113. 路径总和 II
一、题目
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
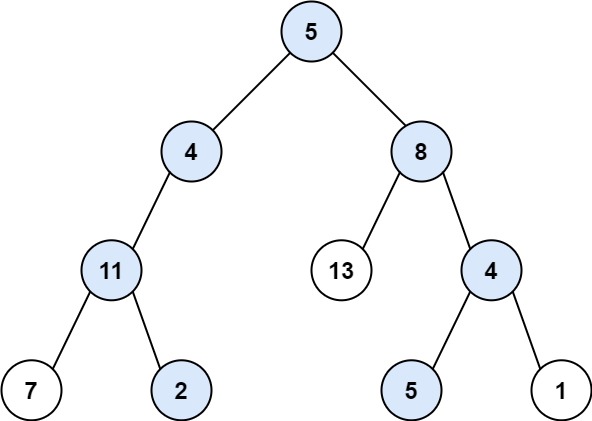
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:
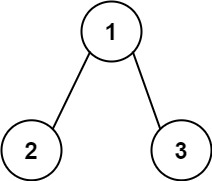
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点总数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
二、题解
方法一:递归
算法思路
-
我们需要遍历二叉树中所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径,以找出满足路径和等于目标和的路径。这提示我们可以使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来遍历树的所有可能路径。
-
我们可以在递归过程中维护一个当前路径的和
count,从根节点开始,每到一个节点,我们将该节点的值在count上进行减法处理。 -
如果当前节点是叶子节点(即没有左右子节点),我们检查
count是否等于0。如果是,我们将当前路径添加到结果中。 -
在递归过程中,我们需要传递当前路径
path,结果数组result,当前路径的和count,以及当前节点root。
具体实现
class Solution {
public:
void findPath(TreeNode *root, vector<vector<int>>&result, vector<int>& path, int count){
if(root == nullptr) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
count -= root->val;
if(count == 0 && !root->left && !root->right){
result.push_back(path);
}
if(root->left){
findPath(root->left, result, path, count);
}
if(root->right){
findPath(root->right, result, path, count);
}
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,移除当前节点,尝试其他路径
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
if(root == nullptr) return result;
findPath(root, result, path, targetSum);
return result;
}
};
算法分析
-
时间复杂度:遍历整个二叉树,每个节点只访问一次,所以时间复杂度为 O(N),其中 N 是树中的节点数。
-
空间复杂度:在递归过程中,我们使用了
path数组来存储当前路径,最坏情况下,路径长度达到树的深度,所以空间复杂度为 O(H),其中 H 是树的高度。在结果数组中,我们存储了满足条件的路径,最坏情况下可能会有 O(N) 个路径,所以结果数组的空间复杂度也是 O(N)。
另一种递归版本
因为cpp的特性,通过去掉 vector<int>& 中的引用符号,我可以在每个递归层次中都创建了一个新的 path 向量,这样可以确保在不同的递归路径之间不会共享相同的 path 对象,相当于进行了回溯。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void findPath(TreeNode *root, vector<vector<int>>&result, vector<int> path, int count){
if(root == nullptr) return;
path.push_back(root->val);
count -= root->val;
if(count == 0 && !root->left && !root->right){
result.push_back(path);
}
if(root->left){
findPath(root->left, result, path, count);
}
if(root->right){
findPath(root->right, result, path, count);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
if(root == nullptr) return result;
int count = targetSum;
findPath(root, result, path, count);
return result;
}
};
方法二:迭代
算法思路
- 我们使用中序遍历来遍历树的节点,同时维护两个栈:
St用于保存遍历节点的信息,pathSt用于保存当前路径的节点值。 - 初始时,我们将根节点
root和对应的路径值root->val入栈,表示从根节点开始的路径。 - 在每一次循环中,我们从
St栈中取出一个节点,同时从pathSt中取出与该节点对应的路径。 - 我们检查该节点是否为叶子节点,如果是叶子节点并且路径值等于
targetSum,则将该路径保存到result中。 - 如果不是叶子节点,我们将其左子节点和右子节点(如果存在的话)入栈,并更新路径值。
- 重复以上步骤直至
St栈为空。
具体实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> result; // 用于存储符合条件的路径
stack<pair<TreeNode*, int>> St; // 用于深度优先搜索的栈,同时保存节点和路径和
stack<vector<int>> pathSt; // 用于保存路径的栈
if (root == nullptr) return result; // 处理根节点为空的情况
// 初始化,将根节点和路径和入栈
St.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(root, root->val));
vector<int> temp;
temp.push_back(root->val);
pathSt.push(temp);
while (!St.empty()) {
pair<TreeNode*, int> node = St.top(); St.pop(); // 弹出栈顶节点
vector<int> pathT = pathSt.top(); pathSt.pop(); // 弹出栈顶路径
// 如果是叶子节点且路径和等于targetSum,将路径保存到result中
if (!node.first->left && !node.first->right && node.second == targetSum) {
result.push_back(pathT);
}
// 将右子节点入栈,更新路径和,并将路径入栈
if (node.first->right) {
St.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->right, node.second + node.first->right->val));
vector<int> newPathT = pathT;
newPathT.push_back(node.first->right->val);
pathSt.push(newPathT);
}
// 将左子节点入栈,更新路径和,并将路径入栈
if (node.first->left) {
St.push(pair<TreeNode*, int>(node.first->left, node.second + node.first->left->val));
vector<int> newPathT = pathT;
newPathT.push_back(node.first->left->val);
pathSt.push(newPathT);
}
}
return result; // 返回所有满足条件的路径
}
};
算法分析
- 时间复杂度:每个节点最多访问一次,所以时间复杂度为 O(N),其中 N 是树的节点数。
- 空间复杂度:栈的最大空间取决于树的高度,所以空间复杂度为 O(H),其中 H 是树的高度。
简化版本
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
stack<TreeNode*> TreeSt;
stack<vector<int>> pathSt;
if(root == nullptr) return result;
// 初始化
TreeSt.push(root);
vector<int> temp;
temp.push_back(root->val);
pathSt.push(temp);
while(!TreeSt.empty()){
TreeNode *node = TreeSt.top();TreeSt.pop();
vector<int> pathT = pathSt.top();pathSt.pop();
if(!node->left && !node->right && accumulate(pathT.begin(), pathT.end(), 0) == targetSum) { //这里直接计算路径上的总和
result.push_back(pathT);
}
if(node->right){
TreeSt.push(node->right);
vector<int> newPathT = pathT;
newPathT.push_back(node->right->val);
pathSt.push(newPathT);
}
if(node->left){
TreeSt.push(node->left);
vector<int> newPathT = pathT;
newPathT.push_back(node->left->val);
pathSt.push(newPathT);
}
}
return result;
}
};























 379
379











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










