愿你纵踩淤泥,也要心向光明

目录
1.认识String类
说起 String ,想必大家都知道它是字符串类型,这个类型属于引用类型。
在C语言当中有字符串的概念,但是没有字符串这个类型,一般存储都需要用数组或是指针来存储。
但是在Java里面提供了字符串类型, 在Java当中用双引号引起来的都是Sting类型的对象,一般是在堆上存储的。说起类大家也都知道它是用来实例化对象的,String 也是一个类,每次使用String定义变量时,都相当实例化了一个String类型的对象。
2.常用方法
2.1 构造字符串
实例化String类型的对象:
①String 字符串名 = "字符";
②String 字符串名 =new String("字符");
③char[] arr = ('a','b','c');
String 字符串名 = new String(arr);
构造字符串的方式非常多,最常用的也就是以上三种方式
String属于引用类型,内部并不存储字符串本身。所以在栈上存储的是在堆上开辟的空间的地址
实例化String类型对象时,只会创建两个属性:
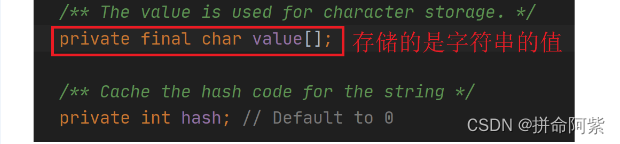
创建的两个属性分别是char类型的数组value还有一个是int类型的hash。value数组一般用来存储字符串的,那么我们现在就明白了字符串实际上是用数组存储的。且这个数组是被final修饰也就说明它不能改变指向,还被private修饰也就说明不能修改值。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
String str2 = "def";
String str3 = str1;
}
}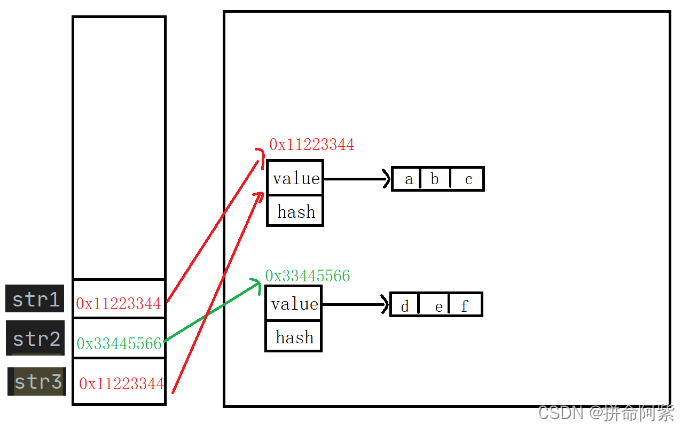
“abc” 是 String 类型的对象,所以它在堆中开辟了一块空间, str1 = "abc",str1 在栈中存储的是“abc” 对象的地址。“def” 是 String 类型的对象,所以它在堆中开辟了一块空间, str2 = "def",str2在栈中存储的是“def”对象的地址。str3 = str1,也就是把 str1 在栈中存的地址赋值给了 str3,所以它们两个指向了同一块空间。
注:在Java中" "引起来的是String类型对象
2.2 字符串比较
1.比较两个String对象中的字符串是否相等
说起比较相等,大多数人应该都会想到运算符中的==。==是用来比较变量中的值,如果比较两个String对象用==,只会比较 String 类型变量在栈中存储的地址 ,也就不会比较 String 对象里面的字符串。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("abc");
if(str1 == str2) {
System.out.println("str1 == str2");
} else {
System.out.println("str1 != str2");
}
}
}运行结果:

画图分析:
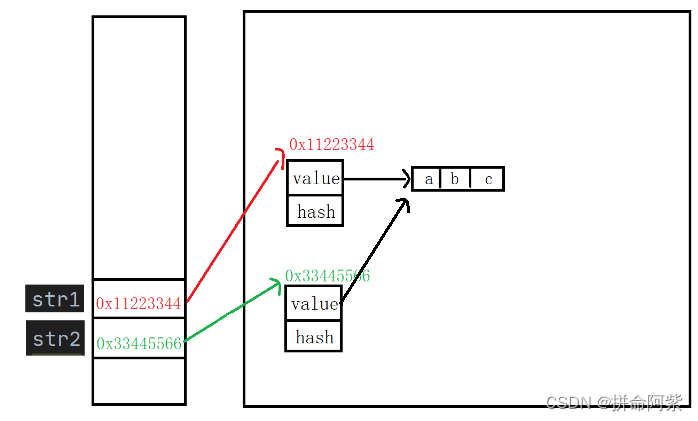
str1 和 str2 里面分别存储的不是同一个 Sting 类实例化的对象,所以str1里面存储的空间地址跟str2里面存储的空间地址不一样。用 == 比较的是str1变量和str2变量中存储的地址,两个不同对象的地址肯定也是不一样的,所以打印的是 str1 != str2
我们现在知道了 == 是比较变量中的值的,如果想要比较对象里面的值,那我们应该用什么方法呢?
字符串名1.equals(字符串名2) : 来判断字符串名1里面存储的字符串是否与字符串名2里面存储的字符串相等,如果相等返回 true,否则返回 false
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("abc");
if(str1.equals(str2)) {
System.out.println("str1 == str2");
} else {
System.out.println("str1 != str2");
}
}
}运行结果:

2.比较两个String对象中的字符串大小关系
字符串名1.compareTo(字符串名2) : 比较两个String对象中的字符串大小关系 。返回值是int类型的,当 返回值 > 0 时,说明 字符串1 > 字符串2;当 返回值 = 0 时,说明 字符串1 = 字符串2; 返回值 < 0 时,说明 字符串1 < 字符串2
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("abd");
int tmp = str1.compareTo(str2);
if(tmp > 0 ) {
System.out.println("str1 > str2");
} else if(tmp == 0) {
System.out.println("str1 == str2");
} else {
System.out.println("str1 < str2");
}
}
}运行结果:

3.忽略大小写比较两个String对象中的字符串大小关系
字符串名1.compareToIgnoreCase(字符串名2) : 比较两个String对象中的字符串大小关系,忽略大小写 。返回值是 int 类型的,当 返回值 > 0 时,说明 字符串1 > 字符串2;当 返回值 = 0 时,说明 字符串1 = 字符串2; 返回值 < 0 时,说明 字符串1 < 字符串2
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Abc");
String str2 = new String("abc");
int tmp = str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2);
if(tmp > 0 ) {
System.out.println("str1 > str2");
} else if(tmp == 0) {
System.out.println("str1 == str2");
} else {
System.out.println("str1 < str2");
}
}
}运行结果:

2.3 字符串查找
1.返回对应下标的字符
字符串名.charAt(下标): 传给 charAt 方法一个 int 类型的数字,将这个数字当做下标,返回对应字符串中的字符
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Abc");
char ch = str1.charAt(1);
System.out.println(ch);
}
}运行结果:

2.返回一个字符在字符串中的位置
①从字符串开头找
字符串名.indexOf('字符'):传给indexOf方法一个字符,返回这个字符第一次出现的位置的下标,没有找到返回-1
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abAbc");
int sum = str1.indexOf('b');
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果

②从指定位置找
字符串名.indexOf('字符',指定字符位置下标):传给 indexOf 方法一个字符,一个数字,将这个数字当做下标,然后从这个位置依次往后查找,找到这个字符,返回这个字符第一次出现的位置的下标,没有找到返回-1
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abAbc");
int sum = str1.indexOf('b',2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果:

3.返回指定字符串在字符串中的位置
①从字符串开头位置找
字符串名.indexOf("字符串") : 在字符串中找指定字符串,找到之后返回指定字符串第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abAbc");
int sum = str1.indexOf("Ab");
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果:

②从指定位置开始查找
字符串名.indexOf("字符串",指定字符位置下标) :传给 indexOf 方法一个字符串,一个数字,将这个数字当做下标,然后从这个位置依次往后查找,找到这个字符串,返回这个字符串第一次出现的位置的下标,没有找到返回-1
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("aAbAbc");
int sum = str1.indexOf("Ab",2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果:

4.从后往前找返回对应下标的字符
①从字符串最后的位置开始依次从后往前查找
字符串名.lastIndexOf('字符'): 从字符串最后的位置开始查找指定的字符,返回第一次找到到的指定字符的位置
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("aAbAbc");
int sum = str1.lastIndexOf('A');
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果:

②从字符串指定的位置开始依次从后往前查找
字符串名.lastIndexOf('字符',指定字符位置下标): 从字符串指定的位置开始查找指定的字符,返回第一次找到的指定字符的位置
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("aAbAbc");
int sum = str1.lastIndexOf('A',2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果:

5. 从后往前查找返回指定字符串在字符串中的位置
①从字符串最后的位置开始查找
字符串名.lastIndexOf("字符串"): 从字符串最后的位置开始依次向前查找指定的字符串,返回第一次找到的指定字符串的位置
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("aAbAbc");
int sum = str1.lastIndexOf("Ab");
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果:

②从字符串指定的位置开始查找
字符串名.lastIndexOf("字符串",指定字符位置下标): 从字符串指定下标的位置开始依次向前查找指定的字符串,返回第一次找到的指定字符串的位置
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("aAbAbc");
int sum = str1.lastIndexOf("Ab",2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}运行结果:

2.4 转化
1.数值和字符串的转换
String.valueOf(数字):将数字转换成字符串
String str1 = String.valueOf(123);Integer.parseInt("字符串"):将一个字符串转换为整型数值
int date1 = Integer.parseInt("123");
int date2 = Integer.valueOf("123");
double date3 = Double.parseDouble("12.3");
double date4 = Double.valueOf("12.3");2.大小写转换
字符串.toUpperCase():将字符串转换为大写
String str = new String("abc");
String str1 = str.toUpperCase();字符串.toLowerCase():将字符串转换为小写
String str = new String("ABC");
String str1 = str.toLowerCase();3.字符串转数组
字符串.toCharArray():将字符串转为数组
String str = new String("abc");
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();new String(数组名):将数组转为字符串,相当于实例化了一个字符类型的对象
char[] arr = {'a','b','c'};
String str = new String(arr);4.格式化
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = String.format("%d-%d-%d",2022,9,26);
System.out.println(str);
}
}运行结果:

2.5 字符串替换
字符串.replaceAll(" ","-"):将字符串中的所有的空格替换为 -
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "I love you";
String str2 = str.replaceAll(" ","-");
System.out.println(str2);
}
}运行结果:

字符串.replaceFirst(" ","-"):将字符串中第一个空格转换为-
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "I love you";
String str2 = str.replaceFirst(" ","-");
System.out.println(str2);
}
}运行结果:

注:由于字符串是不可变对象, 替换不修改当前字符串, 而是产生一个新的字符串
2.6 字符串的拆分
字符串.split(" "):将字符串按照空格分割为若干子字符串
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "I love you";
String[] s = str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
}
}运行结果:

字符串.split(" ",2):将字符串按照空格分割为2个子字符串
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "I love you";
String[] s = str.split(" ",2);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
}
}运行结果:

注意事项:
有些特殊字符作为分割符可能无法正确切分, 需要加上转义
- 字符"|","*","+"都得加上转义字符,前面加上 "\\" .
- 而如果是 "\" ,那么就得写成 "\\\\" .
- 如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符.
多次拆分:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "name=Mike&age=18";
String[] arr = str.split("&");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
String[] tmp = arr[i].split("=");
for (int j = 0; j < tmp.length; j++) {
System.out.println(tmp[j]);
}
}
}
}2.7 字符串截取
字符串.substring(指定位置下标):从指定位置的下标开始截取,一直截取到字符串末尾
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefg";
String str1 = str.substring(2);
System.out.println(str1);
}
}运行结果:

字符串.substring(指定位置下标,指定位置下标):从指定位置的下标开始截取,一直截取到指定位置下标前一个位置,采取前闭后开区间的写法。
str.substring(2,5):包含2下标不包含5下标
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefg";
String str1 = str.substring(2,5);
System.out.println(str1);
}
}运行结果:

























 132
132











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










