1、什么是 JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。易于人阅读和编写。同时也易于机器解析和生成。JSON 采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,而且很多语言都提供了对 json 的支持(包括 C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python 等)。 这样就使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换格式。
json 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。
轻量级:指的是跟 xml 做比较(早期用的是xml)。
数据交换:指的是客户端和服务器之间业务数据的传递格式。
1.1、JSON 在客户端 JavaScript 中的使用。
1.1.1、json 的定义
json 是由键值对组成,并且由花括号(大括号)包围。每个键由引号引起来,键和值之间使用冒号进行分隔, 多组键值对之间进行逗号进行分隔。
注意:value值加不加引号取决于是否为字符串类型。
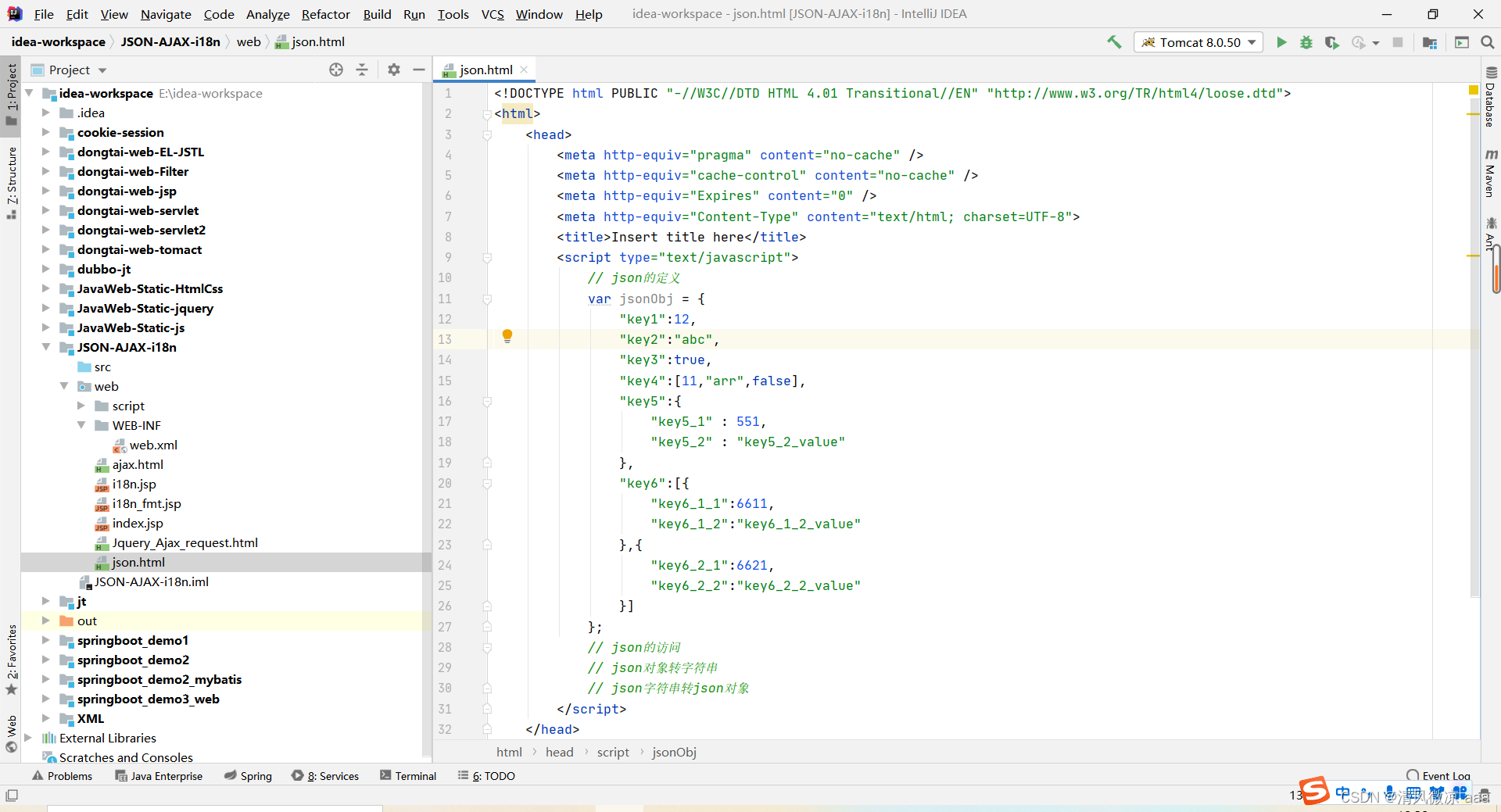
json 定义示例:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 1.json的定义:
//value值可以是:数字,字符串,布尔类型,数组,json对象,json数组等等
var jsonObj = {
"key1":12,
"key2":"abc",
"key3":true,
"key4":[11,"arr",false],
"key5":{
"key5_1" : 551,
"key5_2" : "key5_2_value"
},
"key6":[{
"key6_1_1":6611,
"key6_1_2":"key6_1_2_value"
},{
"key6_2_1":6621,
"key6_2_2":"key6_2_2_value"
}]
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
项目的目录结构:
1.1.2、json 的访问
json 本身是一个对象。
json 中的 key 我们可以理解为是对象中的一个属性。
json 中的 key 访问就跟访问对象的属性一样: json 对象.key
json 访问示例:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 1.json的定义:
//value值可以是:数字,字符串,布尔类型,数组,json对象,json数组等等
var jsonObj = {
"key1":12,
"key2":"abc",
"key3":true,
"key4":[11,"arr",false],
"key5":{
"key5_1" : 551,
"key5_2" : "key5_2_value"
},
"key6":[{
"key6_1_1":6611,
"key6_1_2":"key6_1_2_value"
},{
"key6_2_1":6621,
"key6_2_2":"key6_2_2_value"
}]
};
// 2.json的访问:
alert(typeof(jsonObj));// object json就是一个对象
alert(jsonObj.key1); //12
alert(jsonObj.key2); // abc
alert(jsonObj.key3); // true
alert(jsonObj.key4);// 得到数组[11,"arr",false]
// json 中 数组值的遍历
for(var i = 0; i < jsonObj.key4.length; i++) {
alert(jsonObj.key4[i]);
}
alert(jsonObj.key5.key5_1);//551
alert(jsonObj.key5.key5_2);//key5_2_value 注意在谷歌浏览器中_没有显示出来,显示的是空格
alert( jsonObj.key6 );// 得到json数组
// 取出来每一个元素都是json对象
var jsonItem = jsonObj.key6[0];
alert( jsonItem.key6_1_1 ); //6611
alert( jsonItem.key6_1_2 ); //key6_1_2_value
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
1.1.3、json 的两个常用方法
json 的存在有两种形式:
- 一种是:对象的形式存在,我们叫它 json 对象。
- 一种是:字符串的形式存在,我们叫它 json 字符串。
什么时候用json对象什么时候用json字符串:
- 一般我们要操作 json 中的数据的时候,需要 json 对象的格式。
- 一般我们要在客户端和服务器之间进行数据交换的时候,使用 json 字符串。
2个方法可以实现json对象 和 json字符串之间的转化:
-
JSON.stringify() :把 json 对象转换成为 json 字符串
-
JSON.parse() :把 json 字符串转换成为 json 对象
示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 1.json的定义:
//value值可以是:数字,字符串,布尔类型,数组,json对象,json数组等等
var jsonObj = {
"key1":12,
"key2":"abc",
"key3":true,
"key4":[11,"arr",false],
"key5":{
"key5_1" : 551,
"key5_2" : "key5_2_value"
},
"key6":[{
"key6_1_1":6611,
"key6_1_2":"key6_1_2_value"
},{
"key6_2_1":6621,
"key6_2_2":"key6_2_2_value"
}]
};
//3.json对象和json之间的互转:
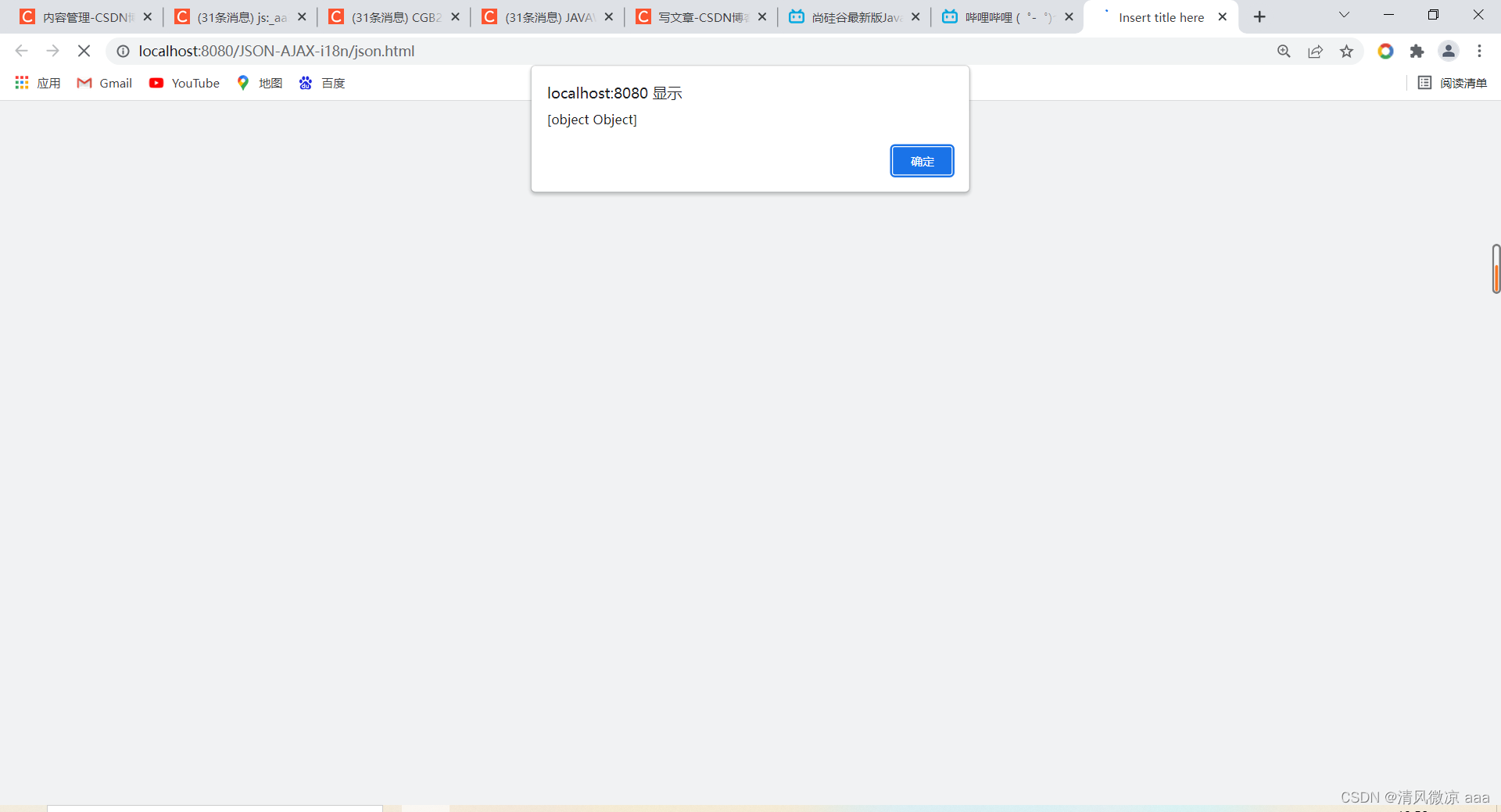
alert(jsonObj);//[object Object]
// 把json对象转换成为 json字符串
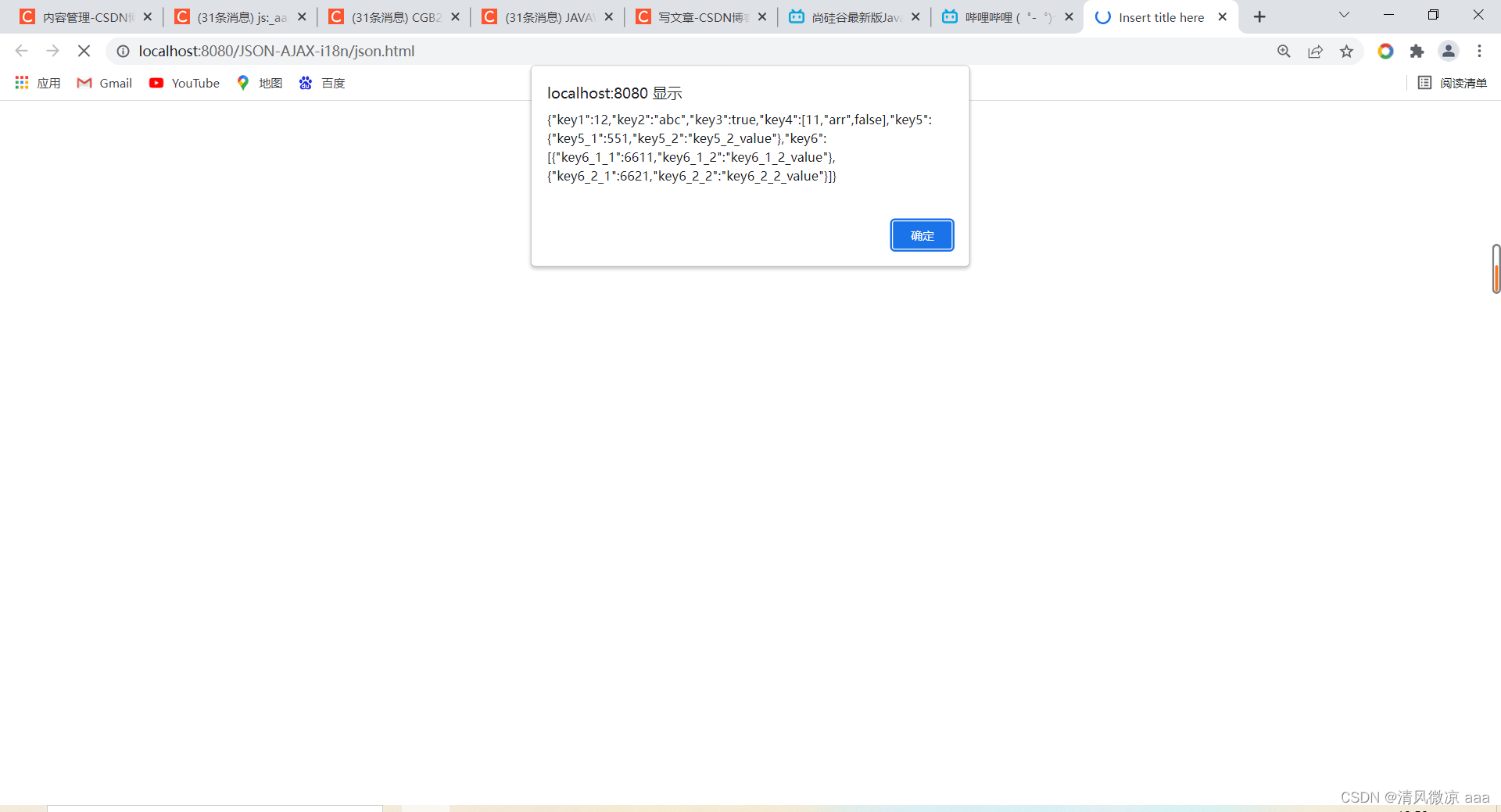
var jsonObjString = JSON.stringify(jsonObj); // 特别像 Java中对象的toString 可以把json里面的值显示出来
alert(jsonObjString)
// 把json字符串。转换成为json对象
var jsonObj2 = JSON.parse(jsonObjString);
alert(jsonObj2.key1);// 12
alert(jsonObj2.key2);// abc
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
总结:
-
直接输出json对象只能显示为object类型,但是可以通过json对象获取里面的值。
-
json对象转化为字符串输出可以直接看到里面的值,但是不能够获取值。
1.2、JSON 在服务端 java 中的使用
说明:在java中使用json首先需要导入jar包。
1.2.1、javaBean 和 json 的互转
Person类:
package com.atguigu.pojo;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + ''' +
'}';
}
}
JsonTest测试类:
package com.atguigu.json;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class JsonTest {
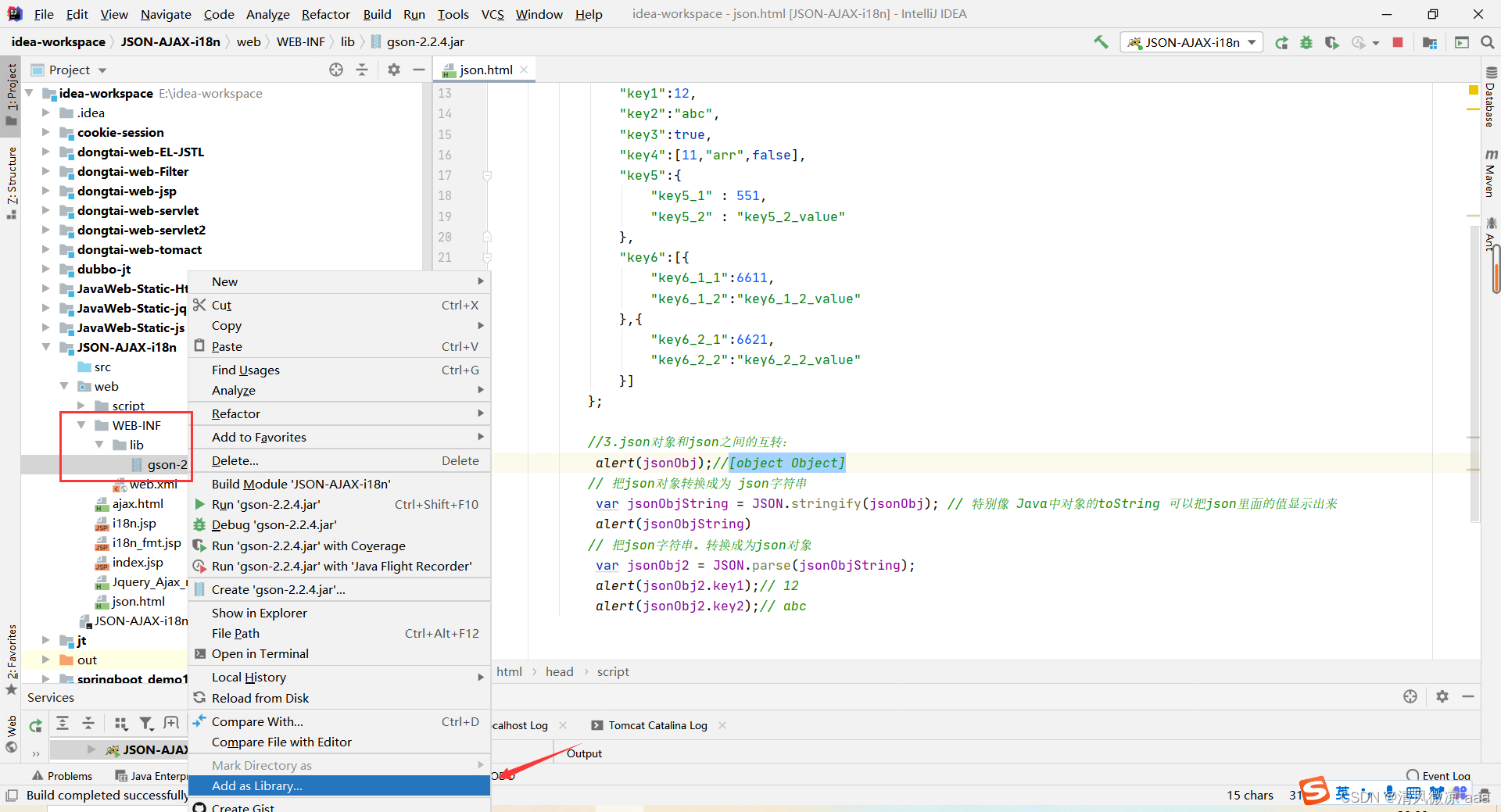
// 1.2.1、javaBean和json的互转
@Test
public void test1(){
Person person = new Person(1,"国哥好帅!");
// 创建Gson对象实例
Gson gson = new Gson();
// toJson方法可以把java对象转换成为json字符串
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
System.out.println(personJsonString);//{"id":1,"name":"国哥好帅!"}
// fromJson把json字符串转换回Java对象
// 第一个参数是json字符串
// 第二个参数是转换回去的Java对象类型
Person person1 = gson.fromJson(personJsonString, Person.class);
System.out.println(person1);//Person{id=1, name='国哥好帅!'}
}
}
1.2.2、List 和 json 的互转
Person类:
package com.atguigu.pojo;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + ''' +
'}';
}
}
PersonListType类:
package com.atguigu.json;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class PersonListType extends TypeToken<ArrayList<Person>> {
}
JsonTest类:
package com.atguigu.json;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class JsonTest {
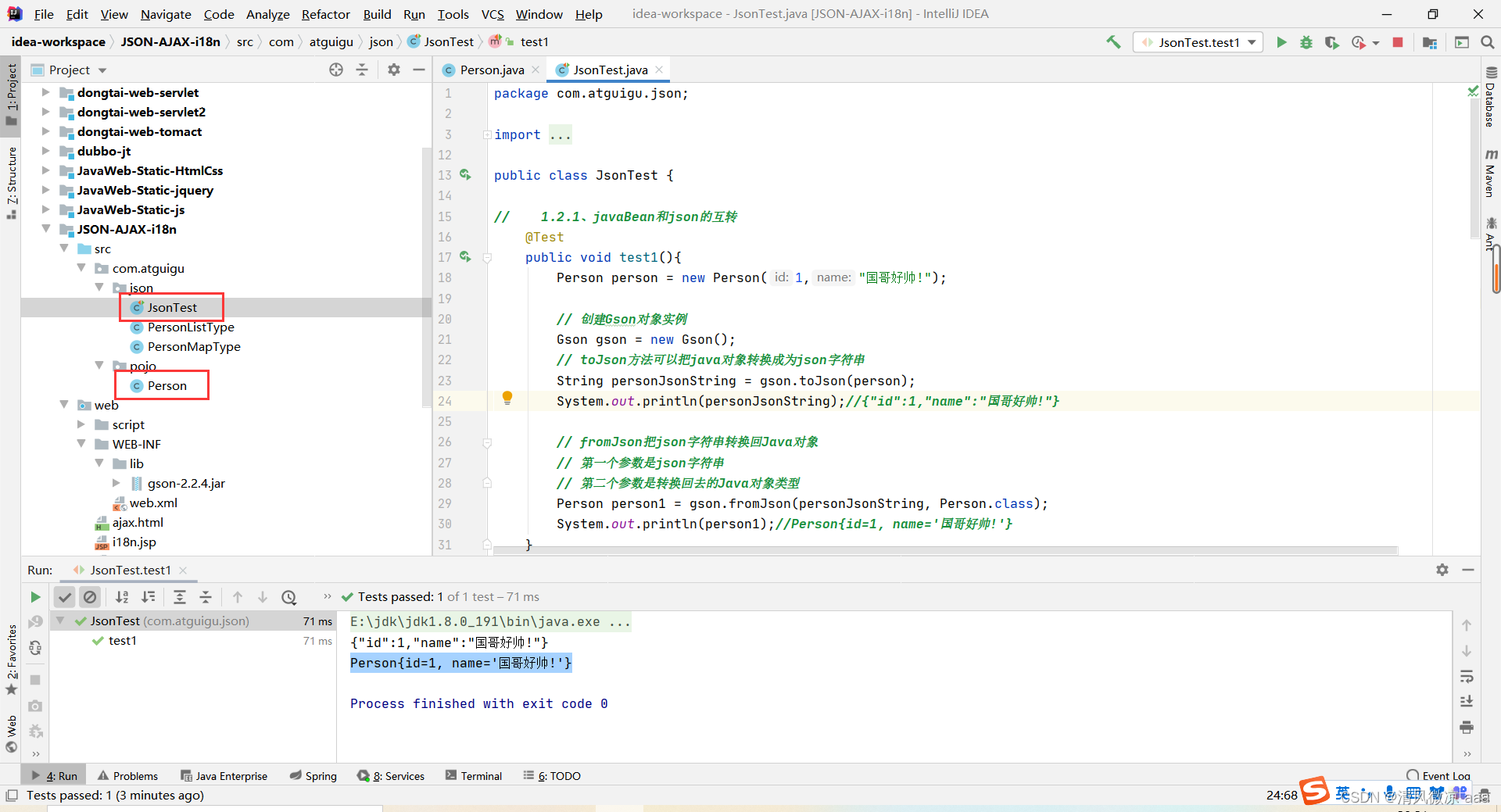
// 1.2.2、List 和json的互转
@Test
public void test2() {
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person(1, "国哥"));
personList.add(new Person(2, "康师傅"));
Gson gson = new Gson();
// 把List转换为json字符串
String personListJsonString = gson.toJson(personList);
System.out.println(personListJsonString);//[{"id":1,"name":"国哥"},{"id":2,"name":"康师傅"}]
// json字符串转换为List
/*第二个参数的类型不能直接写personList.getClass():需要定义一个类继承TypeToken并指定泛型(这个类TypeToken是官方jar包提供的一个
反射的类 ,用于把json字符串转化为集合的),这个泛型就是需要转化回去的类型,可以是List<Person> 也可以是转化回去的具体类型ArrayList<Person>
缺点:每次都要创建一个类继承TypeToken,而又仅仅在json字符串转换为集合时用,太过浪费 代码结构混乱。
解决:使用匿名子类的匿名对象。
*/
List<Person> list = gson.fromJson(personListJsonString, new PersonListType().getType());
System.out.println(list);//[Person{id=1, name='国哥'}, Person{id=2, name='康师傅'}]
Person person = list.get(0);
System.out.println(person);//Person{id=1, name='国哥'}
}
}
1.2.3、map 和 json 的互转
Person类:
package com.atguigu.pojo;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + ''' +
'}';
}
}
PersonMapType类:
package com.atguigu.json;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class PersonMapType extends TypeToken<HashMap<Integer, Person>> {
}
JsonTest类:
package com.atguigu.json;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class JsonTest {
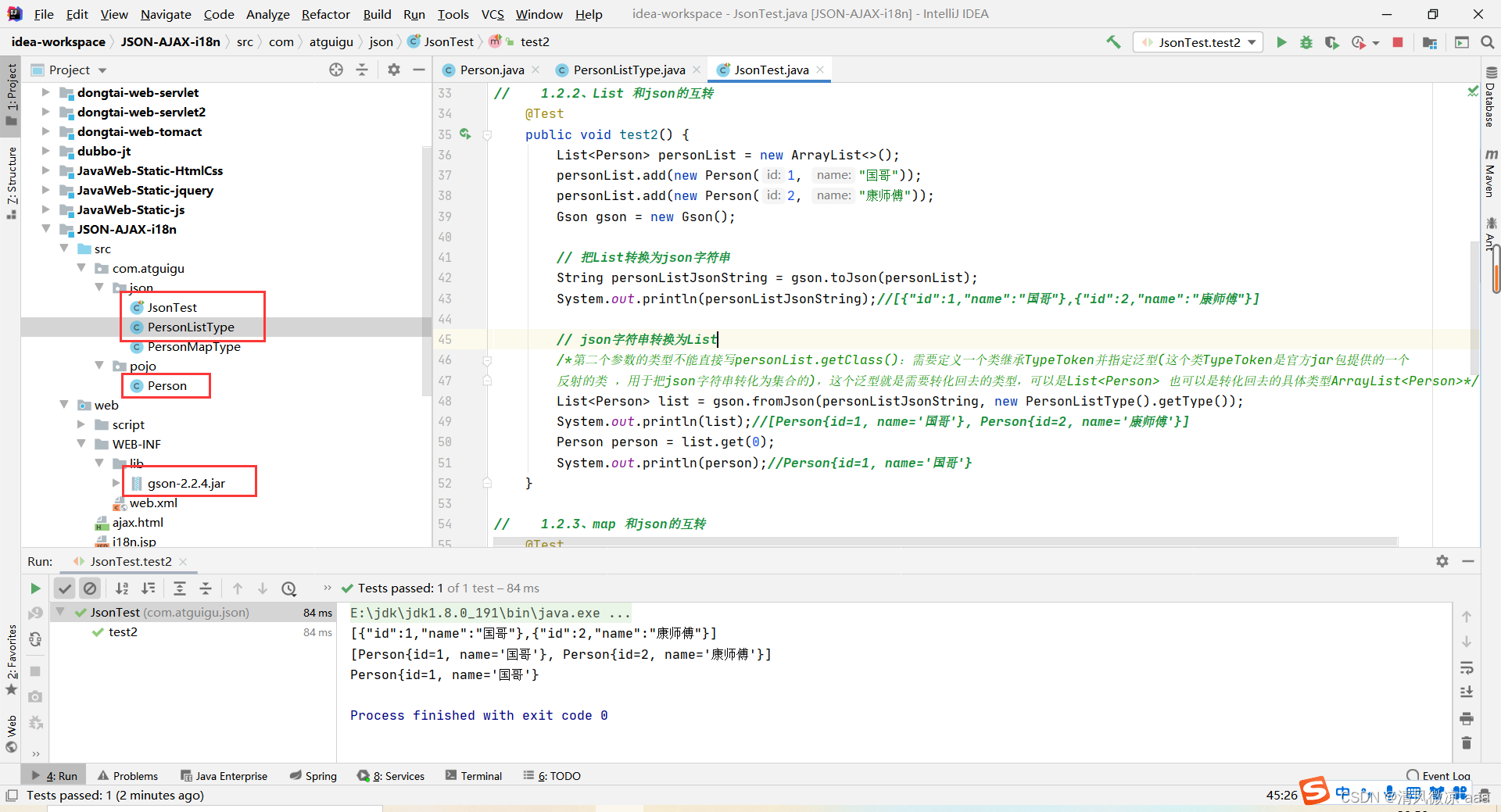
// 1.2.3、map 和json的互转
@Test
public void test3(){
Map<Integer,Person> personMap = new HashMap<>();
personMap.put(1, new Person(1, "国哥好帅"));
personMap.put(2, new Person(2, "康师傅也好帅"));
Gson gson = new Gson();
// 把 map 集合转换成为 json字符串
String personMapJsonString = gson.toJson(personMap);
System.out.println(personMapJsonString);//{"1":{"id":1,"name":"国哥好帅"},"2":{"id":2,"name":"康师傅也好帅"}}
// json字符串转换为map 集合 类似于list
//方式一:每次都要创建一个类继承TypeToken,而又仅仅在json字符串转换为集合时用,太过浪费 代码结构混乱
// Map<Integer,Person> personMap2 = gson.fromJson(personMapJsonString, new PersonMapType().getType());
//方式二:使用匿名子类的匿名对象
Map<Integer,Person> personMap2 = gson.fromJson(personMapJsonString, new TypeToken<HashMap<Integer,Person>>(){}.getType());
System.out.println(personMap2);//{1=Person{id=1, name='国哥好帅'}, 2=Person{id=2, name='康师傅也好帅'}}
Person p = personMap2.get(1);
System.out.println(p);//Person{id=1, name='国哥好帅'}
}
}
2、AJAX 请求
2.1、什么是 AJAX 请求
概念:AJAX 即“Asynchronous Javascript And XML”(异步 JavaScript 和 XML),是指一种创建交互式网页应用的网页开发技术。
概述:ajax 是一种浏览器通过 js 异步发起请求,局部更新页面的技术。
Ajax 请求的局部更新特点:
- 浏览器地址栏不会发生变化`
- 局部更新不会舍弃原来页面的内容
2.2、原生 AJAX 请求的示例:
a.html:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 在这里使用javaScript语言发起Ajax请求,访问服务器AjaxServlet中javaScriptAjax
function ajaxRequest() {
// 1、我们首先要创建XMLHttpRequest
var xmlhttprequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2、调用open方法设置请求参数 (method:请求的类型;GET 或 POST ,url:文件在服务器上的位置 ,async:true(异步)或 false(同步)
xmlhttprequest.open("GET","http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet?action=javaScriptAjax",true);
// 4、在send方法前绑定onreadystatechange事件,处理请求完成后的操作。
//当请求被发送到服务器时,我们需要执行一些基于响应的任务,每当 readyState 改变时,就会触发 onreadystatechange 事件,
// readyState 属性存有 XMLHttpRequest 的状态信息。当 readyState 等于 4 且状态为 200 时,表示响应已就绪
xmlhttprequest.onreadystatechange = function(){
if (xmlhttprequest.readyState == 4 && xmlhttprequest.status == 200) {
//如需获得来自服务器的响应,请使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象的 responseText 或 responseXML 属性。
//responseText 获得字符串形式的响应数据。
//responseXML 获得 XML 形式的响应数据。
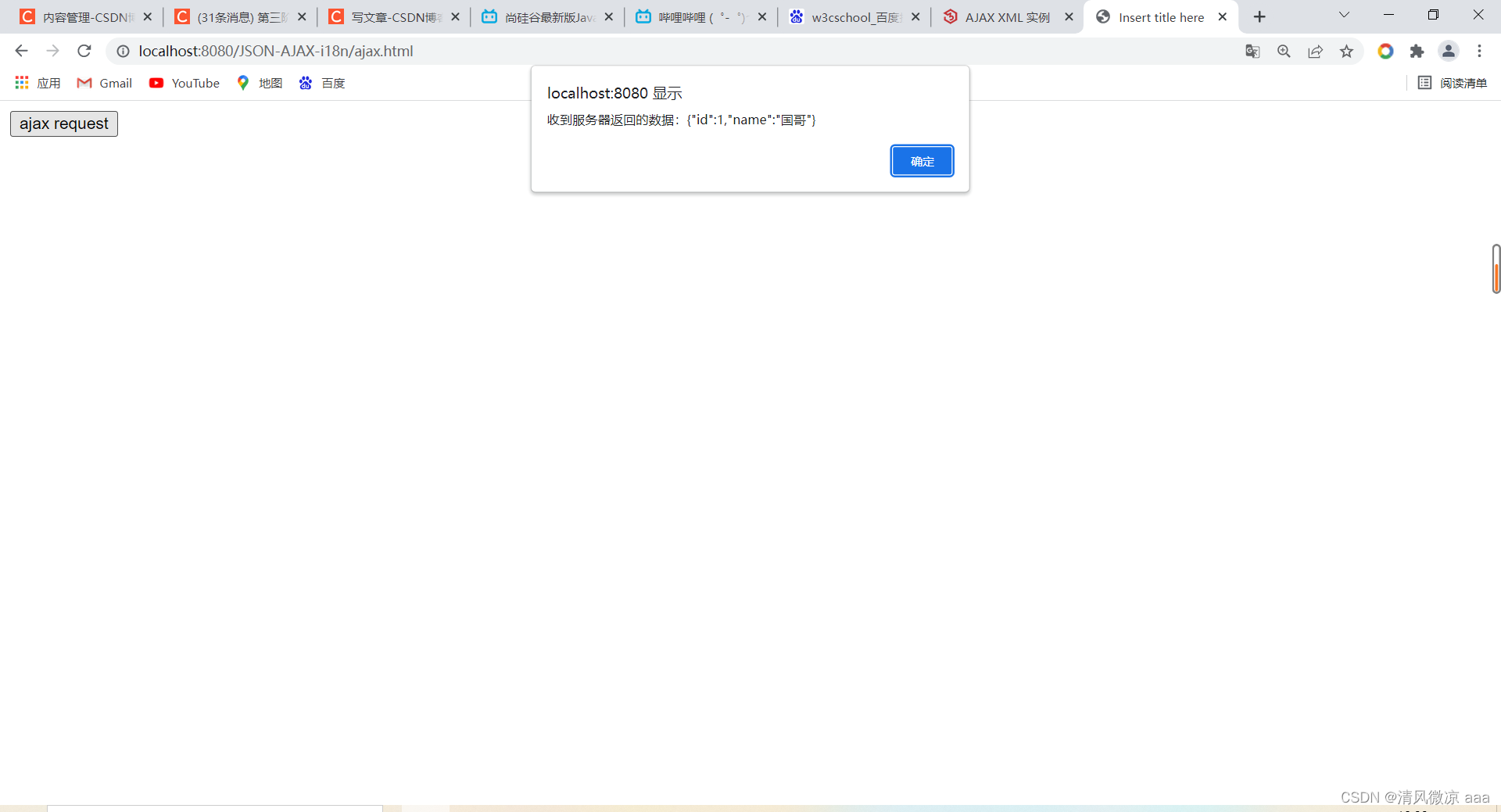
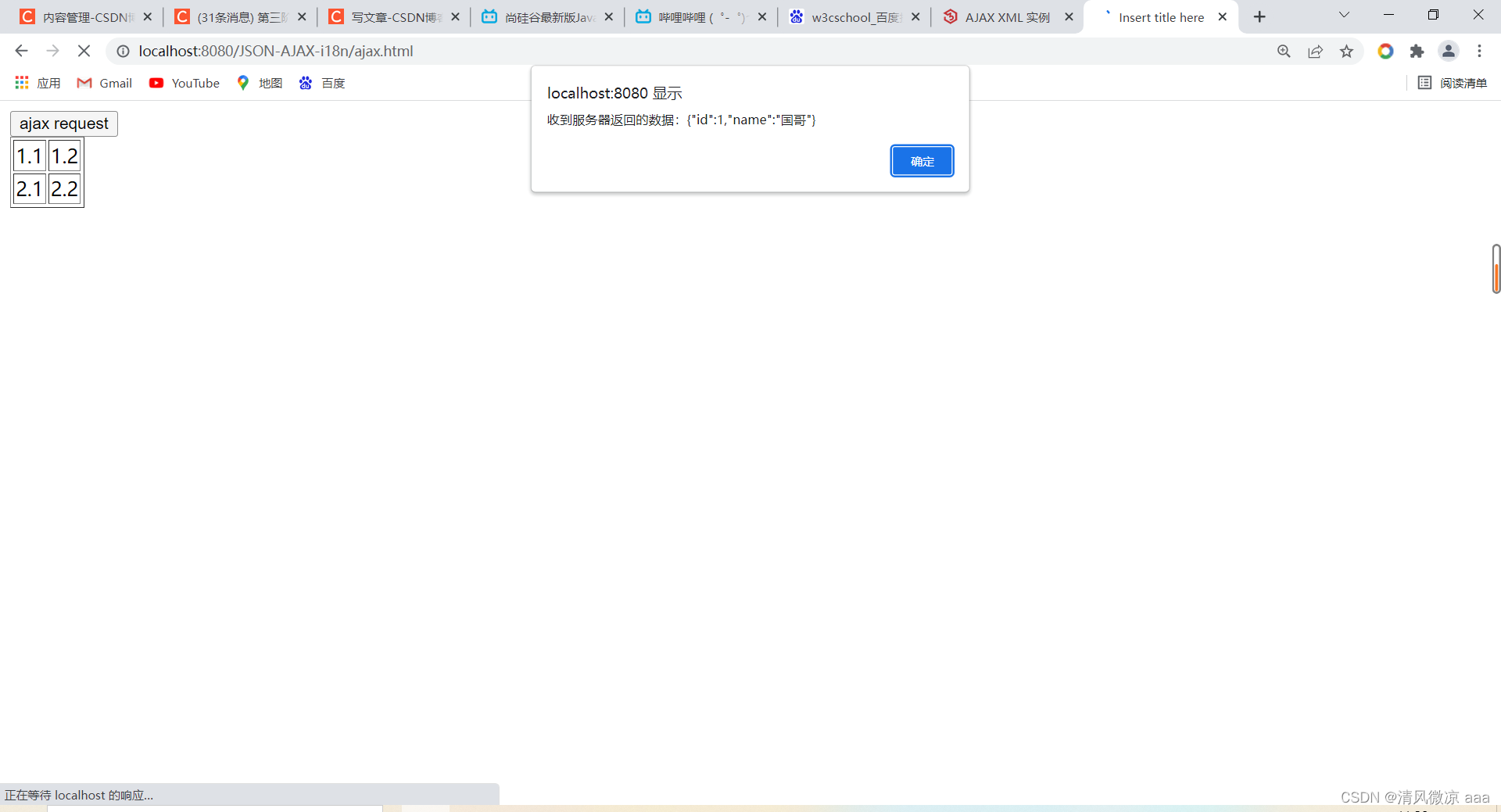
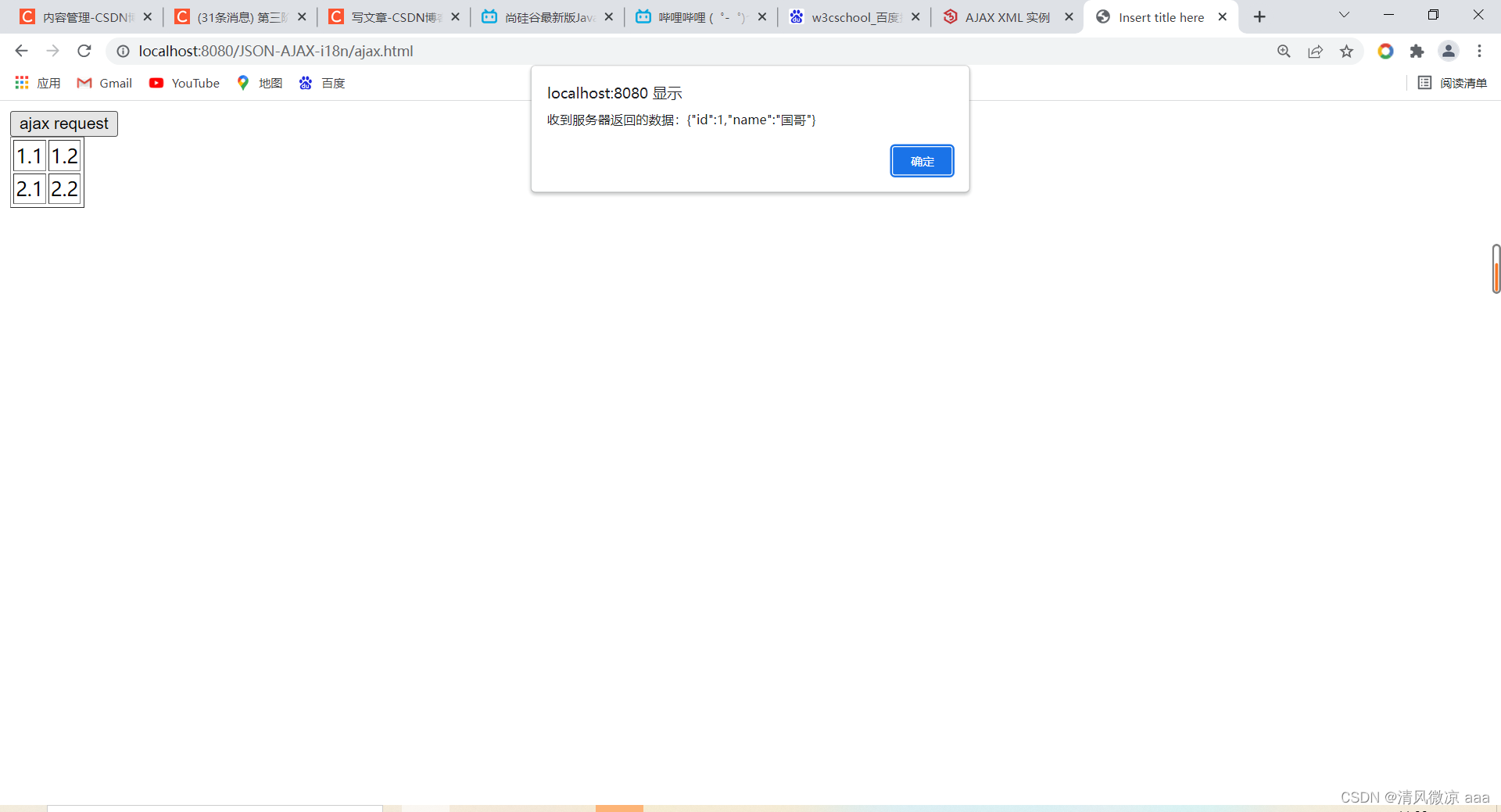
alert("收到服务器返回的数据:" + xmlhttprequest.responseText);
//一般对象返回给客户端页面,客户直接看到的是json字符串对象看不懂,而是把json字符串转化为json对象然后分别
//取出里面的值 显示到页面上。
var jsonObj = JSON.parse(xmlhttprequest.responseText);
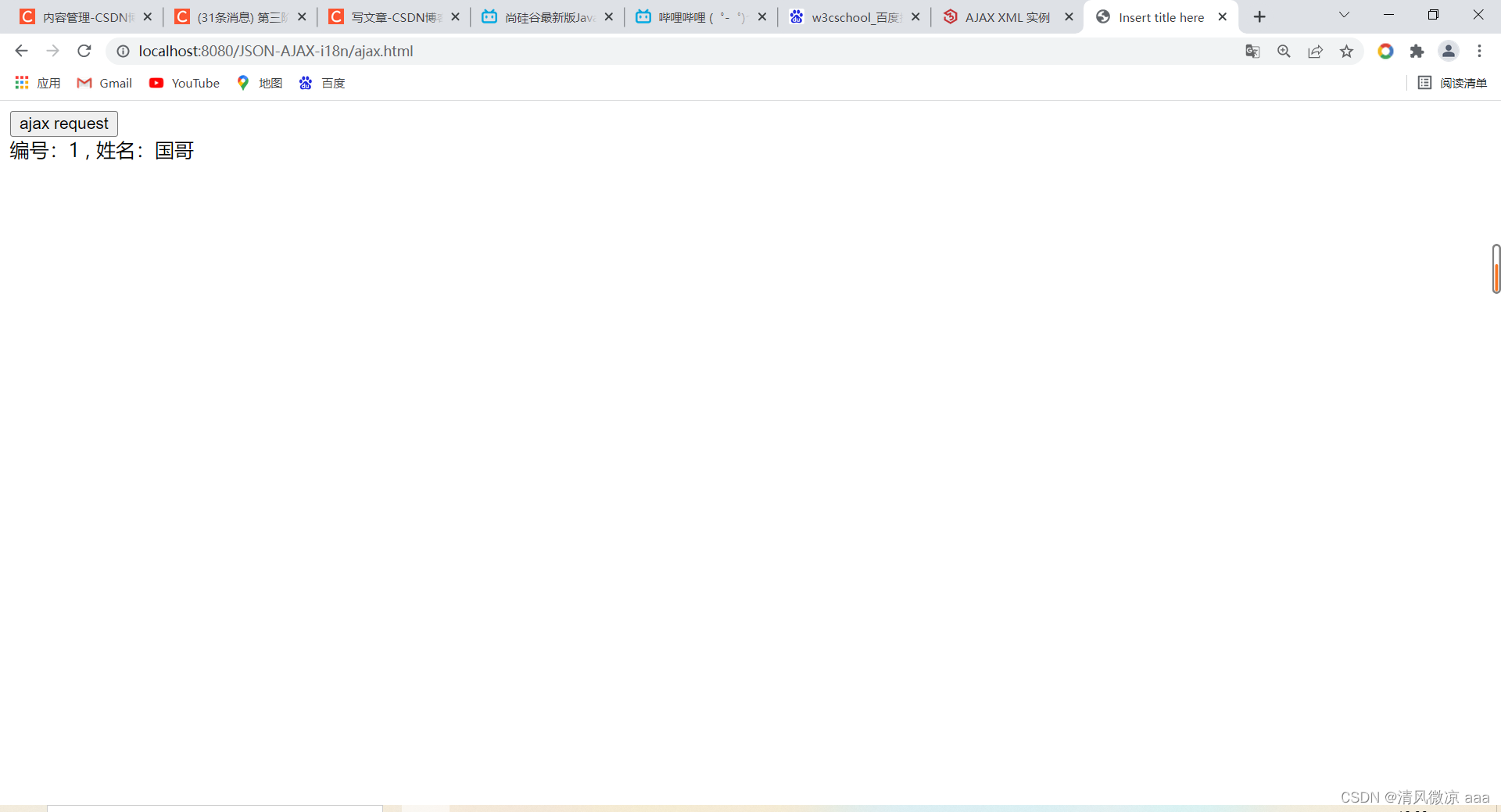
// 把响应的数据显示在页面上
document.getElementById("div01").innerHTML = "编号:" + jsonObj.id + " , 姓名:" + jsonObj.name;
}
}
// 3、调用send方法发送请求
xmlhttprequest.send();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="ajaxRequest()">ajax request</button>
<div id="div01">
</div>
</body>
</html>
BaseServlet:
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public abstract class BaseServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2659767917553822186L;
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(req, resp);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 解决post请求中文乱码问题
// 一定要在获取请求参数之前调用才有效
req.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// 解决响应中文乱码
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
String action = req.getParameter("action");
try {
// 获取action业务鉴别字符串,获取相应的业务 方法反射对象
Method method = this.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(action, HttpServletRequest.class, HttpServletResponse.class);
// System.out.println(method);
// 调用目标业务 方法
method.invoke(this, req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);// 把异常抛给Filter过滤器
}
}
}
AjaxServlet:
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class AjaxServlet extends BaseServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5972839860768196824L;
protected void javaScriptAjax(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Ajax请求过来了");
//解释:返回一个对象,如果客户端和服务器不在同一个电脑上,直接返回的是地址,想要返回里面的内容需要转化为字符串,一般是json格式的字符串。
Person person = new Person(1, "国哥");
// json格式的字符串
Gson gson = new Gson();
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
resp.getWriter().write(personJsonString);
}
}
web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>AjaxServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.atguigu.servlet.AjaxServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>AjaxServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ajaxServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
测试:启动tomact服务器,在浏览器输入访问ajax.html页面,点击按钮发现请求发送到servlet并响应数据给客户端,之后客户端在把数据取出来显示到页面上。

2.2.1 Ajax请求的特点说明
概述:ajax 是一种浏览器通过 js 异步发起请求,局部更新页面的技术。
Ajax 请求的局部更新特点:
- 浏览器地址栏不会发生变化`
- 局部更新不会舍弃原来页面的内容
解释一:局部更新:
修改ajax.html页面:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 在这里使用javaScript语言发起Ajax请求,访问服务器AjaxServlet中javaScriptAjax
function ajaxRequest() {
// 1、我们首先要创建XMLHttpRequest
var xmlhttprequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2、调用open方法设置请求参数 (method:请求的类型;GET 或 POST ,url:文件在服务器上的位置 ,async:true(异步)或 false(同步)
xmlhttprequest.open("GET","http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet?action=javaScriptAjax",true);
// 4、在send方法前绑定onreadystatechange事件,处理请求完成后的操作。
//当请求被发送到服务器时,我们需要执行一些基于响应的任务,每当 readyState 改变时,就会触发 onreadystatechange 事件,
// readyState 属性存有 XMLHttpRequest 的状态信息。当 readyState 等于 4 且状态为 200 时,表示响应已就绪
xmlhttprequest.onreadystatechange = function(){
if (xmlhttprequest.readyState == 4 && xmlhttprequest.status == 200) {
//如需获得来自服务器的响应,请使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象的 responseText 或 responseXML 属性。
//responseText 获得字符串形式的响应数据。
//responseXML 获得 XML 形式的响应数据。
alert("收到服务器返回的数据:" + xmlhttprequest.responseText);
//一般对象返回给客户端页面,客户直接看到的是json字符串对象看不懂,而是把json字符串转化为json对象然后分别
//取出里面的值 显示到页面上。
var jsonObj = JSON.parse(xmlhttprequest.responseText);
// 把响应的数据显示在页面上
document.getElementById("div01").innerHTML = "编号:" + jsonObj.id + " , 姓名:" + jsonObj.name;
}
}
// 3、调用send方法发送请求
xmlhttprequest.send();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet?action=javaScriptAjax">非Ajax</a>
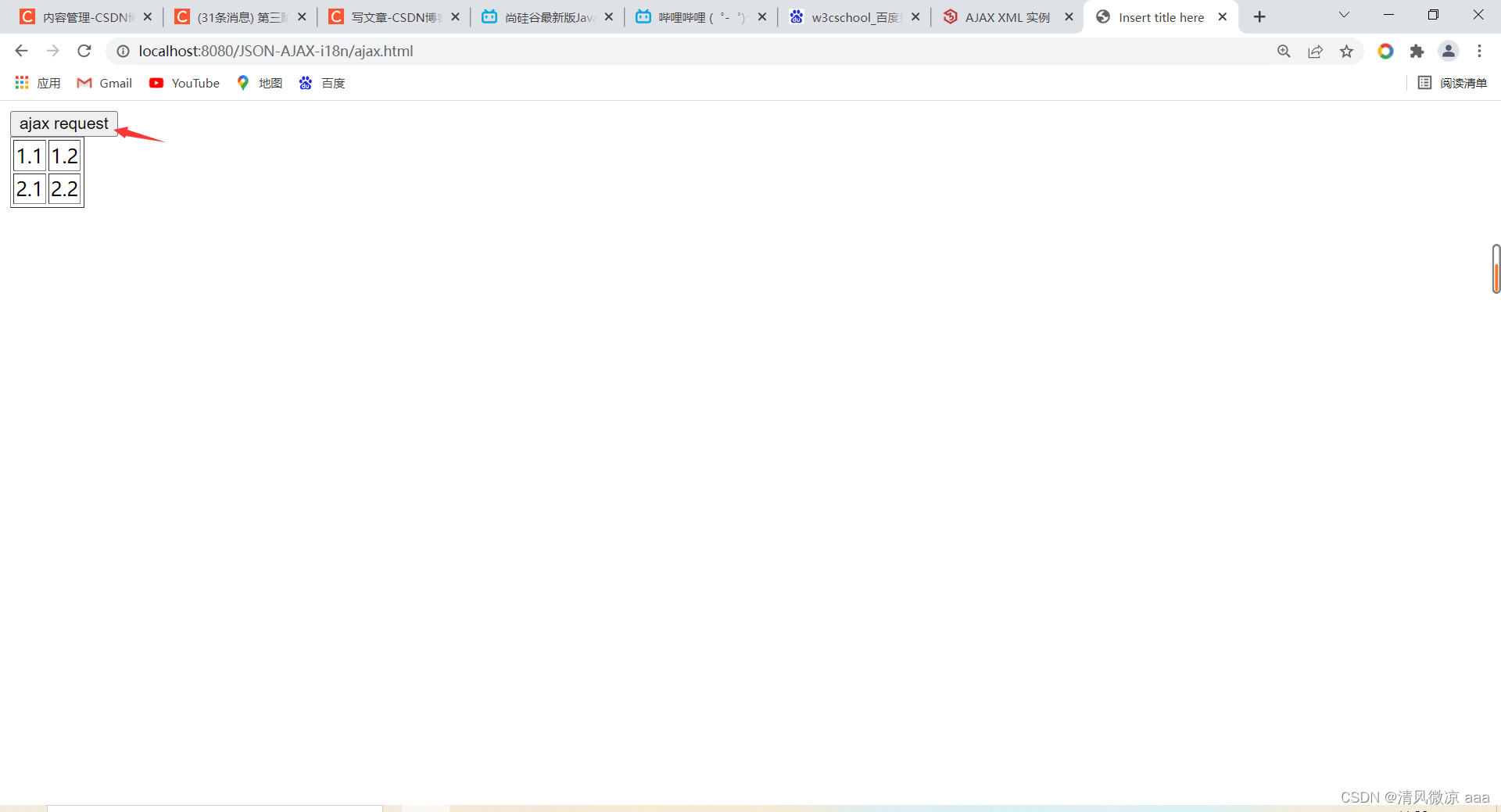
<button onclick="ajaxRequest()">ajax request</button>
<div id="div01">
</div>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td>1.1</td>
<td>1.2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2.1</td>
<td>2.2</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
新添加的内容:

使用Ajax发送请求:
访问前页面的内容和浏览器地址。
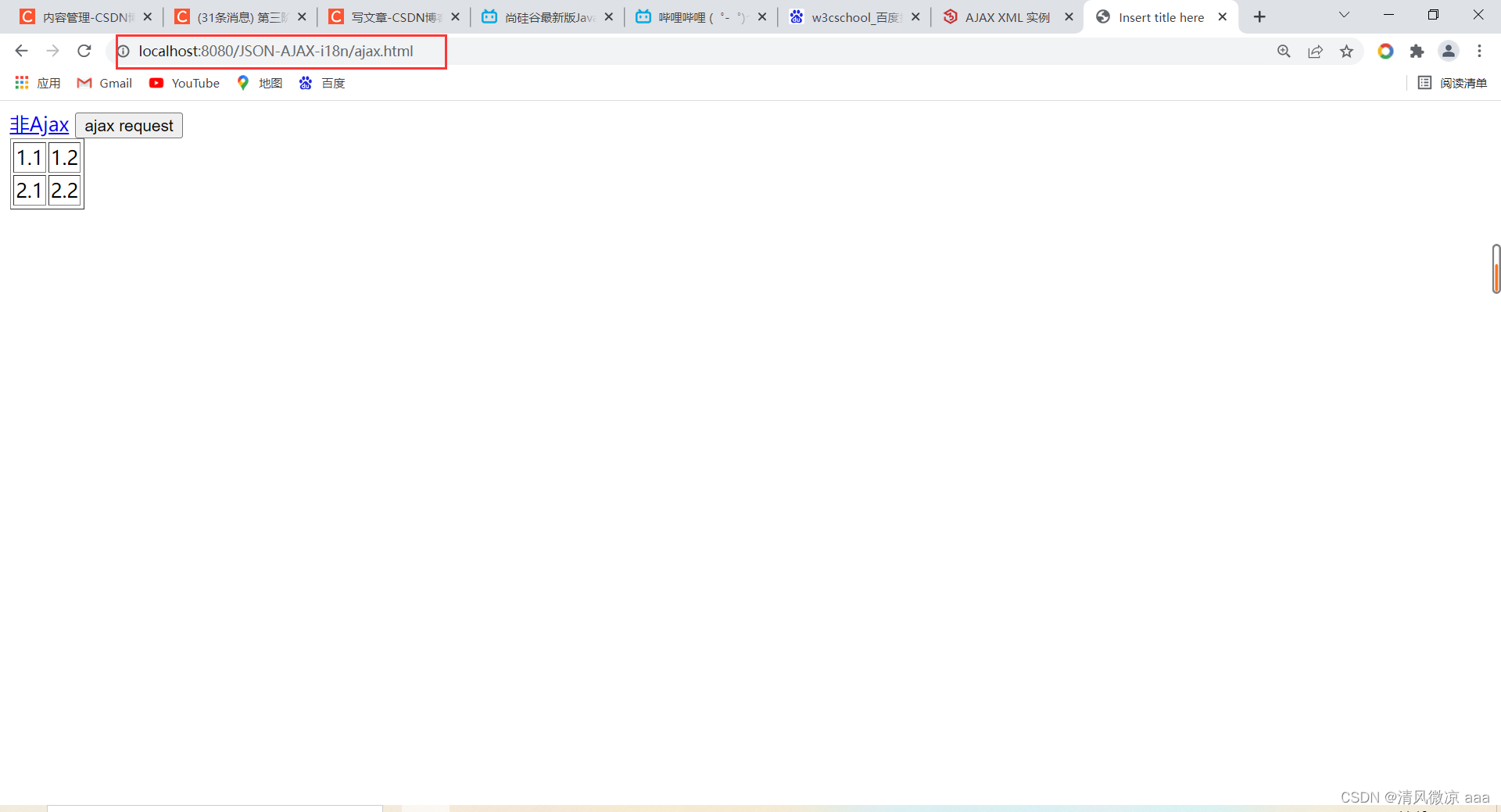
访问后:
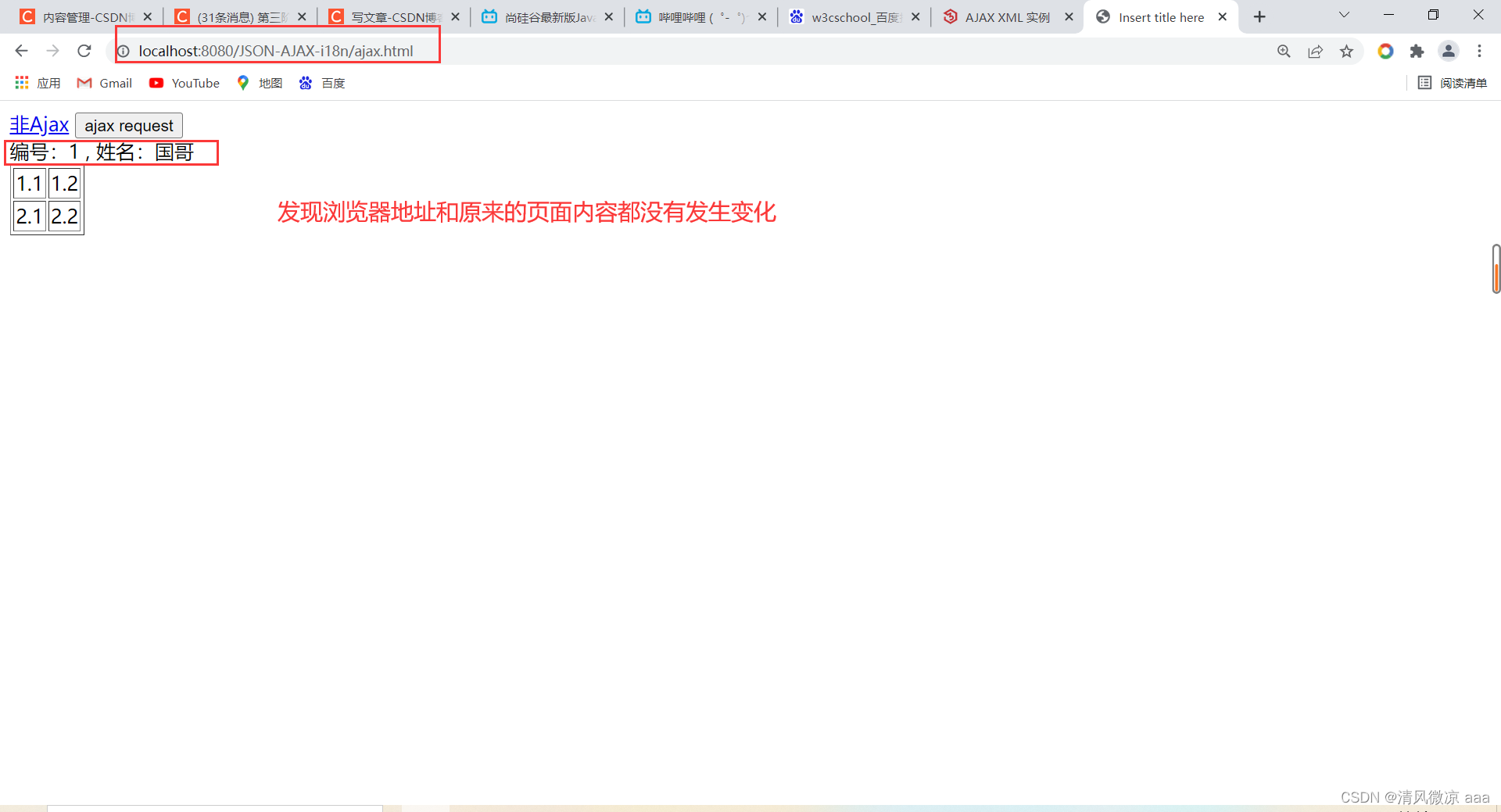
使用非Ajax方式发送请求:发现访问前后的地址栏和页面内容都发生了变化。
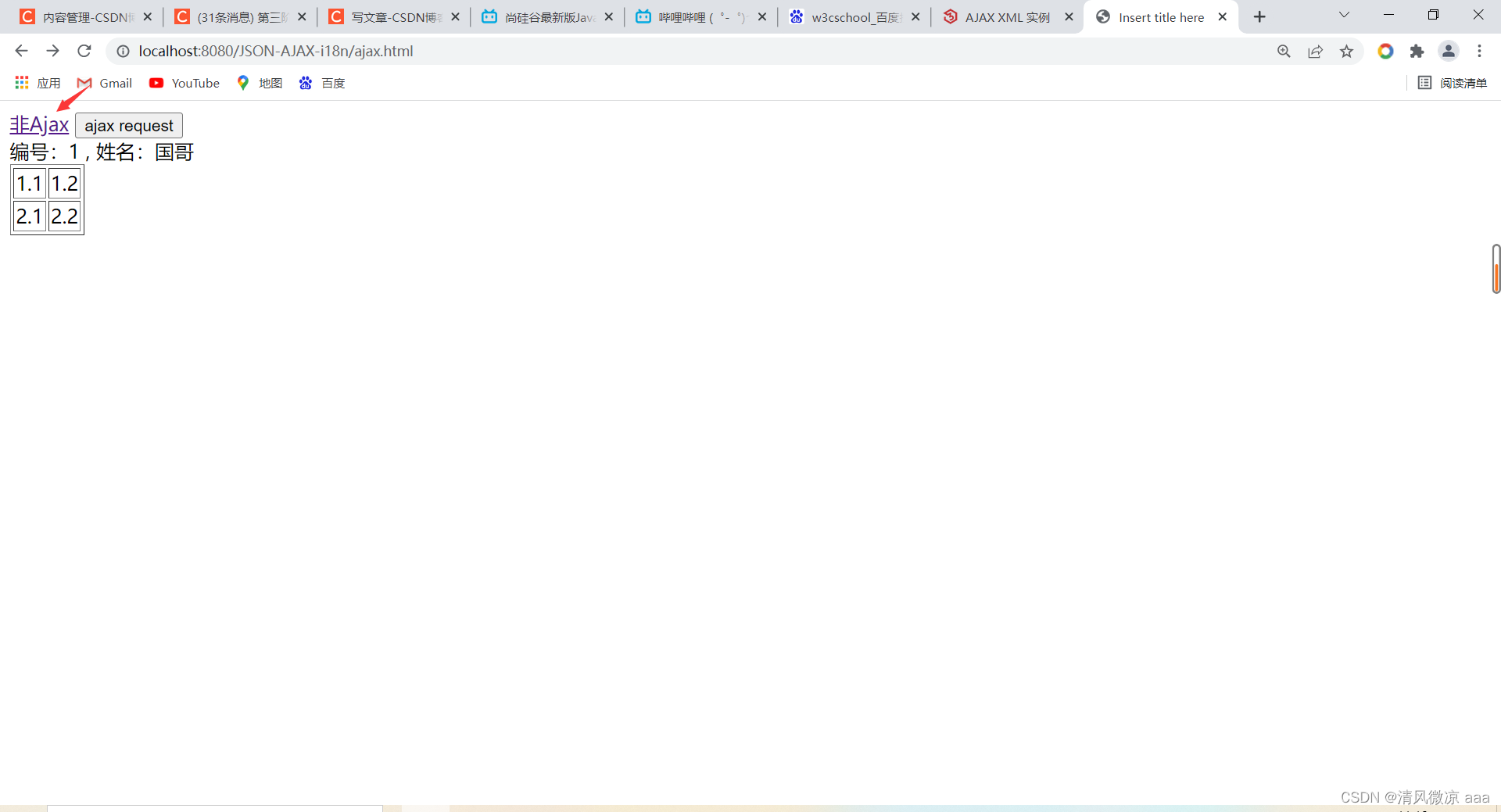
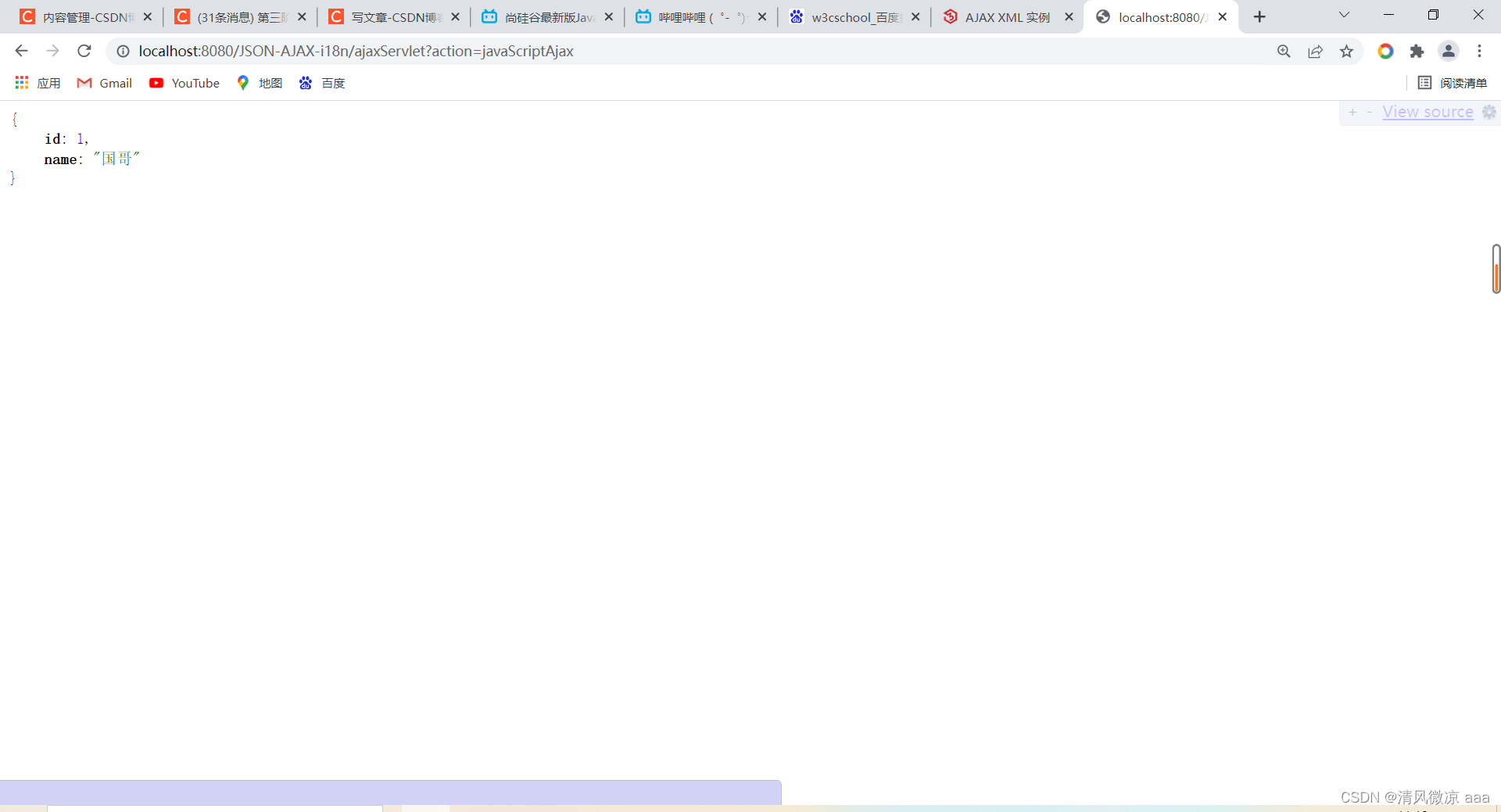
解释二:异步请求:客户端无需等待服务端的响应结果,可以不断向服务端发送请求。好处:比如,用户发送请求不会一直卡在那,可以给用户更好的体验。
修改ajax.html:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 在这里使用javaScript语言发起Ajax请求,访问服务器AjaxServlet中javaScriptAjax
function ajaxRequest() {
// 1、我们首先要创建XMLHttpRequest
var xmlhttprequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2、调用open方法设置请求参数 (method:请求的类型;GET 或 POST ,url:文件在服务器上的位置 ,async:true(异步)或 false(同步)
xmlhttprequest.open("GET","http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet?action=javaScriptAjax",false);
// 4、在send方法前绑定onreadystatechange事件,处理请求完成后的操作。
//当请求被发送到服务器时,我们需要执行一些基于响应的任务,每当 readyState 改变时,就会触发 onreadystatechange 事件,
// readyState 属性存有 XMLHttpRequest 的状态信息。当 readyState 等于 4 且状态为 200 时,表示响应已就绪
xmlhttprequest.onreadystatechange = function(){
if (xmlhttprequest.readyState == 4 && xmlhttprequest.status == 200) {
//如需获得来自服务器的响应,请使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象的 responseText 或 responseXML 属性。
//responseText 获得字符串形式的响应数据。
//responseXML 获得 XML 形式的响应数据。
alert("收到服务器返回的数据:" + xmlhttprequest.responseText);
//一般对象返回给客户端页面,客户直接看到的是json字符串对象看不懂,而是把json字符串转化为json对象然后分别
//取出里面的值 显示到页面上。
var jsonObj = JSON.parse(xmlhttprequest.responseText);
// 把响应的数据显示在页面上
document.getElementById("div01").innerHTML = "编号:" + jsonObj.id + " , 姓名:" + jsonObj.name;
}
}
// 3、调用send方法发送请求
xmlhttprequest.send();
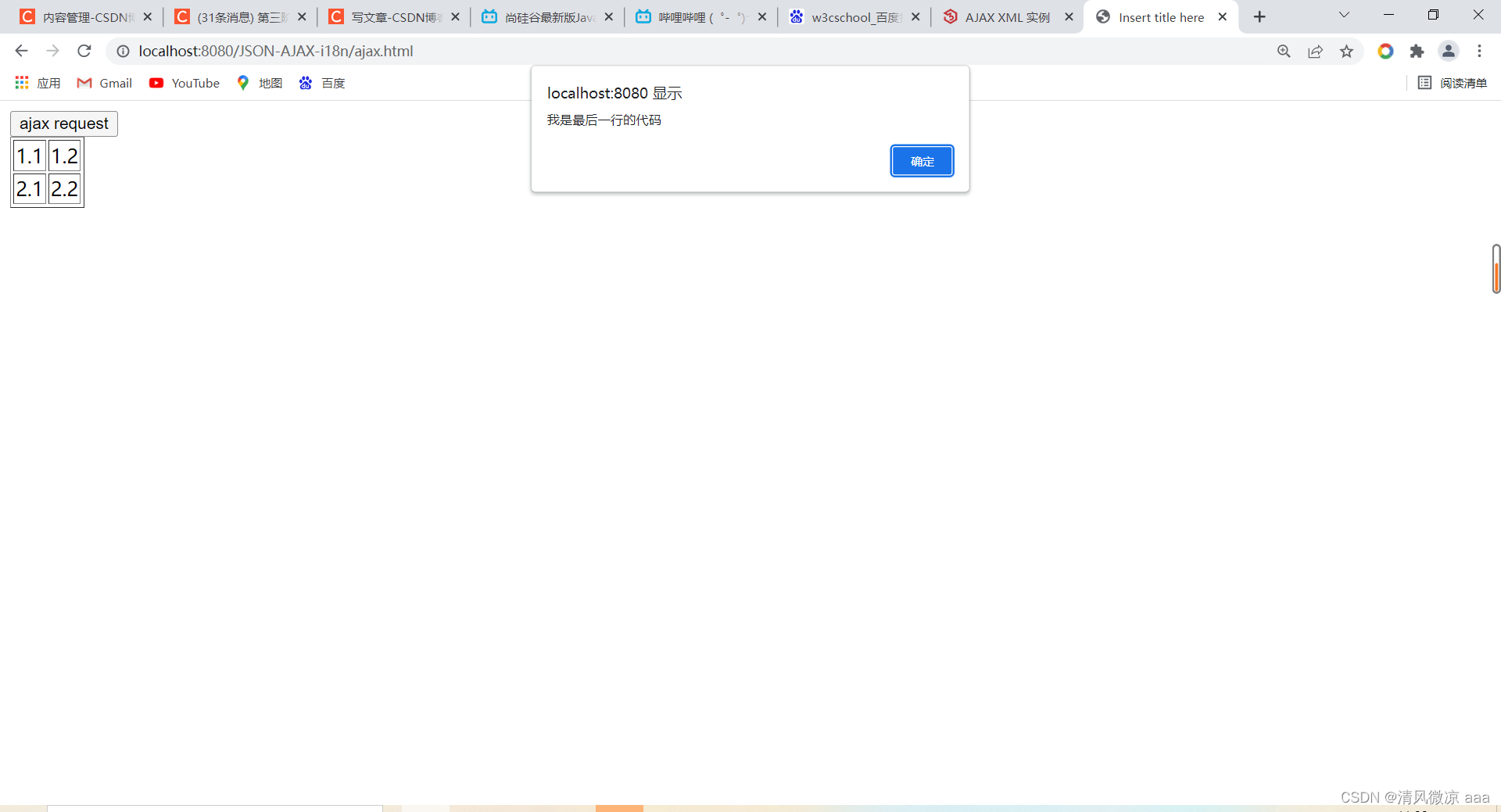
alert("我是最后一行的代码");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!--<a href="http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet?action=javaScriptAjax">非Ajax</a>-->
<button onclick="ajaxRequest()">ajax request</button>
<div id="div01">
</div>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td>1.1</td>
<td>1.2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2.1</td>
<td>2.2</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
修改AjaxServlet:
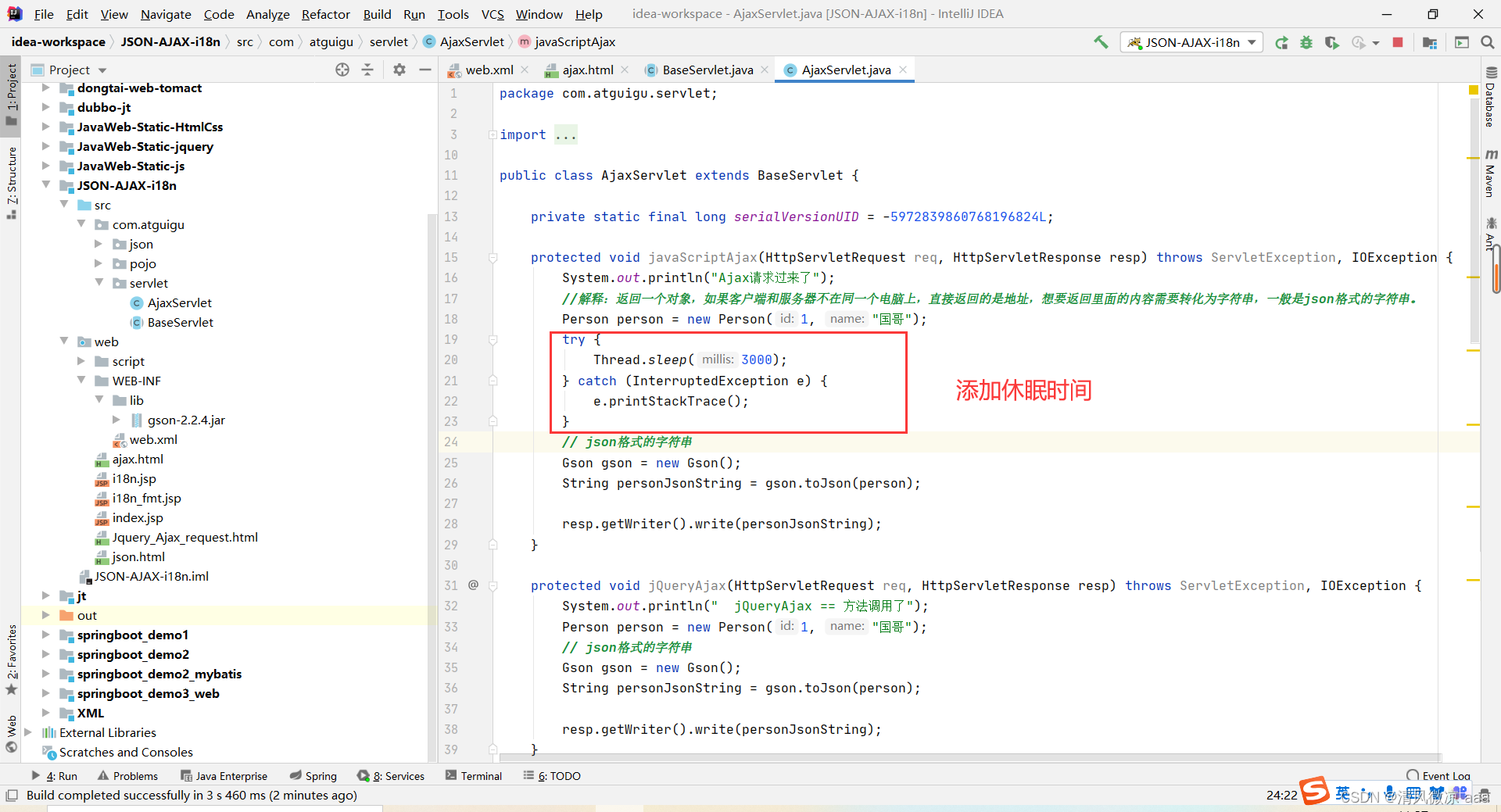
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class AjaxServlet extends BaseServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5972839860768196824L;
protected void javaScriptAjax(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("Ajax请求过来了");
//解释:返回一个对象,如果客户端和服务器不在同一个电脑上,直接返回的是地址,想要返回里面的内容需要转化为字符串,一般是json格式的字符串。
Person person = new Person(1, "国哥");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// json格式的字符串
Gson gson = new Gson();
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
resp.getWriter().write(personJsonString);
}
}
测试:发现同步方式只有等第一个请求范送完,第二个请求才能发送。

改为异步:发现不等第一个请求执行完成就开始执行第二个请求。
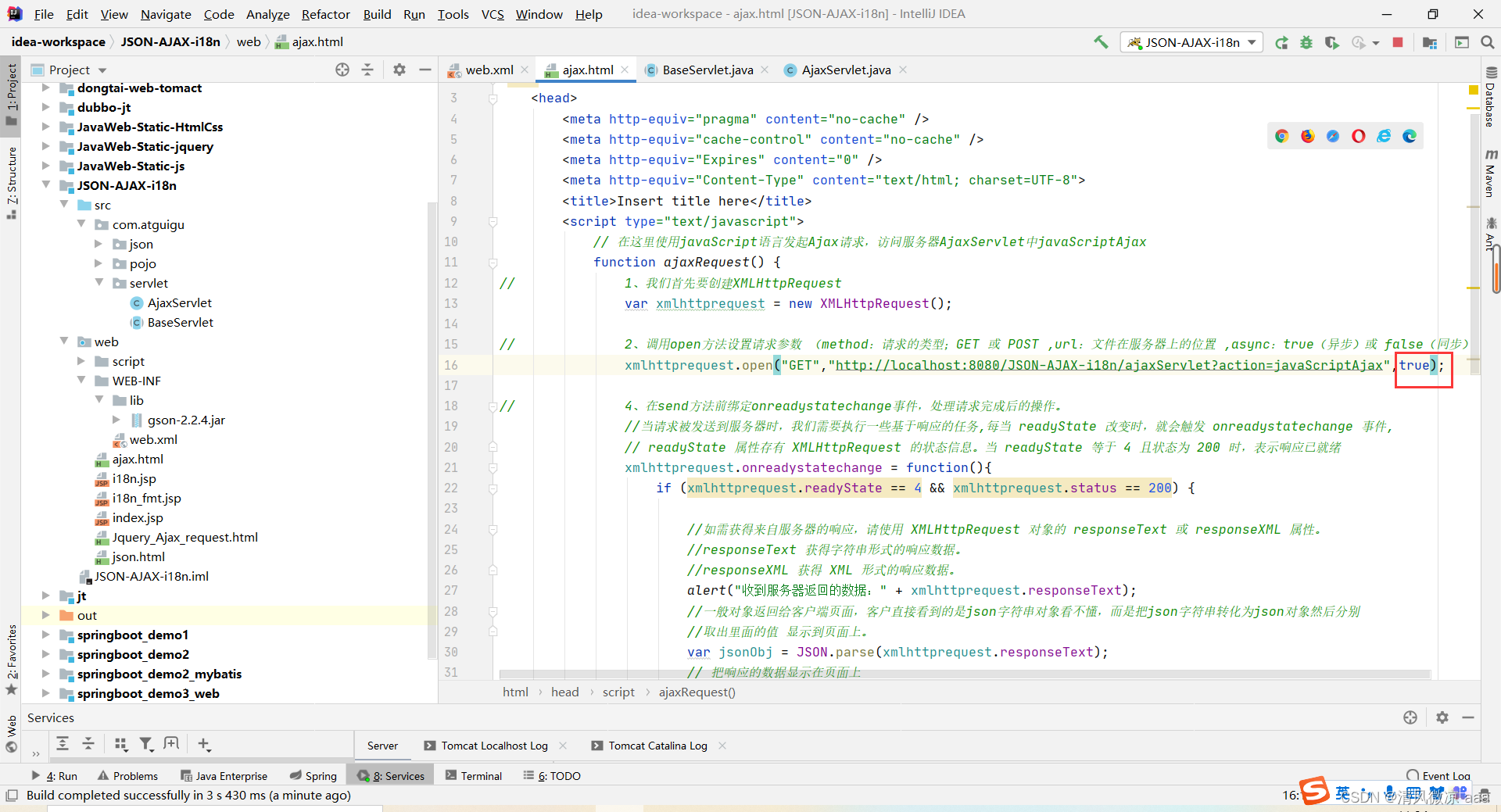
2.3、jQuery 中的 AJAX 请求
2.3.1 常用的Ajax请求 介绍:
1. $.ajax 方法:
url 表示请求的地址
type 表示请求的类型 GET 或 POST 请求
data 表示发送给服务器的数据格式有两种:
一:name=value&name=value
二:{key:value} 会自动转化为上面那种方式
success 请求成功,响应的回调函数
dataType 响应的数据类型
常用的数据类型有:
text 表示纯文本
xml 表示 xml 数据
json 表示 json 对象
2. $.get 方法和$.post 方法:在Ajax的基础上进一步封装的,可以更加简化代码步骤,不用在写type请求类型了,get和post用法相同:
url 请求的 url 地址
data 发送的数据
callback 成功的回调函数
type 返回的数据类型
3. $.getJSON 方法:是get方法的进一步封装,特点是get类型的请求和返回json类型的数据,进一步简化了代码:
url 请求的 url 地址
data 发送给服务器的数据
callback 成功的回调函数
2.3.2 常用的Ajax请求 测试:
web.xml,BaseServlet同上。
Jquery_Ajax_request.html:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="script/jquery-1.7.2.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
// ajax请求
$("#ajaxBtn").click(function(){
$.ajax({
url:"http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet",
// data:"action=jQueryAjax", //方式一
data:{action:"jQueryAjax"}, //方式二
type:"GET",
success:function (data) {//需要传一个参数,在jquery中写一个参数就可以直接接受服务端返回的值了,不需要像js中自己在调用方法获取了
// alert("服务器返回的数据是:" + data);
/*var jsonObj = JSON.parse(data);如果写的dataType是text纯文本类型,接收的值是json字符串,想要
获取里面的数据需要先调用JSON.parse()方法解析为 json对象才能获取。
如果指定为dataType : "json",会直接把json字符串转化为json对象,不用在解析了。*/
$("#msg").html(" ajax 编号:" + data.id + " , 姓名:" + data.name);
},
dataType : "json"
});
});
// ajax--get请求
$("#getBtn").click(function(){
$.get("http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet","action=jQueryGet",function (data) {
$("#msg").html(" get 编号:" + data.id + " , 姓名:" + data.name);
},"json");
});
// ajax--post请求
$("#postBtn").click(function(){
// post请求
$.post("http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet","action=jQueryPost",function (data) {
$("#msg").html(" post 编号:" + data.id + " , 姓名:" + data.name);
},"json");
});
// ajax--getJson请求
$("#getJSONBtn").click(function(){
$.getJSON("http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet","action=jQueryGetJSON",function (data) {
$("#msg").html(" getJSON 编号:" + data.id + " , 姓名:" + data.name);
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button id="ajaxBtn">$.ajax请求</button>
<button id="getBtn">$.get请求</button>
<button id="postBtn">$.post请求</button>
<button id="getJSONBtn">$.getJSON请求</button>
</div>
<div id="msg">
</div>
<br/><br/>
</body>
</html>
AjaxServlet:
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class AjaxServlet extends BaseServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5972839860768196824L;
protected void jQueryAjax(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println(" jQueryAjax == 方法调用了");
Person person = new Person(1, "国哥");
// 把对象转化为json格式的字符串,json字符串用于服务端与页面交互数据
Gson gson = new Gson();
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
resp.getWriter().write(personJsonString);
}
protected void jQueryGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println(" jQueryGet == 方法调用了");
Person person = new Person(1, "国哥");
// json格式的字符串
Gson gson = new Gson();
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
resp.getWriter().write(personJsonString);
}
protected void jQueryPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println(" jQueryPost == 方法调用了");
Person person = new Person(1, "国哥");
// json格式的字符串
Gson gson = new Gson();
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
resp.getWriter().write(personJsonString);
}
protected void jQueryGetJSON(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println(" jQueryGetJSON == 方法调用了");
Person person = new Person(1, "国哥");
// json格式的字符串
Gson gson = new Gson();
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
resp.getWriter().write(personJsonString);
}
}
启动tomact服务器,访问Jquery_Ajax_request.html,依次点击按钮发送Ajax请求。
返回数据到客户端成功。

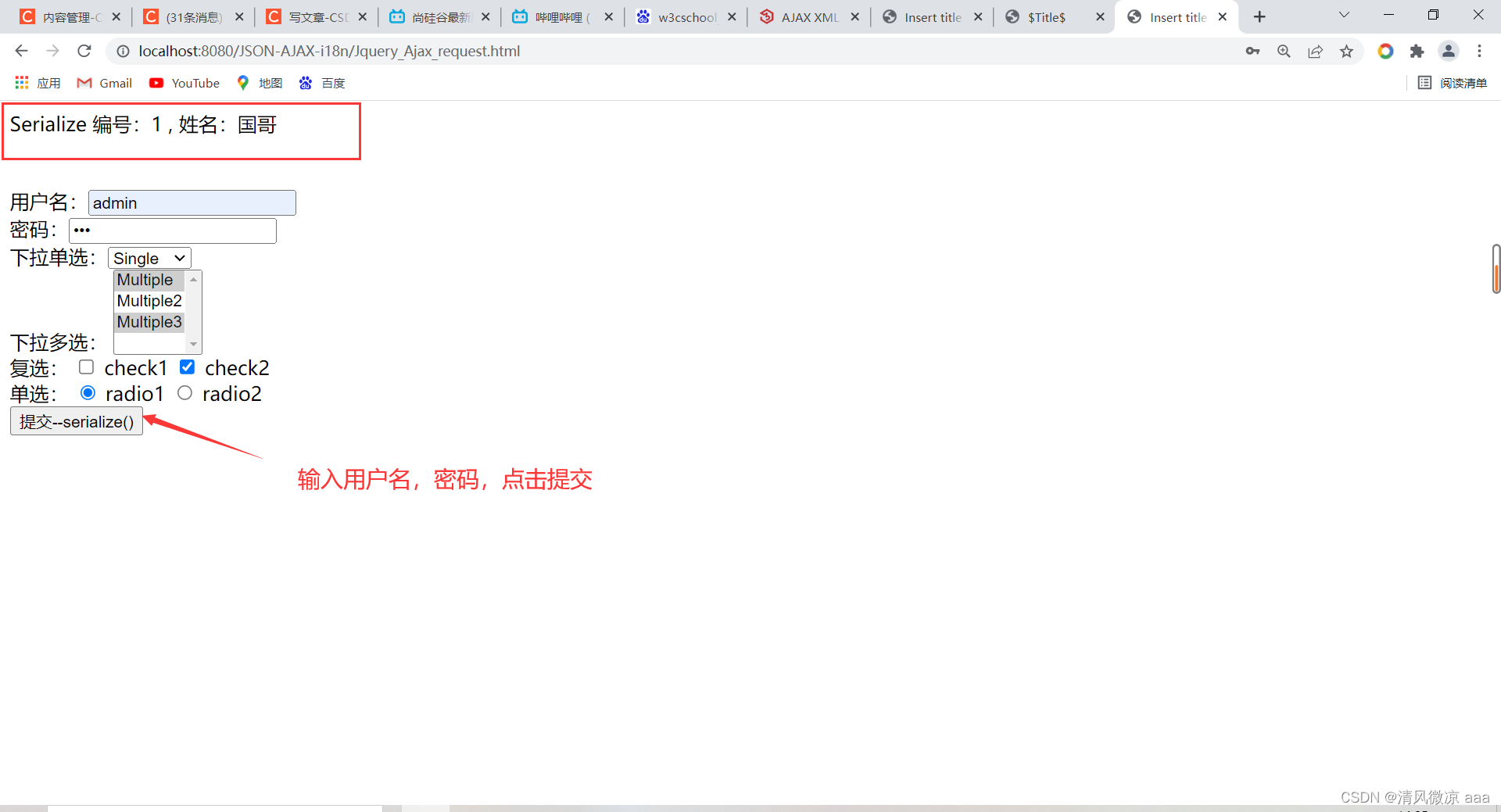
2.3.3 表单序列化 serialize() 介绍:
说明:serialize()可以把表单中所有表单项的内容都获取到,并以name=value&name=value 的形式进行拼接。
使用:在form标签上指定一个id值,之后通过id选择器选中后调用serialize()方法,在把它放到需要传参的ajax请求中。
2.3.4 表单序列化 serialize() 测试:
web.xml,BaseServlet同上。
Jquery_Ajax_request.html:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="script/jquery-1.7.2.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
// ajax请求,以getJSON请求为例
//因为这个地方还没有学框架,需要用action属性指定servlet的方法名
$("#submit").click(function(){
// 把参数序列化
$.getJSON("http://localhost:8080/JSON-AJAX-i18n/ajaxServlet","action=jQuerySerialize&" + $("#form01").serialize(),function (data) {
$("#msg").html(" Serialize 编号:" + data.id + " , 姓名:" + data.name);
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="msg">
</div>
<br/><br/>
<form id="form01" >
用户名:<input name="username" type="text" /><br/>
密码:<input name="password" type="password" /><br/>
下拉单选:<select name="single">
<option value="Single">Single</option>
<option value="Single2">Single2</option>
</select><br/>
下拉多选:
<select name="multiple" multiple="multiple">
<option selected="selected" value="Multiple">Multiple</option>
<option value="Multiple2">Multiple2</option>
<option selected="selected" value="Multiple3">Multiple3</option>
</select><br/>
复选:
<input type="checkbox" name="check" value="check1"/> check1
<input type="checkbox" name="check" value="check2" checked="checked"/> check2<br/>
单选:
<input type="radio" name="radio" value="radio1" checked="checked"/> radio1
<input type="radio" name="radio" value="radio2"/> radio2<br/>
</form>
<button id="submit">提交--serialize()</button>
</body>
</html>
AjaxServlet:
package com.atguigu.servlet;
import com.atguigu.pojo.Person;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class AjaxServlet extends BaseServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5972839860768196824L;
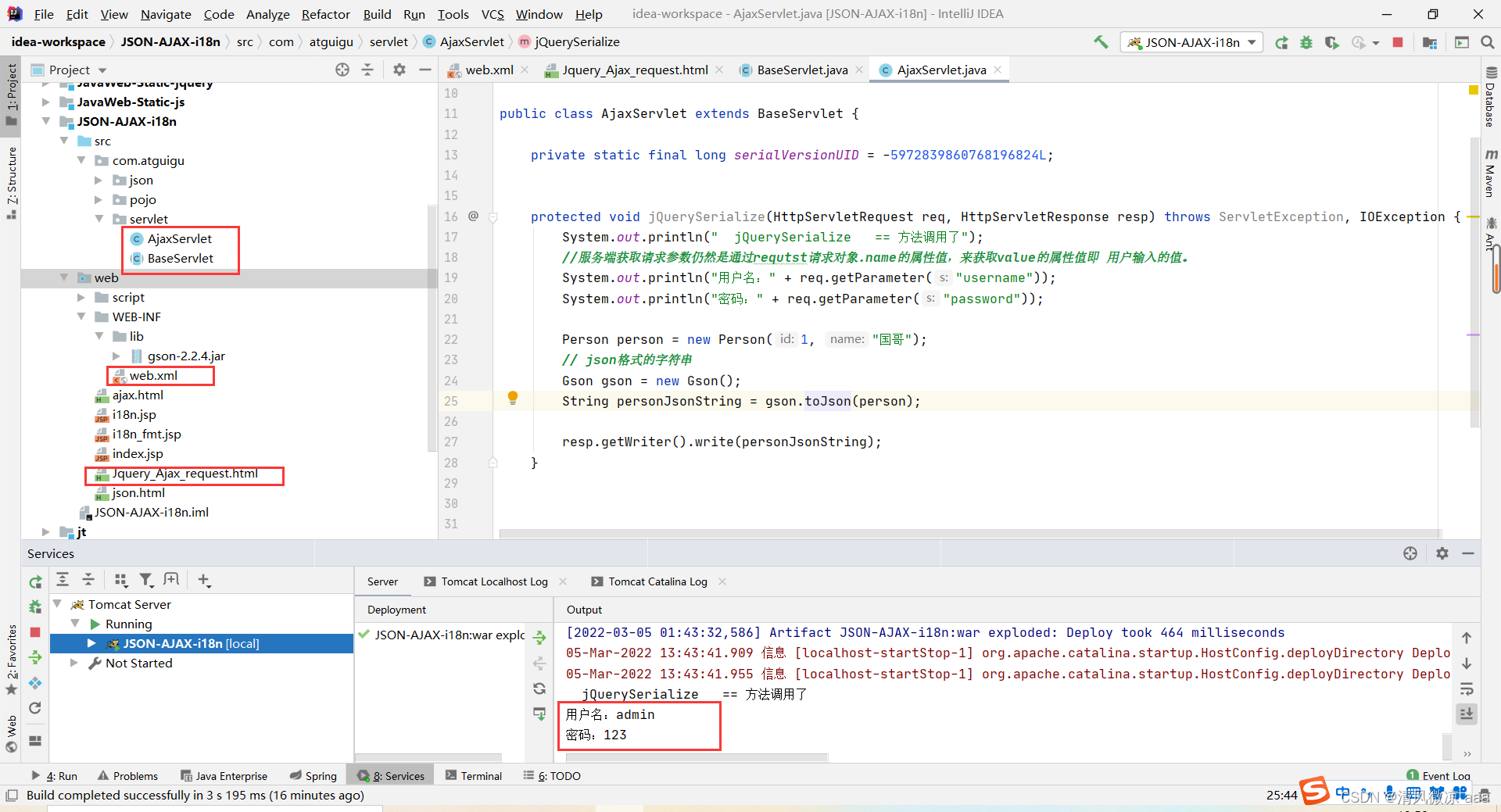
protected void jQuerySerialize(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println(" jQuerySerialize == 方法调用了");
//服务端获取请求参数仍然是通过requtst请求对象.name的属性值,来获取value的属性值即 用户输入的值。
System.out.println("用户名:" + req.getParameter("username"));
System.out.println("密码:" + req.getParameter("password"));
Person person = new Person(1, "国哥");
// json格式的字符串
Gson gson = new Gson();
String personJsonString = gson.toJson(person);
resp.getWriter().write(personJsonString);
}
}
启动tomact服务器访问Jquery_Ajax_request.html页面,并输入参数值点击提交后,发现请求发送成功并且在后台可以获取请求参数数据,说明可以通过serialize()获取表单的请求参数。
3、i18n 国际化(了解内容)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Y7411K7zz?p=320b站
3.1、什么是 i18n 国际化?
- 国际化(Internationalization)指的是同一个网站可以支持多种不同的语言,以方便不同国家,不同语种的用户访问。
- 关于国际化我们想到的最简单的方案就是为不同的国家创建不同的网站, 比如苹果公司, 他的英文官网是:http://www.apple.com 而中国官网是 http://www.apple.com/cn
- 苹果公司这种方案并不适合全部公司,而我们希望相同的一个网站,而不同人访问的时候可以根据用户所在的区域显示 不同的语言文字,而网站的布局样式等不发生改变。
- 于是就有了我们说的国际化,国际化总的来说就是同一个网站不同国家的人来访问可以显示出不同的语言。但实际上这 种需求并不强烈,一般真的有国际化需求的公司,主流采用的依然是苹果公司的那种方案,为不同的国家创建不同的页 面。所以国际化的内容我们了解一下即可。
- 国际化的英文 Internationalization,但是由于拼写过长,老外想了一个简单的写法叫做 I18N,代表的是 Internationalization这个单词,以 I 开头,以 N 结尾,而中间是 18 个字母,所以简写为 I18N。以后我们说 I18N 和国际化是一个意思。
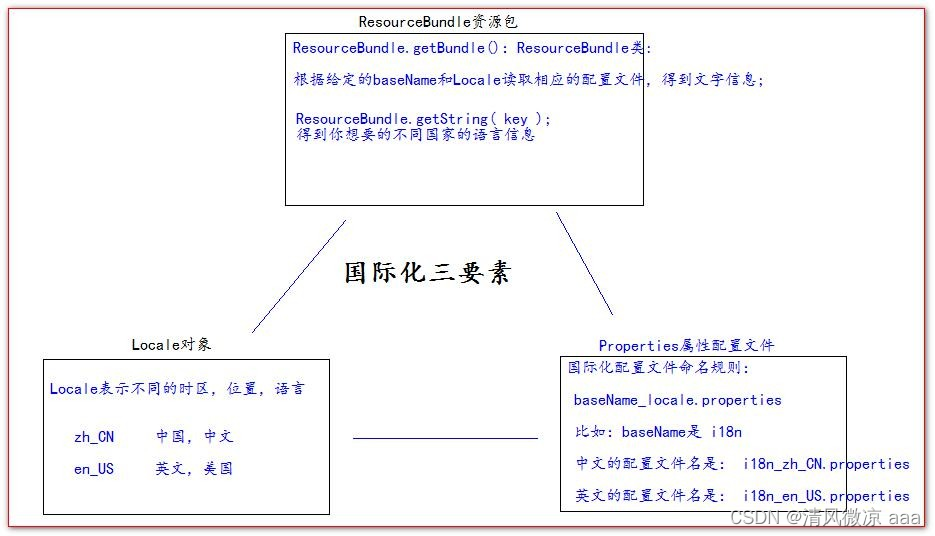
3.2、国际化相关要素介绍
3.3、国际化资源 properties 测试
配置两个语言的配置文件:
i18n_en_US.properties 英文
username=username
password=password
sex=sex
age=age
regist=regist
boy=boy
email=email
girl=girl
reset=reset
submit=submit
i18n_zh_CN.properties 中文
username=用户名
password=密码
sex=性别
age=年龄
regist=注册
boy=男
girl=女
email=邮箱
reset=重置
submit=提交
国际化测试代码:
public class I18nTest {
@Test
public void testLocale(){
// 获取你系统默认的语言。国家信息
// Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
// System.out.println(locale);
//for (Locale availableLocale : Locale.getAvailableLocales()) {
// System.out.println(availableLocale);
//}
// 获取中文,中文的常量的Locale 对象
System.out.println(Locale.CHINA);
// 获取英文,美国的常量的Locale 对象
System.out.println(Locale.US);
}
3.4、通过请求头国际化页面
<%@ page import="java.util.Locale" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.ResourceBundle" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
// 从请求头中获取Locale 信息(语言)
Locale locale = request.getLocale();
System.out.println(locale);
// 获取读取包(根据指定的baseName 和Locale 读取语言信息)
ResourceBundle i18n = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", locale);
%>
<a href="">中文</a>|
<a href="">english</a>
<center>
<h1><%=i18n.getString("regist")%></h1>
<table>
<form>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("username")%></td>
<td><input name="username" type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("password")%></td>
<td><input type="password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("sex")%></td>
<td>
<input type="radio" /><%=i18n.getString("boy")%>
<input type="radio" /><%=i18n.getString("girl")%>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("email")%></td>
<td><input type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center">
<input type="reset" value="<%=i18n.getString("reset")%>" />
<input type="submit" value="<%=i18n.getString("submit")%>" /></td>
</tr>
</form>
</table>
<br /> <br /> <br /> <br />
</center>
国际化测试:
<br /> 1、访问页面,通过浏览器设置,请求头信息确定国际化语言。
<br /> 2、通过左上角,手动切换语言
</body>
</html>
3.5、通过显示的选择语言类型进行国际化
<%@ page import="java.util.Locale" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.ResourceBundle" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
// 从请求头中获取Locale 信息(语言)
Locale locale = null;
String country = request.getParameter("country");
if ("cn".equals(country)) {
locale = Locale.CHINA;
} else if ("usa".equals(country)) {
locale = Locale.US;
} else {
locale = request.getLocale();
}
System.out.println(locale);
// 获取读取包(根据指定的baseName 和Locale 读取语言信息)
ResourceBundle i18n = ResourceBundle.getBundle("i18n", locale);
%>
<a href="i18n.jsp?country=cn">中文</a>|
<a href="i18n.jsp?country=usa">english</a>
<center>
<h1><%=i18n.getString("regist")%></h1>
<table>
<form>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("username")%></td>
<td><input name="username" type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("password")%></td>
<td><input type="password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("sex")%></td>
<td>
<input type="radio" /><%=i18n.getString("boy")%>
<input type="radio" /><%=i18n.getString("girl")%>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><%=i18n.getString("email")%></td>
<td><input type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center">
<input type="reset" value="<%=i18n.getString("reset")%>" />
<input type="submit" value="<%=i18n.getString("submit")%>" /></td>
</tr>
</form>
</table>
<br /> <br /> <br /> <br />
</center>
国际化测试:
<br /> 1、访问页面,通过浏览器设置,请求头信息确定国际化语言。
<br /> 2、通过左上角,手动切换语言
</body>
</html>
3.6、JSTL 标签库实现国际化
<%--1 使用标签设置Locale 信息--%>
<fmt:setLocale value="" />
<%--2 使用标签设置baseName--%>
<fmt:setBundle basename=""/>
<%--3 输出指定key的国际化信息--%>
<fmt:message key="" />
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache" />
<meta http-equiv="Expires" content="0" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%--1 使用标签设置Locale 信息--%>
<fmt:setLocale value="${param.locale}" />
<%--2 使用标签设置baseName--%>
<fmt:setBundle basename="i18n"/>
<a href="i18n_fmt.jsp?locale=zh_CN">中文</a>|
<a href="i18n_fmt.jsp?locale=en_US">english</a>
<center>
<h1><fmt:message key="regist" /></h1>
<table>
<form>
<tr>
<td><fmt:message key="username" /></td>
<td><input name="username" type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><fmt:message key="password" /></td>
<td><input type="password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><fmt:message key="sex" /></td>
<td>
<input type="radio" /><fmt:message key="boy" />
<input type="radio" /><fmt:message key="girl" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><fmt:message key="email" /></td>
<td><input type="text" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center">
<input type="reset" value="<fmt:message key="reset" />" />
<input type="submit" value="<fmt:message key="submit" />" /></td>
</tr>
</form>
</table>
<br /> <br /> <br /> <br />
</center>
</body>
</html>
总结
写到这里也结束了,在文章最后放上一个小小的福利,以下为小编自己在学习过程中整理出的一个关于 java开发 的学习思路及方向。从事互联网开发,最主要的是要学好技术,而学习技术是一条慢长而艰苦的道路,不能靠一时激情,也不是熬几天几夜就能学好的,必须养成平时努力学习的习惯,更加需要准确的学习方向达到有效的学习效果。
由于内容较多就只放上一个大概的大纲,需要更及详细的学习思维导图的 点击我的Gitee获取。
还有 高级java全套视频教程 java进阶架构师 视频+资料+代码+面试题!
全方面的java进阶实践技术资料,并且还有技术大牛一起讨论交流解决问题。
























 298
298











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








