1.if语句
测试条件为false,跳过语句块,为true,执行语句块。
int u;
cin>>u;
if (u<10)
{
cout<<"hello\n";
}
cout<<"bad\n";测试条件为false,跳过语句块1,执行语句块2,为true,执行语句块1,跳过语句块2。
char ch;
if (ch=='z'){
zroo++;
cout<<"hello";
}
else
{
cout<<"not\n";
}if语句和if-else语句可嵌套
2.逻辑运算符|| && !
||和&&优先级低于关系运算符,!优先级高于所有关系运算符和算术运算符,&&优先级高于||
(1)逻辑或运算符 ||
C++规定||是个顺序点(sequence point),所以先看左边在看右边。
int x = 5;
int y = 9;
int z = 9;
cout<< (x == z || x == y || y == z);
//结果为1如果任一操作数或两个操作数为 true,则逻辑“或”运算符 (||) 返回布尔值 true;否则返回 false。
操作数不需要具有相同的类型,但它们必须是布尔值、整数或指针类型。 操作数通常为关系或相等表达式。
仅当第一个操作数的计算结果为 false 时计算第二个操作数,因为当逻辑“或”表达式为 true 时不需要计算。 这称作“短路”计算。
(2)逻辑与运算符&&
如果两个操作数都是 true,则逻辑“与”运算符 (&&) 返回 true,否则返回 false。&&也是顺序点,左侧判断为false,右侧不会再判定。
//测试年龄是否在17-35岁之间
if (age>17 && age<35)(3)逻辑非运算符!
如果操作数是 false,则结果是 true;如果操作数是 true,则结果是 false。
if (!(x<5))与字符相关的字符函数库cctype
isalpha(ch)
//如果ch是字母,函数返回非零值,否则返回0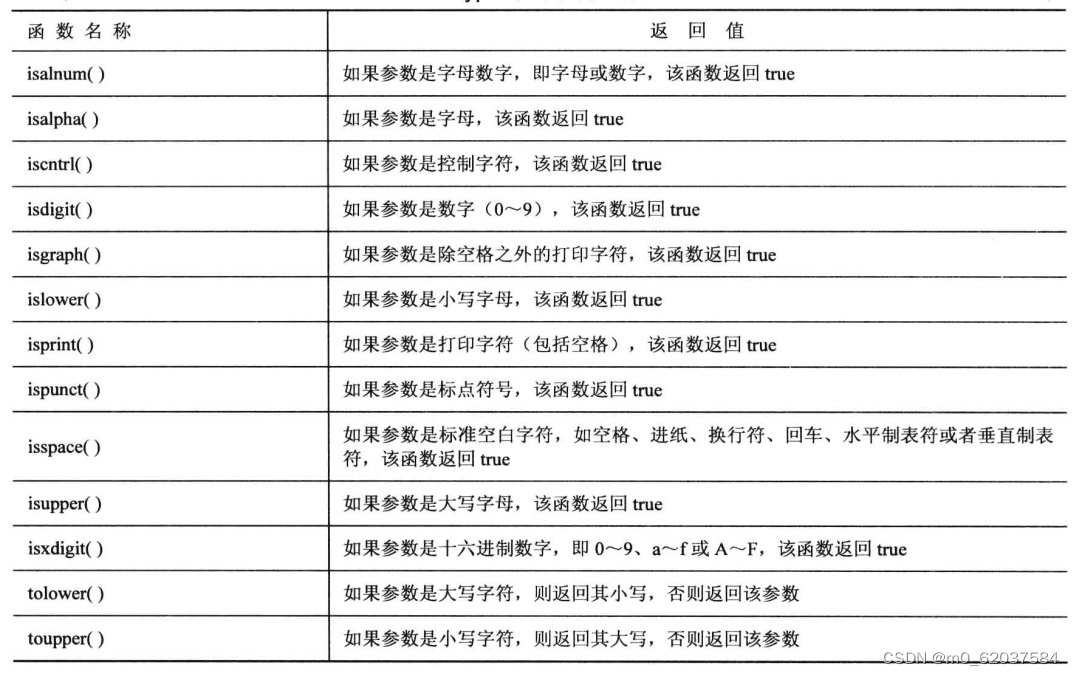
条件运算符?:
唯一一个三个操作数的运算符
-
如果第一个操作数的计算结果为
true(1),则计算第二个操作数。 -
如果第一个操作数的计算结果为
false(0),则计算第三个操作数。
int main() {
int i = 1, j = 2;
cout << ( i > j ? i : j ) << " is greater." << endl;
}
//结果
2 is greater.3.switch语句
如果找到匹配表达式(switch语句使程序跳到括号里面值的那一行),则可以继续执行 case 标签,没有任何匹配直接跳到 default 标签。如果啥也没直接执行switch语句后面的语句。
break语句用于停止执行并将控制转移到 switch 语句之后的语句。 如果没有 break 语句,将执行从匹配的 case 标签到 switch 语句末尾之间的每个语句,包括 default。
char c;
while ( c = *buffer++ )
{
switch ( c )
{
case 'A':
uppercase_A++;
break;
case 'a':
lowercase_a++;
break;
default:
other++;
}
}括号里只能是整数值表达式
case标签都是整数常量表达式,常见有int、char、枚举常量
通常, cin无法识别枚举类型,所以switch语句将int值与枚举量进行比较时,会把枚举量提升为int,while也是。
break语句使程序跳到循环后面的语句执行
continue语句使程序跳过当前循环之后的循环体,执行下一轮循环
4.文件的输入输出
程序将输入视为一系列字节,每个字节都被解释为字符编码。
源代码文件属于文本文件
文本文件输出注意:
- 必须包含头文件fstream
- 头文件fstream定义了一个用于处理输出的ofstream类
- 需声明一个或多个ofstream变量(它没有明确定义,像ostream类中明确定义cout输出)
- 必须指明名称空间std
- 将ofstream对象与文件关联起来的方法之一,使用open()方法
- 使用完文件后,应使用方法close()关闭
- 可结合使用ofstream对象和运算符<<来输出各种类型数据
注意,声明一个ofstream对象并将其同文件关联后,可以像使用cout一样使用它。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char automobile[50];
int year;
double a_price;
double d_price;
ofstream outFile;
outFile.open("carinfo.txt");
//文本没有创建的情况下,运行时,程序会自动创建
//如果打开已有文件接受输出时,默认长度截短为零,原来内容丢失
cout << "Enter the make and model of automobile:";
cin.getline(automobile,50);
cout << "Enter the modle year:";
cin >> year;
cout << "Enter the original asking price: ";
cin >> a_price;
d_price = 0.913 * a_price;
cout << fixed; //设置标记
cout.precision(2); //小数点后两位
cout.setf(ios_base::showpoint);
cout << "Make and model: " << automobile << endl;
cout << "year:" << year << endl;
cout << "was asking$" << a_price << endl;
cout << "Now asking $" << d_price << endl;
outFile << fixed;
outFile.precision(2);
outFile.setf(ios_base::showpoint);
outFile << "Make and model: " << automobile << endl;
//程序的变量等数据流到outFile,在流入文件
outFile << "year:" << year << endl;
outFile << "was asking$" << a_price << endl;
outFile << "Now asking $" << d_price << endl;
outFile.close(); //关闭文件
}
//结果
Enter the make and model of automobile:wenro
Enter the modle year:1986
Enter the original asking price: 12450
Make and model: wenro
year:1986
was asking$12450.00
Now asking $11366.85
文件输入注意:
- 必须包含头文件fstream
- 头文件fstream定义了一个用于处理输入的ifstream类
- 需声明一个或多个ifstream变量(它没有明确定义,像ostream类中明确定义cout输出)
- 必须指明名称空间std
- 将ifstream对象与文件关联起来的方法之一,使用open()方法
- 使用完文件后,应使用方法close()关闭
- 可结合使用ifstream对象和运算符>>来读取各种类型数据
- 可以结合使用ifstream对象和eof()、fail()等方法来判断输入是否成功
- ifstream对象本身被用作测试条件时,如果最后一个读取操作成功,它将会转换为布尔值true,否则转换为false
const int SIZE = 60;
using namespace std;
char filename[SIZE];
ifstream inFile;
cout << "Enter name of data file: ";
//将用户提供的文件名存储到字符数组中
cin.getline(filename,SIZE);
//如果打开一个不存在的文件,会导致ifstream对象进入输入失败,
//所以先判断文件是否成功打开,成功,is_open()返回true
//exit函数在头文件cstdlib中定义,终止程序
inFile.open(filename);
if (!inFile.is_open()) {
cout << "Could not open the file " << filename << endl;
cout << "Program terminating.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
double value;
double sum = 0.0;
int count = 0;
inFile >> value;
//good方法在没有发生任何错误时返回true,指出最后一次读取输入操作是否成功
while (inFile.good()) {
++count;
sum += value;
inFile >> value;
}
//判断循环为何终止
if (inFile.eof()) //eof只能判断是否到达EOF
cout << "End of file reached.\n";
else if (inFile.fail())
//fail用于检查EOF和类型不匹配,如果返回true说明循环终止原因是类型不匹配
cout << "Input terminated by data mismatch.\n";
else
cout << "Input terminated for unknown reason.\n";
if (count == 0)
cout << "No data processed.\n";
else {
cout << "Items read:" << count << endl;
cout << "Sum:" << sum << endl;
cout << "Average:" << sum / count << endl;
}
inFile.close();





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








