目录
一、Collection集合概述和基本使用
集合体系结构
集合类的特点:
提供一种存储空间可变的存储模型,存储的数据容量可以随时发送改变
集合的体系图:
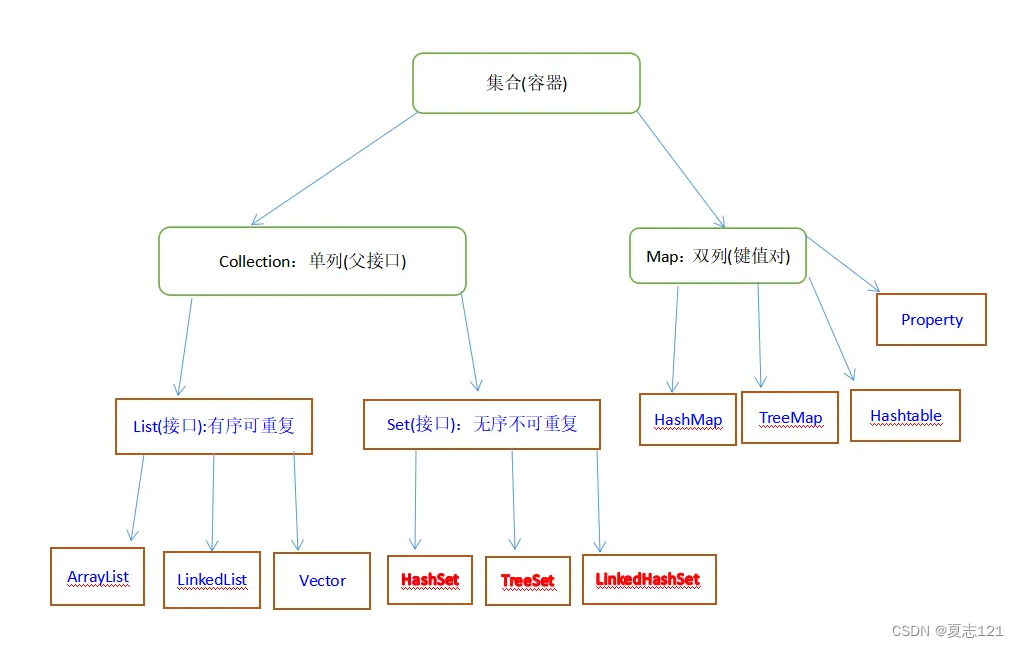
Collection集合概述:
● 是单例集合的顶层接口,它表示一组对象,这些对象也称为Collection的元素
● JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现,它提供更具体的子接口(如Set和List)实现
Collection集合基本使用:
public class CollectionDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Collection集合的对象
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();
//添加元素:boolean add(E e)
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
//输出集合对象
System.out.println(c);
}
}
二、Collection集合的常用方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
| boolean add(E e) | 添加元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 从集合中移除指定的元素 |
| void clear() | 清空集合中的元素 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断集合中是否存在指定的元素 |
| boolean is Empty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| int size() | 集合的长度,也就是集合中元素的个数 |
三、Collection集合的遍历
迭代器的介绍:
● 迭代器,集合的专用遍历方式
● Iterator iterator():返回此集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合的iterator()方法得到
● 迭代器是通过集合的iterator()方法得到的,所以我们说它是依赖于集合而存在的
Collection集合的遍历:
public class IteratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();
//添加元素
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
c.add("javaee");
//Iterator<E> iterator():返回此集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合的iterator()方法得到
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();
//用while循环改进元素的判断和获取
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
四、集合案例-Collection集合存储学生对象并遍历
需求:
创建一个存储学生对象的集合,存储3个学生对象,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该集合
代码实现:
学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
测试类:
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Collection集合对象
Collection<Student> c = new ArrayList<Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("林青霞", 30);
Student s2 = new Student("张曼玉", 35);
Student s3 = new Student("王祖贤", 33);
//把学生添加到集合
c.add(s1);
c.add(s2);
c.add(s3);
//遍历集合(迭代器方式)
Iterator<Student> it = c.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Student s = it.next();
System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge());
}
}
}























 293
293











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










