六、在WEB中应⽤MyBatis(使⽤MVC架构模式)
6.1 需求描述
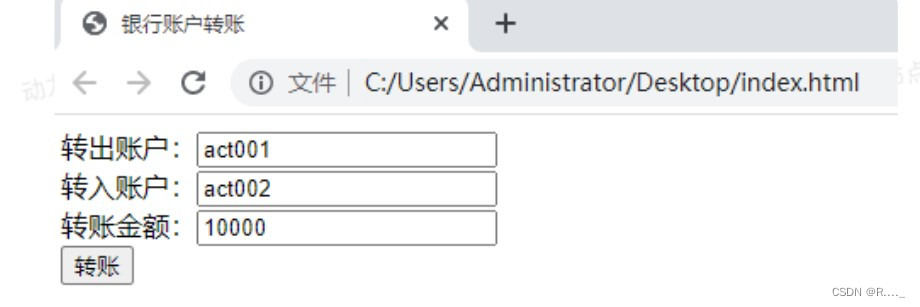
6.2 数据库表的设计和准备数据

6.3 实现步骤

● IDEA配置Tomcat,这⾥Tomcat使⽤10+版本。并部署应⽤到tomcat。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee
http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0"
metadata-complete="false">
</web-app><dependencies>
<dependency>
<!-- mybatis依赖 -->
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql驱动依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!-- logback依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.11</version>
</dependency>
<!-- servlet依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
第⼆步:前端⻚⾯index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>银行账户转账</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/bank/transfer" method="post">
转出账号:<input type="text" name="fromActno"><br>
转入账号:<input type="text" name="toActno"><br>
转账金额:<input type="text" name="money"><br>
<input type="submit" value="转账">
</form>
</body>
</html>//封装数据类
public class Account {
private Long id;
private String actno;
private Double balance;
public Account(){
}
public Account(Long id, String actno, Double balance) {
this.id = id;
this.actno = actno;
this.balance = balance;
}
//后面是get,set,toString方法,太长了
}//账户的DAO对象,负责t_act表中数据CRUD
//强调以下:DAO对象中任何一个方法和业务不挂钩,没有任何业务逻辑在里面
//DAO中的方法就是做CRUD的,所以方法名大部分是:insertXXX deleteXXX updateXXX selectXXX
public interface AccountDao {
//MVC 三层架构就是分层,职能分工,层与层之间用接口衔接,降低耦合度
//根据账号查询账户信息
Account selectByactno(String actno);
//更新账户信息,act被更新的账户对象,return 1表示更新成功,其他值表示失败
int updateByActno(Account act);
}public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Override
public Account selectByactno(String actno) {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
Account account =(Account) sqlSession.selectOne("account.selectByActno", actno);
return account;
}
@Override
public int updateByActno(Account act) {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
int count = sqlSession.update("account.updateByActno", act);
return count;
}
}<mapper namespace="account">
<select id="selectByActno" resultType="com.powernode.bank.bean.Account">
select * from t_act where actno==#{actno}
</select>
<update id="updateByActno">
update t_act set balance=#{balance} where actno=#{actno}
</update>
</mapper>//账户业务类,业务类当中的业务方法的名字在起名的时候,最好见名知意,能够体现出具体的业务是做什么的
public interface AccountService {
//账户转账业务
void transfer(String fromActno,String toActno,double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, TransferException;
}
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDaoImpl();
@Override
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, TransferException {
//添加事物控制代码
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
//1.判断转出账户的余额是否充足(select)
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByactno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
//2.如果转出账户余额不足,提示用户
throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不足");
}
//3.如果转出账户余额充足,更新转出账户余额(update)
//先更新内存中java对象account的余额
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByactno(toActno);
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance()-money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance()+money);
int count = accountDao.updateByActno(fromAct);
//模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
//4.更新转入账户余额(update)
count+=accountDao.updateByActno((toAct));
if(count!=2){
throw new TransferException("转账异常,未知原因");
}
sqlSession.commit();
SqlSessionUtil.close(sqlSession);
}
}
第七步:编写AccountController
@WebServlet("/transfer")
public class AccountServlet extends HttpServlet {
//为了让对象在其他方法中也可以用,声明为实例变量
private AccountService accountService = new AccountServiceImpl();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取表单数据
String fromActno = request.getParameter("fromActno");
String toActno = request.getParameter("toActno");
//将字符串转成Double
double money = Double.parseDouble(request.getParameter("money"));
try {
//调用service的转账方法完成转账,(调用业务层)
accountService.transfer(fromActno,toActno,money);
//程序能够走到这里,表示转账一定成功了
//调用View完成展示结果
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/souccess.html");
} catch (MoneyNotEnoughException e) {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/error1.html");
} catch (TransferException e) {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/error2.html");
} catch (Exception e){
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/error2.html");
}
//调用View完成展示成果
}
}

6.4 MyBatis对象作⽤域以及事务问题
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
这个类可以被实例化、使⽤和丢弃,⼀旦创建了 SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了。 因此SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 实例的最佳作⽤域是⽅法作⽤域(也就是局部⽅法变量)。 你可以重⽤SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 来创建多个 SqlSessionFactory 实例,但最好还是不要⼀直保留着它,以保证所有的 XML 解析资源可以被释放给更重要的事情。
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 你的应⽤逻辑代码
}//MyBatis工具类
public class SqlSessionUtil {
//工具类的构造方法一般都是私有化的
// 工具类中所有的方法都是静态的,直接采用类名即可调用。不需要new对象。
// 为了防止new对象,构造方法私有化。
private SqlSessionUtil() {
}
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// 类加载时执行
// SqlSessionUtil工具类在进行第一次加载的时候,解析mybatis-config.xml文件。创建SqlSessionFactory对象。
// SqlSessionFactory对象:一个SqlSessionFactory对应一个environment,一个environment通常是一个数据库。
//所以写在静态代码块中,在类加载时就执行
static {
try {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//全局的,服务器级别的,一个服务器当中第一一个即可
//为什么把SqlSession对象放到ThreadLocal当中呢?为了保证一个线程对应一个SqlSession
private static ThreadLocal<SqlSession> local = new ThreadLocal<>();
//获取会话对象
public static SqlSession openSession() {
SqlSession sqlSession = local.get();
if (sqlSession == null) {
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//将sqlSession对象绑定到当前线程上
local.set(sqlSession);
}
return sqlSession;
}
//关闭SqlSession对象,进行一个解绑,从当前线程中移除SqlSession对象
public static void close(SqlSession sqlSession){
if(sqlSession!=null){
sqlSession.close();
//注意移除SqlSessiion对象和当前线程的绑定关系
//因为Tomcat服务器支持线程池,也就是说,用过的线程对象t1,可能下一次还会使用这个t1线程,所以要把他移除掉
local.remove();
}
}
}6.5 分析当前程序存在的问题
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Override
public Account selectByactno(String actno) {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
Account account =(Account) sqlSession.selectOne("account.selectByActno", actno);
return account;
}
@Override
public int updateByActno(Account act) {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
int count = sqlSession.update("account.updateByActno", act);
return count;
}
}七、使⽤javassist⽣成类
7.1 Javassist的使⽤
我们要使⽤javassist,⾸先要引⼊它的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.javassist</groupId>
<artifactId>javassist</artifactId>
<version>3.29.1-GA</version>
</dependency>样例代码:
public class JavassistTest {
@Test
public void testGenerateAccountDaoImpl() throws Exception{
// 获取类池
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 制造类
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.powernode.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl");
// 制造接口
CtClass ctInterface = pool.makeInterface("com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDao");
// 实现接口
ctClass.addInterface(ctInterface);
// 实现接口中所有的方法
// 获取接口中所有的方法
Method[] methods = AccountDao.class.getDeclaredMethods();
Arrays.stream(methods).forEach(method -> {
// method是接口中的抽象方法
// 把method抽象方法给实现了。
try {
// public void delete(){}
// public int update(String actno, Double balance){}
StringBuilder methodCode = new StringBuilder();
methodCode.append("public "); // 追加修饰符列表
methodCode.append(method.getReturnType().getName()); // 追加返回值类型
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append(method.getName()); //追加方法名
methodCode.append("(");
// 拼接参数 String actno, Double balance
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
methodCode.append(parameterType.getName());
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append("arg" + i);
if(i != parameterTypes.length - 1){
methodCode.append(",");
}
}
methodCode.append("){System.out.println(11111); ");
// 动态的添加return语句
String returnTypeSimpleName = method.getReturnType().getSimpleName();
if ("void".equals(returnTypeSimpleName)) {
}else if("int".equals(returnTypeSimpleName)){
methodCode.append("return 1;");
}else if("String".equals(returnTypeSimpleName)){
methodCode.append("return \"hello\";");
}
methodCode.append("}");
System.out.println(methodCode);
CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make(methodCode.toString(), ctClass);
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 在内存中生成class,并且加载到JVM当中
Class<?> clazz = ctClass.toClass();
// 创建对象
AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) clazz.newInstance();
// 调用方法
accountDao.insert("aaaaa");
accountDao.delete();
accountDao.update("aaaa", 1000.0);
accountDao.selectByActno("aaaa");
}
@Test
public void testGenerateImpl() throws Exception{
//获取类池
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
//制造类
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.powernode.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl");
//制造接口
CtClass ctInterface = pool.makeInterface("com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDao");
//添加接口到类
ctClass.addInterface(ctInterface); //AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao
//实现接口中的方法
//制造方法
CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make("public void delete(){System.out.println(\"删除\");}", ctClass);
//将方法添加到类中
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
//在内存中生成类
Class clazz = ctClass.toClass();
AccountDao accountDao =(AccountDao) clazz.newInstance();
accountDao.delete();
}
@Test
public void testGenerateFirstClass() throws Exception {
//获取类池,这个类池就是用来给我们生成class的
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
//制造类(需要告诉javassist,类名是啥)
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass("com.powernode.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl");
//制造方法
String methodCode = "public void insert(){System.out.println(123);}";
CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make(methodCode, ctClass);
//将方法添加到类中
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
//在内存中生成class
ctClass.toClass();
//类加载到JVM当中,返回AccountDaoImpl类的字节码
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.powernode.bank.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl");
//创建对象
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
//获取AccountDaoImpl中的insert方法
Method insertMethod = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("insert");
//调用方法insert
insertMethod.invoke(obj);
}
}
7.2 使⽤Javassist⽣成DaoImpl类
/**
* 工具类:可以动态的生成DAO的实现类。(或者说可以动态生成DAO的代理类)
* 注意注意注意注意注意!!!!!!:
* 凡是使用GenerateDaoProxy的,SQLMapper.xml映射文件中namespace必须是dao接口的全名,id必须是dao接口中的方法名。
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @since 1.0
*/
public class GenerateDaoProxy { // GenerateDaoProxy是mybatis框架的开发者写的。
/**
* 生成dao接口实现类,并且将实现类的对象创建出来并返回。
* @param daoInterface dao接口
* @return dao接口实现类的实例化对象。
*/
public static Object generate(SqlSession sqlSession, Class daoInterface){
// 类池
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
// 制造类(com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDao --> com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDaoProxy)
CtClass ctClass = pool.makeClass(daoInterface.getName() + "Proxy"); // 实际本质上就是在内存中动态生成一个代理类。
// 制造接口
CtClass ctInterface = pool.makeInterface(daoInterface.getName());
// 实现接口
ctClass.addInterface(ctInterface);
// 实现接口中所有的方法
Method[] methods = daoInterface.getDeclaredMethods();
Arrays.stream(methods).forEach(method -> {
// method是接口中的抽象方法
// 将method这个抽象方法进行实现
try {
// Account selectByActno(String actno);
// public Account selectByActno(String actno){ 代码; }
StringBuilder methodCode = new StringBuilder();
methodCode.append("public ");
methodCode.append(method.getReturnType().getName());
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append(method.getName());
methodCode.append("(");
// 需要方法的形式参数列表
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
methodCode.append(parameterType.getName());
methodCode.append(" ");
methodCode.append("arg" + i);
if(i != parameterTypes.length - 1){
methodCode.append(",");
}
}
methodCode.append(")");
methodCode.append("{");
// 需要方法体当中的代码
methodCode.append("org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession sqlSession = com.powernode.bank.utils.SqlSessionUtil.openSession();");
// 需要知道是什么类型的sql语句
// sql语句的id是框架使用者提供的,具有多变性。对于我框架的开发人员来说。我不知道。
// 既然我框架开发者不知道sqlId,怎么办呢?mybatis框架的开发者于是就出台了一个规定:凡是使用GenerateDaoProxy机制的。
// sqlId都不能随便写。namespace必须是dao接口的全限定名称。id必须是dao接口中方法名。
String sqlId = daoInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(sqlId).getSqlCommandType();
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.INSERT) {
}
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.DELETE) {
}
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.UPDATE) {
methodCode.append("return sqlSession.update(\""+sqlId+"\", arg0);");
}
if (sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT) {
String returnType = method.getReturnType().getName();
methodCode.append("return ("+returnType+")sqlSession.selectOne(\""+sqlId+"\", arg0);");
}
methodCode.append("}");
CtMethod ctMethod = CtMethod.make(methodCode.toString(), ctClass);
ctClass.addMethod(ctMethod);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 创建对象
Object obj = null;
try {
Class<?> clazz = ctClass.toClass();
obj = clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
}
<!--sqlMapper.xml文件的编写者,提供者是谁?使用你mybatis框架的java程序员负责提供的。-->
<!--要想使用这种机制:namespace必须是dao接口的全限定名称。-->
<mapper namespace="com.powernode.bank.dao.AccountDao">
<select id="selectByactno" resultType="com.powernode.bank.bean.Account">
select * from t_act where actno=#{actno}
</select>
<update id="updateByActno">
update t_act set balance=#{balance} where actno=#{actno}
</update>
</mapper>八、 MyBatis中接⼝代理机制及使⽤
AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao)sqlSession.getMapper(AccountDao.class); 1//MyBatis工具类
public class SqlSessionUtil {
//工具类的构造方法一般都是私有化的
// 工具类中所有的方法都是静态的,直接采用类名即可调用。不需要new对象。
// 为了防止new对象,构造方法私有化。
private SqlSessionUtil() {
}
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// 类加载时执行
// SqlSessionUtil工具类在进行第一次加载的时候,解析mybatis-config.xml文件。创建SqlSessionFactory对象。
// SqlSessionFactory对象:一个SqlSessionFactory对应一个environment,一个environment通常是一个数据库。
//所以写在静态代码块中,在类加载时就执行
static {
try {
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//全局的,服务器级别的,一个服务器当中第一一个即可
//为什么把SqlSession对象放到ThreadLocal当中呢?为了保证一个线程对应一个SqlSession
private static ThreadLocal<SqlSession> local = new ThreadLocal<>();
//获取会话对象
public static SqlSession openSession() {
SqlSession sqlSession = local.get();
if (sqlSession == null) {
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//将sqlSession对象绑定到当前线程上
local.set(sqlSession);
}
return sqlSession;
}
//关闭SqlSession对象,进行一个解绑,从当前线程中移除SqlSession对象
public static void close(SqlSession sqlSession){
if(sqlSession!=null){
sqlSession.close();
//注意移除SqlSessiion对象和当前线程的绑定关系
//因为Tomcat服务器支持线程池,也就是说,用过的线程对象t1,可能下一次还会使用这个t1线程,所以要把他移除掉
local.remove();
}
}
}public class Car {
// 数据库表当中的字段应该和pojo类的属性一一对应。
// 建议使用包装类,这样可以防止null的问题。
private Long id;
private String carNum;
private String brand;
private Double guidePrice;
private String produceTime;
private String carType;
public Car(){}
public Car(Long id, String carNum, String brand, Double guidePrice, String produceTime, String carType) {
this.id = id;
this.carNum = carNum;
this.brand = brand;
this.guidePrice = guidePrice;
this.produceTime = produceTime;
this.carType = carType;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCarNum() {
return carNum;
}
public void setCarNum(String carNum) {
this.carNum = carNum;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public Double getGuidePrice() {
return guidePrice;
}
public void setGuidePrice(Double guidePrice) {
this.guidePrice = guidePrice;
}
public String getProduceTime() {
return produceTime;
}
public void setProduceTime(String produceTime) {
this.produceTime = produceTime;
}
public String getCarType() {
return carType;
}
public void setCarType(String carType) {
this.carType = carType;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"id=" + id +
", carNum='" + carNum + '\'' +
", brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", guidePrice=" + guidePrice +
", produceTime='" + produceTime + '\'' +
", carType='" + carType + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
CarMapper接口:
public interface CarMapper {
//新增
int insert(Car car);
//根据id删除Car
int deleteById(Long id);
//修改汽车信息
int update(Car car);
//根据id查询汽车信息
Car selectById(Long is);
//获取所有的汽车信息
List<Car> selectAll();
}CarMapperTEst类:
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testInsert(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
//面向接口获取接口的代理对象
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = new Car(null, "4646", "布加迪威龙", 50.0, "2023-6-7", "新能源");
int count = mapper.insert(car);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
}
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
int count = mapper.deleteById(29L);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
}
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = new Car(23L, "7878", "mini版", 5.0, "2023-6-7", "新能源");
int count = mapper.update(car);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
}
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = mapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println(car);
}
@Test
public void testSelectAll(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAll();
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
}
}
九、MyBatis⼩技巧
9.1 #{}和${}
//根据car_Type来查汽车信息
List<Car> selectByCarType(String carType);
//查询所有的汽车信息,然后通过asc升序,desc降序
List<Car> selectByAscOrDesc(String ascOrDesc);
//批量删除,根据id
int deleteBatch(String ids);
//根据汽车品牌模糊查询
List<Car> selectByBrandLike(String brand);<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper">
<select id="selectByBrandLike" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car">
select
id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
where
<!--第一种方案 brand like '%${brand}%' -->
<!--第二种方案 brand like concat('%',#{brand},'%')-->
<!--第三种方案 brand like concat('%','${brand}','%') -->
brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</select>
<delete id="deleteBatch">
delete
from t_car
where id in (${ids})
</delete>
<select id="selectByAscOrDesc" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car">
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
order by produce_time ${ascOrDesc}
</select>
<select id="selectByCarType" resultType="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car">
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
where car_type = #{carType}
</select>
</mapper>CarMapperTest类:
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testSelectByBrandLike(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByBrandLike("奔驰");
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testDeleteBatch(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
int count = mapper.deleteBatch("23,28");
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectAllByAscOrDesc(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByAscOrDesc("asc"); //升序 desc降序
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectByCarType(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByCarType("新能源");
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
}执行结果:

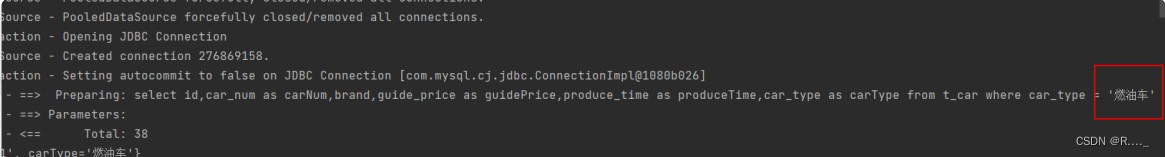
mybatis小技巧 1. #{}和${}的区别 #{}的执行结果: [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = ? [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Parameters: 新能源(String) [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - <== Total: 2 ${}的执行结果: [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = 新能源 [main] DEBUG c.p.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper.selectByCarType - ==> Parameters: org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException: ### Error querying database. Cause: java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column '新能源' in 'where clause' ### The error may exist in CarMapper.xml ### The error may involve defaultParameterMap ### The error occurred while setting parameters ### SQL: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car where car_type = 新能源 ### Cause: java.sql.SQLSyntaxErrorException: Unknown column '新能源' in 'where clause' #{}和${}的区别: #{}: 底层使用PreparedStatement。特点:先进行SQL语句的编译,然后给SQL语句的占位符问号?传值。可以避免SQL注入的风险。 ${}:底层使用Statement。特点:先进行SQL语句的拼接,然后再对SQL语句进行编译。存在SQL注入的风险。 优先使用#{},这是原则。避免SQL注入的风险。 #{}的执行结果: Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car order by produce_time ? Parameters: asc(String) select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car order by produce_time 'asc' ${}的执行结果: Preparing: select id, car_num as carNum, brand, guide_price as guidePrice, produce_time as produceTime, car_type as carType from t_car order by produce_time asc Parameters: 如果需要SQL语句的关键字放到SQL语句中,只能使用${},因为#{}是以值的形式放到SQL语句当中的。 2. 向SQL语句当中拼接表名,就需要使用${} 现实业务当中,可能会存在分表存储数据的情况。因为一张表存的话,数据量太大。查询效率比较低。 可以将这些数据有规律的分表存储,这样在查询的时候效率就比较高。因为扫描的数据量变少了。 日志表:专门存储日志信息的。如果t_log只有一张表,这张表中每一天都会产生很多log,慢慢的,这个表中数据会很多。 怎么解决问题? 可以每天生成一个新表。每张表以当天日期作为名称,例如: t_log_20220901 t_log_20220902 .... 你想知道某一天的日志信息怎么办? 假设今天是20220901,那么直接查:t_log_20220901的表即可。 3.批量删除:一次删除多条记录。 批量删除的SQL语句有两种写法: 第一种or:delete from t_car where id=1 or id=2 or id=3; 第二种int:delete from t_car where id in(1,2,3); 应该采用${}的方式: delete from t_car where id in(${ids}); 4.模糊查询:like 需求:根据汽车品牌进行模糊查询 select * from t_car where brand like '%奔驰%'; select * from t_car where brand like '%比亚迪%'; 第一种方案: '%${brand}%' 第二种方案:concat函数,这个是mysql数据库当中的一个函数,专门进行字符串拼接 concat('%',#{brand},'%') 第三种方案:比较鸡肋了。可以不算。 concat('%','${brand}','%') 第四种方案: "%"#{brand}"%"
9.2 typeAliases
<!-- 起别名-->
<typeAliases>
<!-- type:指定给那个类型起别名
alias:指定别名
注意:别名不区分大小写
alias属性是可以省略的,有默认的别名
-->
<!-- <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car" alias="aaa"/>-->
<!-- <typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log" alias="bbb"/>-->
<!-- 省略alias之后,别名就是类的简名,比如:com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car 的别名就是Car/car/caR....不区分大小写-->
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"/>
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log"/>
</typeAliases>CarMapper.xml:
<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper">
<select id="selectByBrandLike" resultType="CAr">
select
id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
where
<!--第一种方案 brand like '%${brand}%' -->
<!--第二种方案 brand like concat('%',#{brand},'%')-->
<!--第三种方案 brand like concat('%','${brand}','%') -->
brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</select>
<delete id="deleteBatch">
delete
from t_car
where id in (${ids})
</delete>
<select id="selectByAscOrDesc" resultType="car">
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
order by produce_time ${ascOrDesc}
</select>
<select id="selectByCarType" resultType="caR">
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
where car_type = #{carType}
</select>
</mapper><typeAliases>
<package name="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
5. 关于MyBatis中别名机制:
<typeAliases>
<!--别名自己指定的-->
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car" alias="aaa"/>
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log" alias="bbb"/>
<!--采用默认的别名机制-->
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Car"/>
<typeAlias type="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Log"/>
<!--包下所有的类自动起别名。使用简名作为别名。-->
<package name="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
所有别名不区分大小写。
namespace不能使用别名机制。
9.3 mappers
<mappers>
<!-- 加载前面编写的SQL语句的文件 -->
<mapper resource="CarMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="LogMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>url
这种⽅式显然使⽤了绝对路径的⽅式,这种配置对SQL映射⽂件存放的位置没有要求,随意。
<mappers>
<mapper url="file:///d:/CarMapper.xml"/> 要求在d:/下有CarMapper.xml文件
</mappers><mappers>
<mapper class="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper"/>
<mapper class="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.LogMapper"/>
</mappers>
package
<!-- 将包内的映射器接⼝实现全部注册为映射器 -->
<!--这种方式在开发中是使用的-->
<!--前提是:XML文件必须和接口放在一起,并且名字一致-->
<mappers>
<package name="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>9.4 idea配置⽂件模板
9.5 插⼊数据时获取⾃动⽣成的主键
//插入Car信息,并且使用生成的主键值
int insertCarUseGeneratedKeys(Car car);CarMapper.xml文件:
<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper">
<!--
useGeneratedKeys="true" 使用自动生成的主键值
keyProperty="id" 指定主键值赋值给对象的哪个属性,这个就表示将主键值赋值给Car 的id 属性
-->
<insert id="insertCarUseGeneratedKeys" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into t_car values (null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})
</insert>
</mapper>CarMapperTest类:
@Test
public void testInsertCarUseGeneratedKeys(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = new Car(null, "9991", "大众", 30.0, "2023-08-01", "燃油车");
mapper.insertCarUseGeneratedKeys(car);
System.out.println(car); //Car{id=31, carNum='9991', brand='大众', guidePrice=30.0, produceTime='2023-08-01', carType='燃油车'}
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}⼗、MyBatis参数处理
模块名:mybatis-007-param
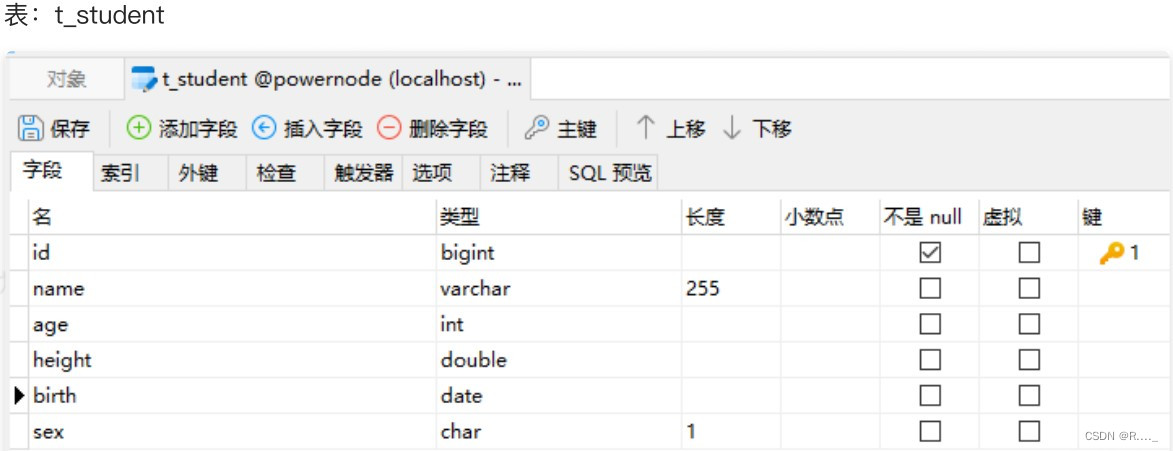

先搭建好mybatis所需的环境,以及pojo类:
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
private Date birth;
private Character sex;
public Student(){}
public Student(Long id, String name, Integer age, Double height, Date birth, Character sex) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
this.birth = birth;
this.sex = sex;
}
后面get,set,toString方法10.1 单个简单类型参数
public interface StudentMapper {
//通过Pojo参数保存学生信息,Student是单个参数,但是参数的类型不是简单类型
int insertStudentByPojo(Student student);
//通过Map参数保存学生信息,以下是单个参数,但是参数的类型不是简单类型,是Map集合
int insertStudentByMap(Map<String, Object> map);
//当接口中的方法的参数只有一个(单个参数),并且参数的数据类习惯都是简单类型
//根据id查询、name查询、birth查询、sex查询
List<Student> selectById(Long id);
List<Student> selectByName(String name);
List<Student> selectByBirth(Date birth);
List<Student> selectBySex(Character sex);
}<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<insert id="insertStudentByPojo">
insert into t_student(id,name,age,sex,birth,height) values (null,#{name},#{age},#{sex},#{birth},#{height})
</insert>
<insert id="insertStudentByMap">
insert into t_student(id,name,sex,age,birth,height) values(null,#{姓名},#{性别},#{年龄},#{生日},#{身高})
</insert>
<!-- parameterType属性的作用:
告诉mybatis框架,我这个方法的参数类型是什么类型。
mybatis框架自身带有类型自动推断机制,所以大部分情况下parameterType属性都是可以省略不写的。
SQL语句最终是这样的:
select * from t_student where id = ?
JDBC代码是一定要给?传值的。
怎么传值?ps.setXxx(第几个问号, 传什么值);
ps.setLong(1, 1L);
ps.setString(1, "zhangsan");
ps.setDate(1, new Date());
ps.setInt(1, 100);
...
mybatis底层到底调用setXxx的哪个方法,取决于parameterType属性的值。
注意:mybatis框架实际上内置了很多别名。可以参考开发手册。-->
<select id="selectById" resultType="student" parameterType="_Long">
select * from t_student where id=#{id}
</select>
<select id="selectByName" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where name=#{name,javaType=String,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</select>
<select id="selectByBirth" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where birth=#{birth}
</select>
<select id="selectBySex" resultType="student">
select * from t_student where sex=#{sex}
</select>
</mapper>public class StudentMapperTest {
@Test
public void testInsertStudentByPojo(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = new Student(null, "猪猪侠", 24, 1.81, new Date(), '男');
mapper.insertStudentByPojo(student);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testInsertStudentByMap(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("姓名","王五");
map.put("年龄",20);
map.put("身高",1.71);
map.put("生日",new Date());
map.put("性别",'女');
mapper.insertStudentByMap(map);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectById(1L);
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectByName(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByName("李四");
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectByBirth() throws ParseException {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date birth = sdf.parse("1999-10-11");
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByBirth(birth);
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectBySex(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Character sex = Character.valueOf('男');
List<Student> students = mapper.selectBySex(sex);
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
sqlSession.close();
}
}10.2 多参数
/*
* Param注解。
* mybatis框架底层的实现原理:
* map.put("name", name);
* map.put("sex", sex);
**/
//使用Param注解
List<Student> selectByNameAndSex2(@Param("name")String name,@Param("sex") Character sex);
/*
* 这是多参数。
* 根据name和sex查询Student信息。
* 如果是多个参数的话,mybatis框架底层是怎么做的呢?
* mybatis框架会自动创建一个Map集合。并且Map集合是以这种方式存储参数的:
* map.put("arg0", name);
* map.put("arg1", sex);
* map.put("param1", name);
* map.put("param2", sex);
*
*/
//这是多参数,需求:通过name和sex查询
List<Student> selectByNameAndSex(String name, Character sex);<!--使用了@Param注解就用注解里的,但是arg0,arg1不能使用了,但param1,param2还可以使用-->
<select id="selectByNameAndSex2" resultType="student">
<!--select * from t_student where name = #{param1} and sex = #{param2}-->
select * from t_student where name=#{name} and sex=#{sex}
</select>
<select id="selectByNameAndSex" resultType="student">
<!--select * from t_student where name=#{arg0} and sex=#{arg1}-->
<!--select * from t_student where name = #{param1} and sex = #{param2}-->
select * from t_student where name=#{param1} and sex=#{param2}
</select> @Test
public void testSelectByNameAndSex2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameAndSex2("猪猪侠", '男');
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectByNameAndSex(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameAndSex("李四", '女');
students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
sqlSession.close();
}10.3 @Param源码分析
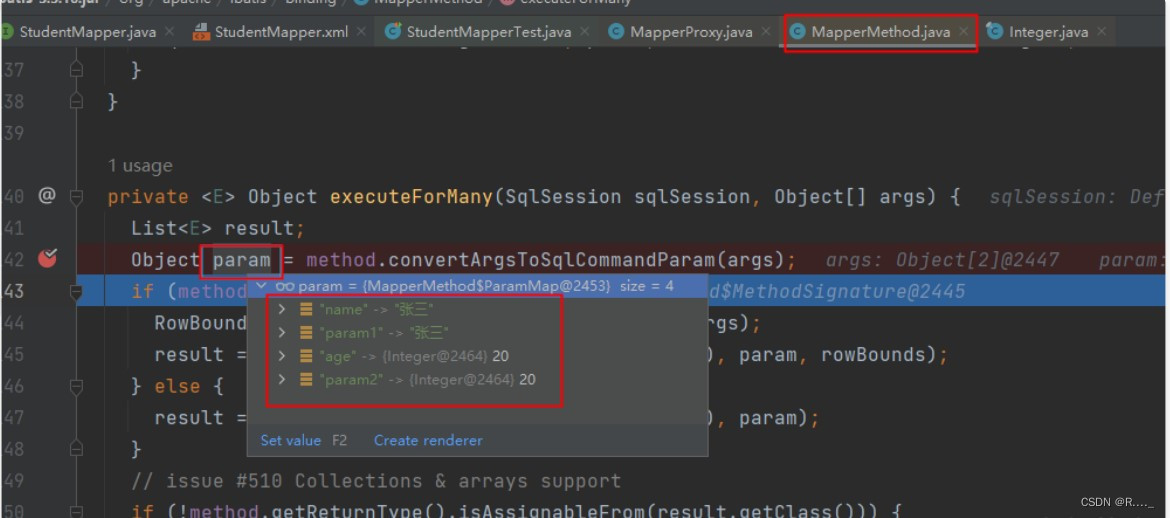

⼗⼀、MyBatis查询语句专题
11.1 返回Car,返回List<Car> ,返回Map ,返回List<Map>
CarMapper接口:
public interface CarMapper {
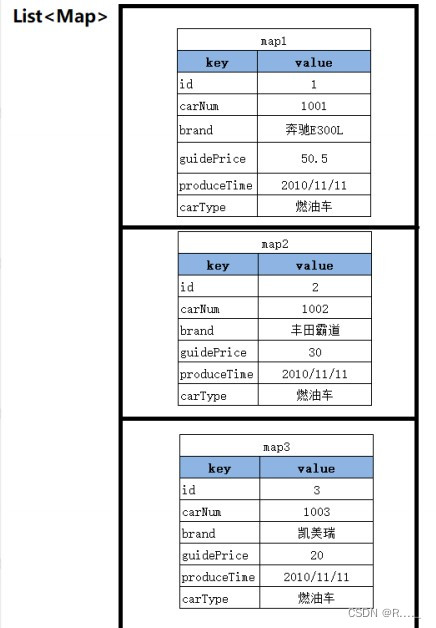
//查询所有car信息,返回一个存放Map集合的List集合
List<Map<String,Object>> selectAllRetListMap();
/*
* 根据id获取汽车信息。将汽车信息放到Map集合中。
* +-----+---------+----------+-------------+--------------+----------+
* | id | car_num | brand | guide_price | produce_time | car_type |
* +-----+---------+----------+-------------+--------------+----------+
* | 158 | 1111 | 比亚迪汉 | 3.00 | 2000-10-10 | 新能源 |
* +-----+---------+----------+-------------+--------------+----------+
*
* Map<String, Object>
* k v
* -----------------------
* "id" 158
* "car_num" 1111
* "brand" 比亚迪汉
* ....*/
//使用Map集合接收
Map<String,Object> selectByIdRetMap(Long id);
//根据brand查询car
Car selectByBrand(String brand);
//根据id获取信息
Car selectById(Long id);
//获取所有的car
List<Car> selectAll();
}CarMapper.xml:
<select id="selectAllRetListMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_car
</select>
<select id="selectByIdRetMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_car where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="selectByBrand" resultType="car">
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
where
brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</select>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="car">
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
</select>
<select id="selectById" resultType="car">
select id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
from t_car
where id = #{id}
</select>CarMapperTest类:
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testSelectAllRetListMap() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Map<String,Object>> cars = mapper.selectAllRetListMap();
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectByIdRetMap() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> car =mapper.selectByIdRetMap(6L);
System.out.println(car);
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectByBrand() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
//TooManyResultsException
//当想查询一条记录,实际查询出多条记录,但是只用了Car接收,就会TooManyResultsException
Car car = mapper.selectByBrand("比亚迪");
System.out.println(car);
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectAll() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAll();
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testSelectById() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = mapper.selectById(18L);
System.out.println(car);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
11.2 返回Map<String,Map>

CarMapper接口:
//查询所有的car 返回一个大Map集合
//Map集合的key是每条记录的主键值
//Map集合的value是每条记录
/*
* {
* 32={car_num=7777, id=32, guide_price=50.90, produce_time=2023-8-2, brand=比亚迪汉, car_type=电车},
* 1={car_num=1001, id=1, guide_price=10.00, produce_time=2020-10-11, brand=宝马520, car_type=燃油车},
* 2={car_num=1002, id=2, guide_price=55.00, produce_time=2020-11-11, brand=奔驰E300L, car_type=新能源},
* 18={car_num=1006, id=18, guide_price=40.00, produce_time=2022-03-14, brand=劳斯莱斯, car_type=新能源},
* 19={car_num=1111, id=19, guide_price=10.00, produce_time=2020-11-11, brand=比亚迪唐, car_type=电车},
* 4={car_num=8888, id=4, guide_price=15.00, produce_time=2023-1-1, brand=凯美瑞, car_type=新能源},
* 5={car_num=1003, id=5, guide_price=40.00, produce_time=2022-03-14, brand=丰田霸道, car_type=燃油车},
* 21={car_num=3333, id=21, guide_price=18.00, produce_time=2020-11-1, brand=奇瑞, car_type=油车},
* 6={car_num=1003, id=6, guide_price=40.00, produce_time=2022-03-14, brand=凯迪拉克, car_type=新能源},
* 24={car_num=8888, id=24, guide_price=30.00, produce_time=2023-4-12, brand=沃尔沃, car_type=燃油车},
* 30={car_num=9991, id=30, guide_price=30.00, produce_time=2023-08-01, brand=大众, car_type=燃油车},
* 31={car_num=9991, id=31, guide_price=30.00, produce_time=2023-08-01, brand=大众, car_type=燃油车}
* }*/
@MapKey("id")//将查询结果的id指作为整个大Map集合的key
Map<Long,Map<String,Object>> selectAllRetMap();CarMapper.xml:
<select id="selectAllRetMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_car
</select>CarMapperTest类:
@Test
public void testSelectAllRetMap(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Map<Long,Map<String,Object>> cars = mapper.selectAllRetMap();
System.out.println(cars);
sqlSession.close();
}11.3 resultMap结果映射
//查询所有的Car信息,使用resultMap标签进行结果映射
List<Car> selectAllByResultMap(); <!--
1.转门定义一个结果映射,在这个结果映射当中指定数据库表的字段名和Java类的属性名的对应关系
2.type属性:用来指定POJO类的类名
3.id属性,指定resultMap的唯一表示,这个id将来要在select标签中使用
-->
<resultMap id="carResultMap" type="car">
<!--如果数据库表中有主键,一般都是有主键,要不然不符合数据库设计第一范式。-->
<!--如果有主键,建议这里配置一个id标签,注意:这不是必须的。但是官方的解释是什么呢?这样的配置可以让mybatis提高效率。-->
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<!--<result property="id" column="id"/>-->
<!--property后面填写POJO类的属性名-->
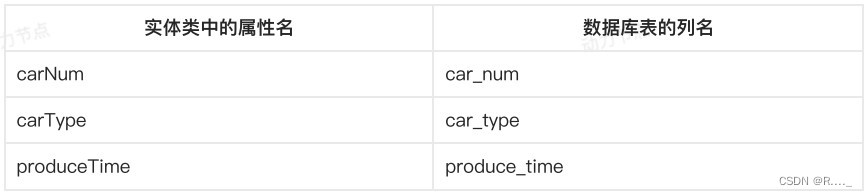
<!--column后面填写数据库表的字段名-->
<result property="carNum" column="car_num" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<!--如果column和property是一样的,这个可以省略。-->
<!--<result property="brand" column="brand"/>-->
<result property="guidePrice" column="guide_price"/>
<result property="produceTime" column="produce_time"/>
<result property="carType" column="car_type" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
</resultMap>
<!--select标签的resultMap属性,用来指定使用哪个结果映射,resultMap后面的值是resultMap的id-->
<select id="selectAllByResultMap" resultMap="carResultMap">
select * from t_car
</select> @Test
public void testSelectAllByResultMap() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> cars = mapper.selectAllByResultMap();
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
如何启⽤该功能,在mybatis-config.xml⽂件中进⾏配置:
<!--mybatis的全局设置-->
<!--开启驼峰命名⾃动映射-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>CarMapper接口:
//使用驼峰命名自动映射
List<Car> selectMapUnderscoreToCamelCase();CarMapper.xml:
<select id="selectMapUnderscoreToCamelCase" resultType="car">
select * from t_car
</select>CarMapperTest类:
@Test
public void testSelectMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
List<Car> cars=mapper.selectMapUnderscoreToCamelCase();
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}11.4 返回总记录条数
//获取Car的总记录条数
Long selectTotal(); <select id="selectTotal" resultType="long">
select count(*) from t_car
</select> @Test
public void testSelectTotal(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Long total=mapper.selectTotal();
System.out.println("总记录条数:"+total); //总记录条数:12
sqlSession.close();
}⼗⼆、动态SQL

delete from t_car where id in(1,2,3,4,5,6,......这⾥的值是动态的,根据⽤户选择的
id不同,值是不同的);●多条件查询
select * from t_car where brand like '丰⽥%' and guide_price > 30 and .....;12.1 if标签
public interface CarMapper {
//多条件查询
List<Car> selectByMultiCondition(@Param("brand") String brand,
@Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice,
@Param("carType") String carType);
}<mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper">
<select id="selectByMultiCondition" resultType="car">
select * from t_car where 1=1
<!--
1. if标签中test属性是必须的
2. if标签中test属性值是false或者true
3. 如果test是true,则if标签中的sql语句就会拼接。反之,则不会拼接
4. test当中可以使用是:
当使用了@Param注解,那么test中要出现的是@Param注解指定的参数名,@Param("brand),那么这里只能使用brand或param1
当没有使用@Param,那么test中要出现的是:param1,param2....arg0,arg1.....
当使用了POJO,那么test中出现的是POJO类的属性名
5. 在mybatis的动态SQL当中,不能使用&&,只能使用and
-->
<if test="brand!=null and brand!=''">
and brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</if>
<if test="guidePrice!=null and guidePrice!=''">
and guide_price>#{guidePrice}
</if>
<if test="carType!=null and carType!=''">
and car_type = #{carType}
</if>
</select>
</mapper>public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testSelectByMultiCondition(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
//假设三个条件都不是空
// List<Car> cars= mapper.selectByMultiCondition("比亚迪",2.0,"电车");
//假设三个条件都为空
//List<Car> cars= mapper.selectByMultiCondition("",null,""); //定义了where 1=1 可以把所有查出来
//假设第一个条件为空,后面两个不为空
//List<Car> cars= mapper.selectByMultiCondition("",2.0,"电车");
//假设第一个条件不是空,后面两个为空
List<Car> cars= mapper.selectByMultiCondition("比亚迪",null,"");
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
}12.2 where标签
//使用where标签,让where子句更加的智能,多条件查询
List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithWhere(@Param("brand") String brand,
@Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice,
@Param("carType") String carType); <select id="selectByMultiConditionWithWhere" resultType="car">
select * from t_car
<!--where标签是专门负责where子句动态生成的。-->
<where>
<if test="brand!=null and brand!=''">
and brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</if>
<if test="guidePrice!=null and guidePrice!=''">
and guide_price>#{guidePrice}
</if>
<if test="carType!=null and carType!=''">
and car_type=#{carType}
</if>
</where>
</select> @Test
public void testSelectByMultiConditionWithWhere(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
//假设三个条件都不是空
//List<Car> cars =mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("比亚迪",2.0,"电车");
//假设三个条件都为空
//List<Car> cars =mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("",null,"");//使用了where表签 都不满足,自动全部打印
//假设第一个条件为空,后面两个不为空
List<Car> cars =mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithWhere("",2.9,"电车");//会自动将前面的and去掉
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}12.3 trim标签
//使用Trim标签多条件查询
List<Car> selectByMultiConditionWithTrim(@Param("brand") String brand,
@Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice,
@Param("carType") String carType); <select id="selectByMultiConditionWithTrim" resultType="car">
select * from t_car
<!--
prefix:加前缀
suffix:加后缀
prefixOverrides:删除前缀
suffixOverrides:删除后缀
-->
<!--prefix="where" 是在trim标签所有内容的前面添加 where-->
<!--suffixOverrides="and|or" 把trim标签中内容的后缀and或or去掉-->
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and">
<if test="brand!=null and brand!=''">
brand like "%"#{brand}"%" and
</if>
<if test="guidePrice!=null and guidePrice!=''">
guide_price>#{guidePrice} and
</if>
<if test="carType!=null and carType!=''">
car_type=#{carType}
</if>
</trim>
</select> @Test
public void testSelectByMultiConditionWithTrim(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
//假设三个条件都不是空
//List<Car> cars =mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("比亚迪",2.0,"电车");
//假设第一个条件不是空,后面两个为空
//suffixOverrides="and" 会把后面不满足的and去掉
//List<Car> cars= mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("比亚迪",null,"");
//假设三个条件都为空
// Preparing: select * from t_car 没有在前面加where
//List<Car> cars =mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("",null,"");
//假设第一个条件为空,后面两个不为空
//Preparing: select * from t_car where guide_price>? and car_type=? 即加了where,也把第一不满足后面的and删了
List<Car> cars =mapper.selectByMultiConditionWithTrim("",2.9,"电车");
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}12.4 set标签
//使用Set标签
int updateBySet(Car car);
//正常的update语句
int updateById(Car car); <update id="updateBySet">
update t_car
<set>
<if test="carNum!= null and carNum!=''">car_num=#{carNum},</if>
<if test="brand!= null and brand!=''">brand=#{brand},</if>
<if test="guidePrice!= null and guidePrice!=''">guide_price=#{guide_price},</if>
<if test="produceTime!= null and produceTime!=''">produce_time=#{produceTime},</if>
<if test="carType!= null and carType!=''">car_type=#{carType},</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
<update id="updateById">
update t_car set
car_num=#{carNum},
brand=#{brand},
guide_price=#{guidePrice},
produce_time=#{produceTime},
car_type=#{carType}
where
id=#{id}
</update> @Test
public void testUpdateBySet(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
//Preparing: update t_car SET brand=?, car_type=? where id=? 只有这两个改了,其他的没改
Car car = new Car(31L,null,"别克",null,null,"燃油车");
mapper.updateBySet(car);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void testUpdateById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
//这样会直接将原来不为空的字段改成空的字段,这不是我们所希望的
Car car = new Car(31L,null,"别克",null,null,"燃油车");
mapper.updateById(car);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}12.5 choose when otherwise
< choose >< when ></ when >< when ></ when >< when ></ when >< otherwise ></ otherwise ></ choose >
if (){} else if (){} else if (){} else if (){} else {}
//使用choose when otherwise
List<Car> selectByChoose(@Param("brand") String brand,
@Param("guidePrice") Double guidePrice,
@Param("produceTime") String produceTime); <select id="selectByChoose" resultType="car">
select * from t_car
<where>
<choose>
<when test="brand!=null and brand!=''">
brand like "%"#{brand}"%"
</when>
<when test="guidePrice!=null and guidePrice!=''">
guide_price=#{guidePrice}
</when>
<otherwise>produce_time=#{produceTime}</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select> @Test
public void testSelectByChoose(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
//三个条件都不为空
//Preparing: select * from t_car WHERE brand=?
//List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose("宝",17.7,"2023-05-11");
//第一个条件为空
//Preparing: select * from t_car WHERE guide_price=?
//List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose(null,30.0,"2023-05-11");
//前两个为空
//Preparing: select * from t_car WHERE produce_time=?
//List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose(null,null,"2023-05-11");
//都为空
//Preparing: select * from t_car WHERE produce_time=?
//Parameters: null 还是会走produce_time 只是将null传给了它
List<Car> cars = mapper.selectByChoose(null,null,null);
cars.forEach(car -> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}12.6 foreach标签
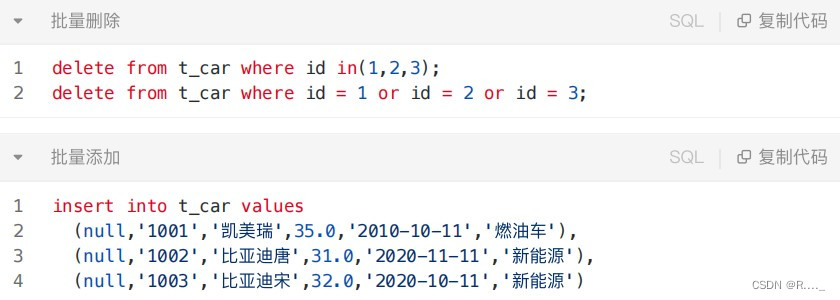
批量删除
●⽤in来删除
//批量删除,使用in关键字+foreach标签
int deleteByIds(@Param("ids") Long[] ids); <delete id="deleteByIds">
<!--
foreach标签的属性:
collection:指定数组或者集合
item:代表数组或集合中的元素,自己定义,上面定义什么下面的#{和上面写一样}就写什么
separator:循环之间的分隔符
open: foreach循环拼接的所有sql语句的最前面以什么开始。
close: foreach循环拼接的所有sql语句的最后面以什么结束。
collection="ids" 第一次写这个的时候报错了,错误信息是:[array, arg0]
什么意思?
map.put("array", 数组);
map.put("arg0", 数组);
-->
<!--delete from t_car where id in(
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
)-->
delete from t_car where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete> @Test
public void testDeleteByIds(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Long[] ids ={33L,34L,35L};
int count = mapper.deleteByIds(ids);
//Preparing: delete from t_car where id in( ? , ? , ? )
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}●⽤or来删除
//根据id批量删除,使用or关键字+foreach标签
int deleteByIds2(@Param("ids") Long[] ids); <delete id="deleteByIds2">
delete from t_car where
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="or">
id=#{id}
</foreach>
</delete> @Test
public void testDeleteByIds2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Long[] ids = {39L,40L,41L,42L};
int count = mapper.deleteByIds2(ids);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
} //批量插入,一次插入多条Car信息
int insertBatch(@Param("cars") List<Car> cars); <insert id="insertBatch">
insert into t_car values
<foreach collection="cars" item="car" separator="," >
(null,#{car.carNum},#{car.brand},#{car.guidePrice},#{car.produceTime},#{car.carType})
</foreach>
</insert> @Test
public void testInsertBatch(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car1 = new Car(null, "3456","兰博基尼", 100.0, "2023-01-01", "新能源");
Car car2 = new Car(null, "9456","特斯拉", 35.0, "2023-06-01", "电车");
Car car3 = new Car(null, "0456","本田", 25.0, "2023-04-01", "燃油车");
List<Car> cars = new ArrayList<>();
cars.add(car1);
cars.add(car2);
cars.add(car3);
//Preparing: insert into t_car values (null,?,?,?,?,?) , (null,?,?,?,?,?) , (null,?,?,?,?,?)
mapper.insertBatch(cars);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}12.7 sql标签与include标签
<sql id="carCols">
id,
car_num as carNum,
brand,
guide_price as guidePrice,
produce_time as produceTime,
car_type as carType
</sql>
<select id="selectAllRetMap" resultType="map">
select <include refid="carCols"/> from t_car
</select>
<select id="selectAllRetListMap" resultType="map">
select <include refid="carCols"/> carType from t_car
</select>
<select id="selectByIdRetMap" resultType="map">
select <include refid="carCols"/> from t_car where id = #{id}
</select>





















 773
773











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








