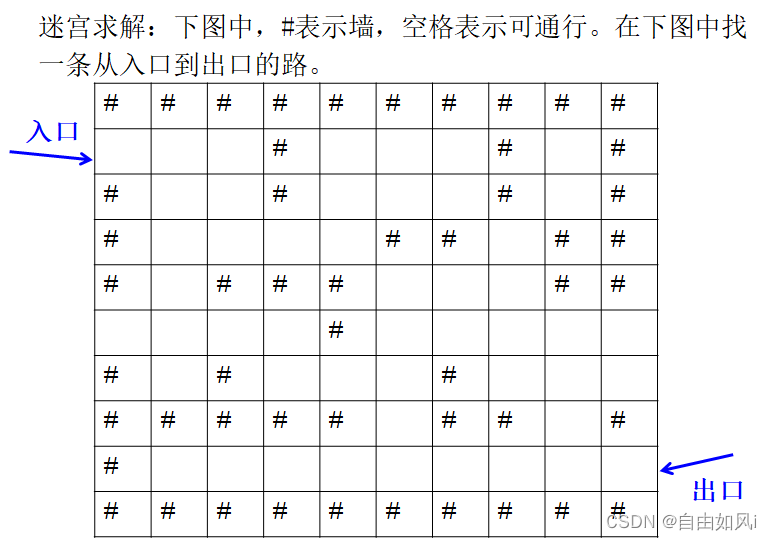
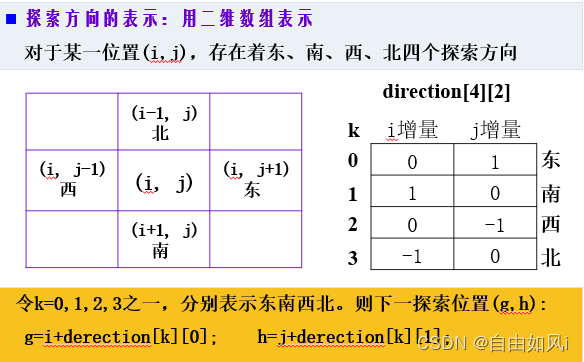
相关知识
为了完成本关任务,你需要掌握:1.栈的基本操作,2.深度优先访问算法。
编程要求
根据提示,在右侧"// ---- begin ----- … // ------- end -----" 部分补充代码。注意不要删除 begin、end注释。
测试说明
平台会对你编写的代码进行测试:
测试输入:无;
预期输出:
(8,9)
(8,8,0)
(8,7,0)
(8,6,0)
(8,5,0)
(7,5,1)
(6,5,1)
(6,4,0)
(6,3,0)
(5,3,1)
(5,2,0)
(5,1,0)
(4,1,1)
(3,1,1)
(3,2,2)
(2,2,1)
(1,2,1)
(1,1,0)
(1,0,0)
上面的输出是一条从入口(1,0)到出口(8,9)的一条逆向路径。输出的每一个三元组表示(横坐标,纵坐标,前进方向),例如(1,0,0)表示在位置(1,0)沿东方(0:东方;1:南方:2:西方;3:北方)前进。
开始你的任务吧,祝你成功!
maze/stack.h
#ifndef STACK_H
#define STACK_H
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
int d;
}DataType;
typedef struct {
DataType* data; //在栈构造之前和销毁之后,data的值为空。
int top; //top指示栈顶
int stacksize; //当前已分配的存储空间,以数据元素为单位
}SeqStack, * PSeqStack;
//构造一个空栈
PSeqStack createEmptyStack_seq(int m)
{
PSeqStack S = (PSeqStack)malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
if (S)
{
S->data = (DataType*)malloc(m * sizeof(DataType));
if (!S->data)
{
free(S); return 0;
}//存储分配失败
S->top = -1;
S->stacksize = m;
}
return S;
}//createEmptyStack_seq
//若栈S为空栈,返回1;否则,返回0
int isEmptyStack_seq(PSeqStack S)
{
return (S->top == -1 ? 1 : 0);
}
//入栈
void Push_Seq(PSeqStack S, DataType x)
{
//插入元素x为新的栈顶元素
// --------- 补充代码(1)begin ---------
S->top=S->top+1;
S->data[S->top]=x;
// --------- 补充代码(1)end ---------
}//Push_Seq
//出栈
int Pop_Seq(PSeqStack S) {
//若栈不为空,删除栈顶元素并返回OK;否则返回ERROR.
if (isEmptyStack_seq(S)) {
printf("\n Stack is free!");
return 0;
}
// --------- 补充代码(2)begin ---------
else{
S->top = S->top-1;
}
// --------- 补充代码(2)end ---------
return 1;
}//Pop_Seq
//取栈顶元素
DataType Top_Seq(PSeqStack S)
{ //若栈S不空,则返回栈顶元素; 否则给出相应提示.
DataType e;
if (isEmptyStack_seq(S))
{
e.x = e.y = e.d = -1;
printf("\n Stack is free!");
}
else
{
e=S->data[S->top];
}
// --------- 补充代码(3)begin ---------
return e;
// --------- 补充代码(3)end ---------
}//GetTop
#endif // !STACK_H
maze/solveMaze.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "stack.h"
void mazePath(int maze[10][10],int derection[4][2],int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
{
//(x1,y1)为入口;(x2,y2)为出口
int i, j, k; //k表示试探的方向,分别为0,1,2,3
int g, h; //(g,h)为(i,j)的下一探索方向
DataType term;
PSeqStack S = NULL;
if (S)
free(S);
S = createEmptyStack_seq(25);
maze[x1][y1] = 2; //标记入口
term.x = x1;
term.y = y1;
term.d = -1;
Push_Seq(S, term);
while (!isEmptyStack_seq(S))
{
//取栈顶元素并出栈
term = Top_Seq(S);
Pop_Seq(S);
//记录当前位置(i,j)
i = term.x;
j = term.y;
//当前位置的下一探索方向
k = term.d + 1;
while (k <= 3)
{
g = i + derection[k][0];
h = j + derection[k][1];
if (g == x2 && h == y2)
{
printf("(%d,%d)\n", g, h);//打印出口
printf("(%d,%d,%d)\n", i, j, k);//打印通路上的倒数第二个位置
while (!isEmptyStack_seq(S))
{
term = Top_Seq(S);
Pop_Seq(S);
printf("(%d,%d,%d)\n", term.x, term.y, term.d);
}
return;
}
// --------- 补充代码(4) begin ---------
if(maze[g][h]==0){
maze[g][h]=2;
term.x=i;
term.y=j;
term.d=k;
Push_Seq(S,term);
i=g;
j=h;
k=-1;
}
k++;
// --------- 补充代码(4)end ---------
}
}
if (!isEmptyStack_seq(S))
printf("没找到路径\n");
}
int main()
{
int maze[10][10] = { {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},
{0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1},
{1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}};
int derection[4][2] = { {0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0} };
mazePath(maze, derection, 1, 0, 8, 9);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
























 1740
1740











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








