那下面我会带着大家来一起了解一下Nginx的强大的功能!
一、Nginx 简介
Nginx 同 Apache 一样都是一种 Web 服务器。基于 REST 架构风格,它是由 C 语言写的,以统一资源描述符 URI 或者 统一资源定位符 URL 作为沟通依据,通过 HTTP 协议提供各种网络服务。
Nginx是一款高性能轻量级的 Web 服务器、反向代理、负载均衡服务器,配置SSL证书、防盗链、解决跨域问题、缓存、限流、动静资源分离等等。由于它的内存占用少,启动极快,高并发能力强,在互联网项目中广泛应用。
下面为 Nginx 的官网: https://nginx.org/en/
接下来带着你们做一个最简单的网页进行访问!
1.1 环境要求
操作系统为:Linux CentOS 7、关闭SELinux和防火墙。(不关闭防火墙会导致无法访问)
这里我们配置了新的网络源
curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
yum clean all
yum makecache1.2 搭建一个最简单的网站

这里通过 yum list nginx 查看 nginx 版本为 1.20.1
我们直接通过 YUM 命令去安装 Nginx
yum -y install nginx安装完成后,通过下面命令可以直接启动!
systemctl start nginx这里虚拟机的 ip 为 172.16.2.29,我们直接通过网页访问 Nginx
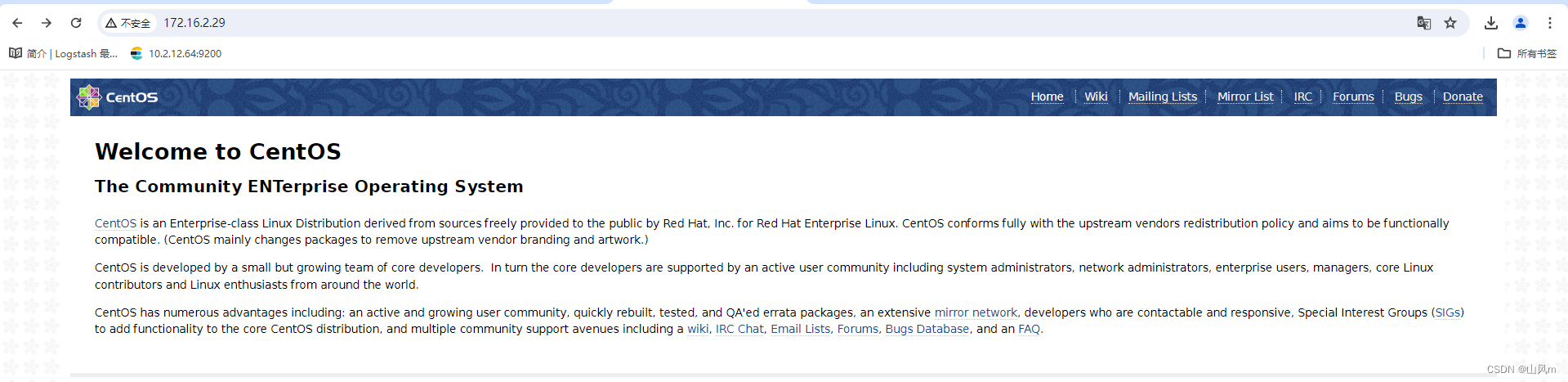
成功访问!这里我们再次修改添加一点内容!
cd /usr/share/nginx/html # 这里为nginx默认的网页主路径
rm -rf ./*
echo "Hello, world" > index.html当我们再次刷新网页时,网页发生了变化。
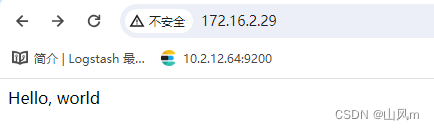

二、Nginx 配置
刚刚我们用的是yum的方式去安装的 Nginx,这种方法更适合第一次接触 Nginx 的小白使用,但是通过 yum 安装的 nginx ,配置文件非常混乱,在很多目录下都有 nginx 的文件,在 /run 目录下有 pid 文件,在 /var下有 log 日志,在 /etc 目录下有配置文件,不利于我们学习!而且通过 yum安装的nginx 版本比较老,我们下面使用源码的方式去安装 Nginx
Nginx 官网下载页面:https://nginx.org/en/download.html
2.1 Nginx 下载和解压--1.27版本
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.27.0.tar.gz
tar -zxvf nginx-1.27.0.tar.gz2.2 Nginx 源码安装
yum -y install gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel
useradd -r -s /sbin/nologin nginx # 创建一个nginx系统用户
cd nginx-1.27.0
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --with-http_ssl_module
make && make install安装完成后,如果无法确定是否为正常安装,通过命令 echo $? 来判断结果是否为 0。
2.3 Nginx 配置文件
Nginx 配置文件下有四个目录: 分别为 conf、html、logs、sbin。作用分别是 配置文件相关、网页主路径、日志相关以及和命令相关。
Nginx 配置文件详解
/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
Nginx 配置文件
-------
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
这里我用图片的方式给大家讲解一下,因为 CSDN 的代码模式真滴很不好用!

user nginx; # 这里取消注释,改为nginx,这是在我们之前安装时创建的一个系统用户nginx
worker_processes 1; # 这里要根据实际环境修改
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
pid logs/nginx.pid; # 取消注释,添加pid进程号文件
events {
worker_connections 1024; # nginx的默认最大连接数
}pid 文件的作用就是存放了启动 nginx 的进程号
我们可以通过 kill $(cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid) 的方式去关闭和杀死 nginx 进程
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on; # 启用了sendfile机制,用于在文件传输时提高性能
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65; # keep-alive 连接的超时时间
#gzip on; # nginx的gzip压缩功能,网页的加载速度和用户体验
server {
listen 80; # 监听端口
server_name localhost; # 域名
#charset koi8-r; #设置Nginx服务器的字符集,默认为 utf-8
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
下面的配置我会根据一些不同的功能来介绍各个配置三、Nginx 的使用
下面我会给大家介绍如何一步一步的使用nginx!

1.启动nginx
# 我们通过源码安装nginx,在目录/usr/local/nginx,启动命令就是nginx目录下的sbin/nginx
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx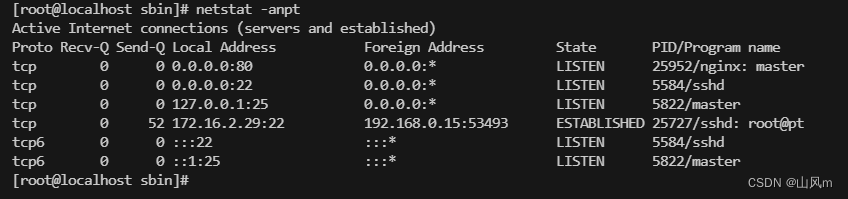
通过 netstat 命令查看, 80 端口已经监听
我们通过网页访问一下,查看是否可以正常访问
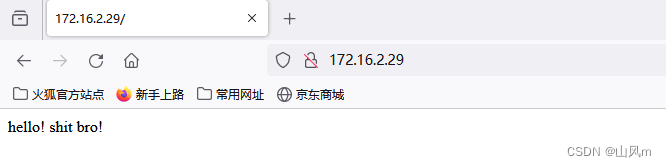
那么如何关闭nginx呢?
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop我们还可以通过软连接的方式来更简单的开启和关闭nginx
ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/bin这样我们可以直接执行 nginx 这条命令来去执行,非常的方便简捷
这里我们还可以使用 system 命令去管理 nginx,在yum中有添加好的 systemctl,而源码安装则需要我们自己去手动添加 system命令管理,这里我为大家已经准备好了,复制粘贴即可!
cat>/usr/local/nginx/nginx.service<<EOF
[Unit]
Description=nginx web server
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
ExecQuit=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOFln -s /usr/local/nginx/nginx.service /lib/systemd/system/
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl status nginx2.nginx 运行用户和监听端口
来到 /usr/local/nginx/conf 目录下查看

看到这里大家会有个疑惑,为什么有.default 的文件,实际上这是官方给我们预留的默认配置模板。以防修改后找不到原版的配置文件。
这里我们修改 /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
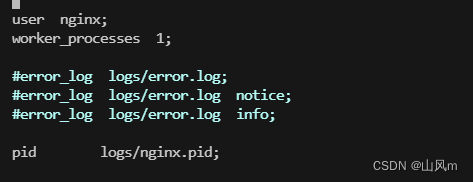
修改 user 的用户 为 nginx ,保存文件后重启 nginx 服务。
systemctl restart nginx.service
ps -aux | grep nginx
这里的 worker 进程的执行用户为 nginx ,并不是整个nginx的执行用户都是 nginx。
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
...
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
...
server {
listen 80; # 监听端口
...一般默认用到的WEB端监听端口都是 80 或者 443,80 为 http 协议,而 443 为 https 协议。
这里我们修改了 nginx 的监听端口为 8000,重启了nginx。
再次访问时,发现无法打开网页。这是因为客户端的网页浏览器,默认监听的是80端口,所以当端口不是 80 时,需要手动添加才可以正常访问。 如下图 (记住中间的冒号必须是半角的哦)

3.nginx 域名
这里 我们把 localhost 修改为 我们需要的域名,除此之外我们还不能进行访问。因为域名是我们私人的,其他人包括我们自己也无法通过这个域名去访问到这个 IP。
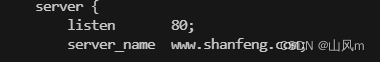
所以需要在 电脑上修改添加 本机的 hosts文件,路径位置在 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts

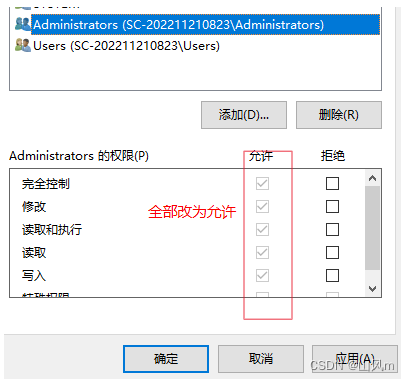
如果遇到无法保存的问题,看下图如何解决
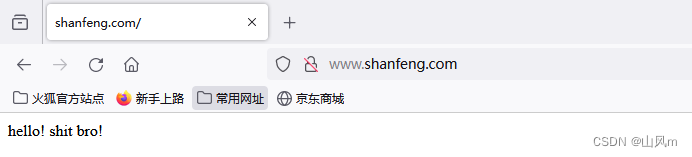 访问成功!
访问成功!






















 687
687











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








