文章目录
一.Java异常类
异常的概念
- Java异常是Java提供的用于处理程序中错误的一种机制
- 分类:Throwable主要分为Error和Exception。Error和它的子类的实例,代表JVM本身的错误,错误不能被程序员通过代码处理。Excception以及它的子类,代表程序运行时发送的各种不期望发生的事件,可以被Java异常处理机制使用,是异常处理的核心。

异常的处理和捕获
try,catch,finally的用法
- try,catch就是直接捕获。try{}是捕获可能发生的异常,catch后()的异常类型是能捕获的类型,catch{}是具体异常的处理过程。
try{
int i=10/0;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("处理异常");
}
- try,catch,finally增加了finally关键字,finally是有无异常都要继续执行的动作。
try{
int i=10/10;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("处理异常");
} finally{
System.out.println("有无异常都会执行");
}
结果:有无异常都会执行。
try{
int i=10/0;
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("处理异常");
} finally{
System.out.println("有无异常都会执行");
}
结果:处理异常
有无异常都会执行
- 一个try{}块后面可以跟随多个catch块,多个catch块需要按照具体异常的级别由低到高排列
try{
int num[]=new int[2] ;
num[0]=10;
num[1]=20;
int n=num[0]/0;//在这里出现异常
num[2]=n;//该语句不会被执行
}catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("数组下标越界");
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("除数为0");
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("exception异常");
}finally{
System.out.println("有无异常都会执行");
}
结果:除数为0
有无异常都会被执行
- 如果try,catch,finally出现在一个有返回值的方法中,finally中的内容是在本方法的return语句之前运行。
public class Textclass {
public int Text() {
try {
int num[] = new int[2];
num[0] = 10;
int n = num[0] / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("除数为0");
} finally {
System.out.println("有无异常都会执行");
}
return 1;
}
}
public class Testmain {
public static void main(String[] args){
Textclass t=new Textclass();
System.out.println(t.Text());
}
}
结果:除数为0
有无异常都会执行
1
throw和throws关键字的用法
- throws:
格式:访问限制修饰符+返回值类型+方法名称+()+throws+具体类型异常{}
提示:当我们无法判断具体异常类型的时候使用Exception或Throwable代替
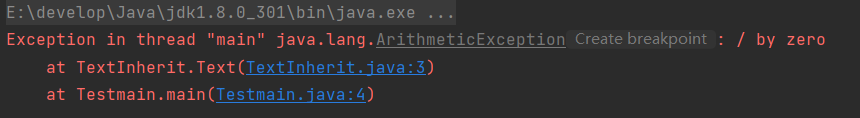
public class TextInherit {
public int Text() throws Exception {
int num=10/0;
return num;
}
}
public class Testmain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TextInherit t=new TextInherit();
System.out.println(t.Text());
}
}
结果:
- throw:
自定义异常,编写一个新类,继承Exception/Throwable,在构造方法中访问父类的构造方法。
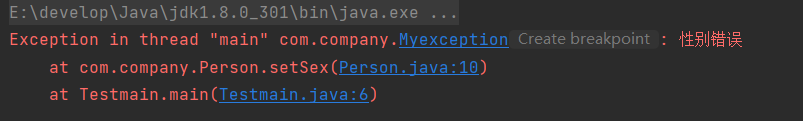
package com.company;
public class Myexception extends Exception{
public Myexception(String s){
super(s);
}
}
package com.company;
public class Person {
private char sex;
public void setSex(char sex1) throws Myexception{
if(sex1=='f'||sex1=='m'){
sex=sex1;
}
else{
throw new Myexception("性别错误");
}
}
public char getSex(){
return sex;
}
}
import com.company.Person;
public class Testmain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Person p=new Person();
p.setSex('a');
System.out.println(p.getSex());
}
}
结果:
二.Java常用类
String类
创建方式
1.赋值常量:
String str1 = “Bluemsun”;
String str2 = “Bluemsun”;
String str3 = “Bluem”+“sun”;
String str 4 = “Bluem”;
String str5 = str4 +”sun“;
System.out.println(str1==str2); //输出trueSystem.out.println(str1==str3); //输出true
System.out.println(str1.equals(str5)); //输出ture
System.out.println(str1 ==str5);//输出false
分析:如果加号两边出现了变量,那么内存将在堆区创建对象导致不相等,而字符串的连接依旧是在常量池中进行查找。equals方法比较的是字符串序列内容。
2.使用new创建对象
String str1 = new String(“Bluemsun”);
注:使用new都会在堆中创建新的对象
String常用方法
- int length() 获取字符串长度
- int indexof() 获得子字符串出现的位置
- int indexOf(String s)
在字符串中查找子字符第一次出现的位置,没找到返回-1 - int lastIndexOf(String s) 指定了开始查找的位置
- String substring(int start,int end)
String substring(int start) 截取字符串 - String replace(String oldStr,String newStr) 替换
- boolean equals(String s) 是否完全相同
boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String s) 忽略大小写进行比较
boolean startsWith(String s) 判断字符串是否以某字符串开头
boolean endsWith(String s) 判断字符串是否以某字符串结尾
int compareTo(String s)
比较大小,返回正数(大于)、负数(小于)、0(相等) - String toUpperCase() 大写
String toLowerCase() 小写
StringBuilder类
String与StringBuilder的区别
String的字符串是不可修改,如果修改会创建新字符串,浪费内存。
StringBuilder的字符串是可以修改的,不会创建新字符串。
创建方式
创建空值的对象
StringBuilder strb = new StringBuilder();
创建有默认值的对象
StringBuilder strb = new StringBuilder("abc);
StringBuilder常用方法
- String toString() 转为String
- StringBuilder append(String str) 追加
- StringBuilder replace(int start,int end,String newS) 替换
- StringBuilder insert(int offset,String s) 插入
- StringBuilder delete(int start,int end) 删除
- StringBuilder reverse() 反转
Date类
创建方式
1.Date date = new Date(); 获得当前的时间
2.Date date = new Date(long); 指定时间的1900-1-1到现在的毫秒数
常用方法
- int getYear() 获得年
- int getMonth() 获得月
- int getDate() 获得天
- int getHours() 获得小时
- int getMinutes() 获得分钟
- int getSeconds() 获得分钟
- void setYear(int year) 设置年
…
Calendar类
创建方式
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
常用方法
- get(日期类型) 获得日期的某个部分
- Calendar.YEAR
- Calendar.MONTH 月份从0开始
- set(日期类型,数值) 设置日期的某个部分
- add(日期类型,数值) 实现日期某个部分的追溯
Math类
常用方法
- Math.abs(int a) 求绝对值
- Math.round(double f) 四舍五入取整
- Math.max(int a,int b) 求最大值
- Math.min(int a,int b) 求最小值
- Math.random() --> 0 ~ 1之间任意小数 随机数
- Math.sqrt(int a) 求平方根
- Math.pow(int x,int y) 求幂,x的y次方
Random类
生成随机数
Random random = new Random();
random.nextInt(100); //0 ~ 100间随机整数
Runtime类
系统运行时,获得和系统有关的信息
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
常用方法
- freeMemory() 获得系统空闲内存数
- totalMemory() 获得总内存数
- availableProcessors() 获得处理器个数
- gc() 调用垃圾收集器
- exec(String cmd) 调用系统程序
- exit(int status) 退出系统
总结
怎么说,我感觉要掌握的东西真滴很多,第二周有点点焦头烂额,还有容器那一块的知识还没开始学(等过两天再来写吧…),然后不过对上一节的内容掌握会好很多了现在。这一节的话我觉得异常那方面真的要处理错误的话还是需要更多联系,尤其是throw和throws这两个关键字的应用,然后常用类的话主要还是在记忆这方面吧…总而言之 继续加油吧…ovo





















 673
673











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








