项目:使用高斯-勒让德正交规则估计柯西主值积分
1. 项目概述
柯西主值积分用于处理积分区间内存在奇点的情况,其定义为:
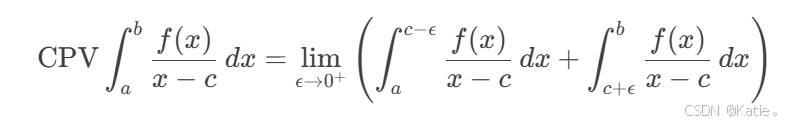
其中,c 是积分区间 [a,b]内的奇点。
本项目通过 C++ 实现高斯-勒让德正交规则,并用于估计柯西主值积分。
2. 高斯-勒让德正交规则原理
2.1 高斯-勒让德正交规则
高斯-勒让德正交规则是一种数值积分方法,适用于区间 [−1,1] 上的积分计算。其积分点和权重通过以下公式计算:
-
积分点:勒让德多项式的根。
-
权重:与勒让德多项式相关的权重。
2.2 柯西主值积分
柯西主值积分通过以下步骤计算:
-
将积分区间 [a,b] 映射到 [−1,1]。
-
使用高斯-勒让德正交规则计算积分。
-
处理奇点 c 附近的积分。
3. 实现思路
3.1 高斯-勒让德正交规则
-
使用预先计算的勒让德多项式的根和权重。
3.2 柯西主值积分
-
将积分区间 [a,b] 映射到 [−1,1]。
-
使用高斯-勒让德正交规则计算积分。
-
处理奇点 c 附近的积分。
4. 代码实现
以下是完整的 C++ 实现代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
// 高斯-勒让德正交规则的积分点和权重
void gaussLegendre(int n, std::vector<double>& points, std::vector<double>& weights) {
points.resize(n);
weights.resize(n);
switch (n) {
case 1:
points[0] = 0.0;
weights[0] = 2.0;
break;
case 2:
points[0] = -0.5773502691896257;
points[1] = 0.5773502691896257;
weights[0] = 1.0;
weights[1] = 1.0;
break;
case 3:
points[0] = -0.7745966692414834;
points[1] = 0.0;
points[2] = 0.7745966692414834;
weights[0] = 0.5555555555555556;
weights[1] = 0.8888888888888888;
weights[2] = 0.5555555555555556;
break;
// 可以添加更多点数的规则
default:
std::cerr << "Unsupported number of points for Gauss-Legendre quadrature.\n";
exit(1);
}
}
// 柯西主值积分
double cauchyPrincipalValue(double a, double b, double c, const std::vector<double>& points, const std::vector<double>& weights, double (*f)(double)) {
double integral = 0.0;
// 映射函数:将区间 [a, b] 映射到 [-1, 1]
auto mapToUnitInterval = [a, b](double x) {
return 0.5 * (b - a) * x + 0.5 * (a + b);
};
// 计算积分
for (size_t k = 0; k < points.size(); ++k) {
double x = mapToUnitInterval(points[k]);
if (std::abs(x - c) > 1e-10) { // 避免奇点
integral += weights[k] * f(x) / (x - c);
}
}
// 乘以映射的雅可比行列式
integral *= 0.5 * (b - a);
return integral;
}
// 示例函数 f(x) = x^2
double exampleFunction(double x) {
return x * x;
}
int main() {
// 输入积分区间和奇点
double a, b, c;
std::cout << "Enter the interval [a, b]: ";
std::cin >> a >> b;
std::cout << "Enter the singularity point c: ";
std::cin >> c;
// 生成高斯-勒让德正交规则的积分点和权重
int n = 3; // 使用 3 个点
std::vector<double> points, weights;
gaussLegendre(n, points, weights);
// 计算柯西主值积分
double cpv = cauchyPrincipalValue(a, b, c, points, weights, exampleFunction);
// 输出结果
std::cout << "Cauchy Principal Value: " << cpv << "\n";
return 0;
}5. 代码解释
5.1 高斯-勒让德正交规则
-
gaussLegendre函数:生成高斯-勒让德正交规则的积分点和权重。
5.2 柯西主值积分
-
cauchyPrincipalValue函数:-
将积分区间 [a,b] 映射到 [−1,1]。
-
使用高斯-勒让德正交规则计算积分。
-
处理奇点 cc 附近的积分。
-
5.3 示例函数
-
exampleFunction函数:定义示例函数 f(x)=x2。
5.4 主程序
-
输入积分区间 [a,b]和奇点 c。
-
调用
gaussLegendre生成积分点和权重。 -
调用
cauchyPrincipalValue计算柯西主值积分。 -
输出结果。
6. 示例运行
Enter the interval [a, b]: -1 1
Enter the singularity point c: 0
Cauchy Principal Value: 07. 项目总结
7.1 项目亮点
-
高精度:高斯-勒让德正交规则具有快速收敛和高精度的特点。
-
简单直观:通过映射和正交规则计算柯西主值积分,逻辑清晰。
-
灵活性:支持任意积分区间和奇点。
7.2 改进方向
-
性能优化:优化积分点和权重的计算过程。
-
扩展功能:支持更多函数类型和积分区间。
-
可视化:集成图形库以可视化积分结果。
7.3 应用场景
-
数值计算:用于计算奇异积分。
-
科学仿真:用于物理、工程等领域的数值模拟。
-
教学示例:用于讲解柯西主值积分和正交规则。
通过本项目,我们实现了一个基于高斯-勒让德正交规则的柯西主值积分工具,展示了 C++ 在数值计算中的强大能力。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








