public @interface RepeatablesTest {
String value() default “哈哈哈”;
}
例子
==
我们简单的介绍了注解的常用的5个注解元,解下来我们通过例子来实现注解。
代码如下,根据上面的提示我们进行测试。
在看例子之前我们先来了解一下常用的几个方法。
-
Class.getAnnotations() 获取所有的注解,包括自己声明的以及继承的
-
Class.getAnnotation(Class< A > annotationClass) 获取指定的注解,该注解可以是自己声明的,也可以是继承的
-
Class.getDeclaredAnnotations() 获取自己声明的注解
-
Class.getDeclaredField(String name); //获取该类的声明字段
-
Class.getDeclaredMethods();//返回的是一个Method[]数组
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AnnotationTest {
String name() default “小明”; //表示默认为小明。
}
@AnnotationTest() //在该类添加注解
public class TestAnnotationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean hasAnnotation = TestAnnotationMain.class.isAnnotationPresent(AnnotationTest.class);
if (hasAnnotation) {
AnnotationTest annotation = TestAnnotationMain.class.getAnnotation(AnnotationTest.class);
System.out.println(annotation.name());
}
}
}
打印输出结果:
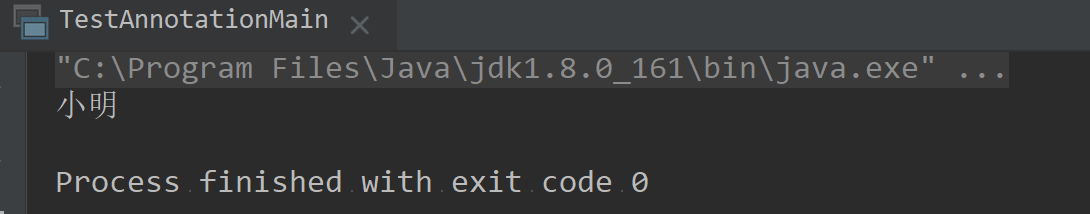
如果我们想更改name的值可以这么弄
@AnnotationTest(name = “小刚”)
public class TestAnnotationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean hasAnnotation = TestAnnotationMain.class.isAnnotationPresent(AnnotationTest.class);
if (hasAnnotation) {
AnnotationTest annotation = TestAnnotationMain.class.getAnnotation(AnnotationTest.class);
System.out.println(annotation.name());
}
}
}

如果我们想给一个类的属性进行赋值可以这么做
1.创建一个注解如下
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AnnotationTest1 {
String value(); //value来定义
}
2.引用该主解
public class Test {
@AnnotationTest1(value = “小云”) //引用注解进行赋值
public String name;
}
3.测试
public class TestAnnotation1Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Field name = Test.class.getDeclaredField(“name”);//该该类的字段
name.setAccessible(true);
AnnotationTest1 annotationTest1 = name.getAnnotation(AnnotationTest1.class);//获取该字段的注解
if (annotationTest1
《一线大厂Java面试题解析+后端开发学习笔记+最新架构讲解视频+实战项目源码讲义》
【docs.qq.com/doc/DSmxTbFJ1cmN1R2dB】 完整内容开源分享
!= null) {
System.out.println(annotationTest1.value()); //输出值
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
获取方法上的注解类 如AnnotationTest2
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface AnnotationTest2 {
//todo无任何方法或者属性
}
public class Test {
@AnnotationTest1(value = “小云”)
public String name;
@AnnotationTest2 //目的获取该AnnotationTest2
public void fun() {
System.out.println(“方法执行”);
}
}
获取
public class TestAnnotation1Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Field name = Test.class.getDeclaredField(“name”); //获取该类的声明字段
name.setAccessible(true);
AnnotationTest1 annotationTest1 = name.getAnnotation(AnnotationTest1.class);//获取该字段的注解
if (annotationTest1 != null) {
System.out.println(annotationTest1.value()); //输出值
}
Method fun = Test.class.getDeclaredMethod(“fun”);
if (fun != null) {
Annotation[] annotations = fun.getAnnotations();
for (int i = 0; i < annotations.length; i++) {
System.out.println(annotations[i].annotationType().getSimpleName());
}
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
举例
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
}
public class MyTest { //进行获取注解方法的全部数据
@MyAnnotation
public void mytestLoad() {
System.out.println(“测试加载”);
}
@MyAnnotation
public void mytestRequest() {
System.out.println(“测试请求”);
}
@MyAnnotation
public void mytestProgress() {
System.out.println(“测试进度”);
}
@MyAnnotation
public void mytestError() {
System.out.println(1 );
}
///该方法不执行
public void mytestNoAnno(){
System.out.println(“没有注解的方法”);
}
}
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTest myTest = new MyTest();
Method[] methods = myTest.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
Method method = methods[i];
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)) {
try {
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(myTest, null);//调用该类的注解方法
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(“输出完成!==”);
}
}

下载
==
总结
==
我们在开发中长见的注解如下:
| 常用注解 | 解释 |
| — | — |
| @Override | 方法重写 |
| @SuppressWarnings | 提示警告 |
| @SafeVarargs | 参数安全 |
| @Deprecated | 作用是对不应该再使用的方法添加注解 |
| @FunctionalInterface | 函数式编程,用于Lambda 表达式 |
注解给我们带来了许多方便,但是我们也得知道其优缺点。
- 优点
注解方便我们进行单元测试,有利于进行开发。
代码整洁,通过注解的方式变可知修饰的变量,或者方法。
节省配置,减少配置文件大小。
- 缺点
通过反射进行设置,可能会产生性能上的问题。
若要对配置进行修改需要重新编译,扩展性差。
9)]
下载
==
总结
==
我们在开发中长见的注解如下:
| 常用注解 | 解释 |
| — | — |
| @Override | 方法重写 |
| @SuppressWarnings | 提示警告 |
| @SafeVarargs | 参数安全 |
| @Deprecated | 作用是对不应该再使用的方法添加注解 |
| @FunctionalInterface | 函数式编程,用于Lambda 表达式 |
注解给我们带来了许多方便,但是我们也得知道其优缺点。
- 优点
注解方便我们进行单元测试,有利于进行开发。
代码整洁,通过注解的方式变可知修饰的变量,或者方法。
节省配置,减少配置文件大小。
- 缺点
通过反射进行设置,可能会产生性能上的问题。
若要对配置进行修改需要重新编译,扩展性差。






















 255
255











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








