一、改造HashTable
实现了哈希表(开散列),再将其封装为unordered_map和unordered_set。
HashTable的改造与RBTree的改造大致相同:
- 改造节点
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
//std::pair<K, V> _kv;
//HashNode<K, V>* _next;
T _data;
HashNode<T>* _next;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
- 改造HashTable
// 这里的Hash可以不用给缺省参数,由上层传递
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{
public:
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
// ……
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
KeyOfT kot; // --> 用kot获取data中的key
if (Find(kot(data)))
return false;
// ……
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
// ……
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfT()(cur->_data) == key)
{
return cur;
}
else
{
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
// ……
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfT()(cur->_data) == key)
{
// ……
}
// ……
}
}
private:
std::vector<Node*> _tables;// 指针数组
size_t _n = 0;
};
- unordered_map:
namespace nb
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const std::pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
private:
bucketHash::HashTable < K, std::pair<const K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT> _ht;
};
};
- unordered_set:
namespace nb
{
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
private:
bucketHash::HashTable <K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT> _ht;
};
};
二、实现迭代器
首先要知道的是哈希表的迭代器是单向迭代器,先看源码的实现:
迭代器类:

operator++:
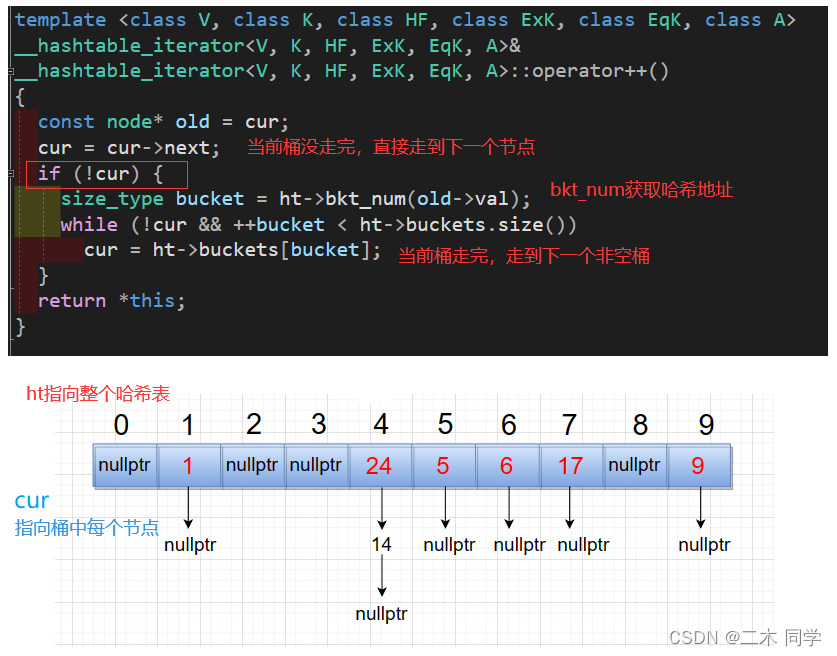
- 迭代器类
// 类的前置声明
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
struct _HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next) // node下一个不为空走到下一个节点
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else // node的下一个为空找非空桶
{
// 计算哈希地址
size_t hashi = Hash()(KeyOfT()(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();
++hashi;
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi])//找到非空桶
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
// 所有桶走完了,走到end
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
_node = nullptr;
return *this;
}
}
bool operator != (const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
Node* _node;
HT* _ht;
};
HashTable层:
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{
// 声明 _HTIterator 为HashTable类的友元
// 可以让 _HTIterator 结构体访问哈希表中的私有成员和保护成员
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
friend struct _HTIterator;
public:
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
return iterator(_tables[i], this);
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
};
源码中const迭代器并没有复用普通迭代器的代码:
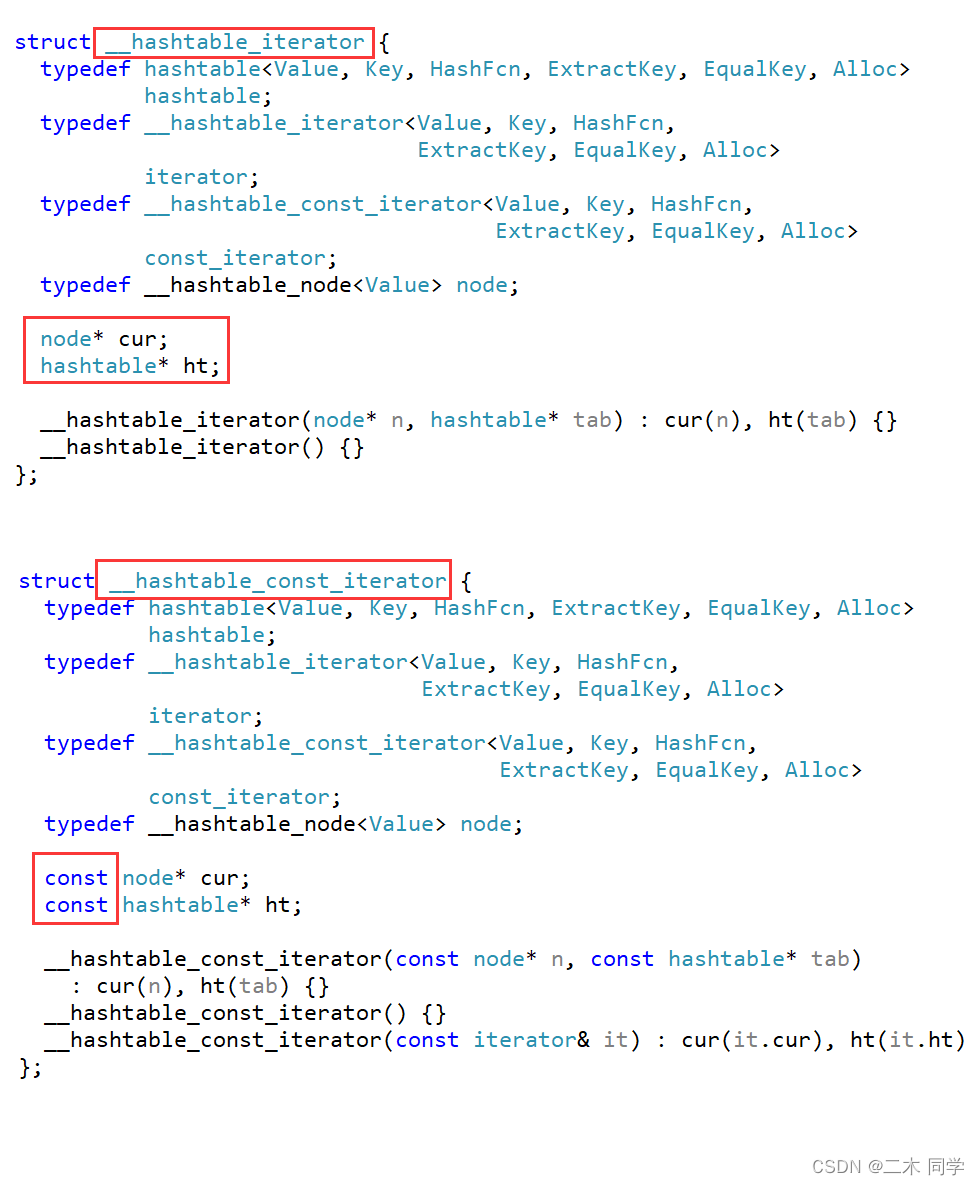
为什么不复用?为什么不按照之前map和set迭代器的实现方式呢?实现一遍看看有什么问题
- 迭代器类:
//template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
struct _HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
//typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, T&, T*, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
_HTIterator(Node* node, HT* ht)
:_node(node)
, _ht(ht)
{}
//T& operator*()
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//T* operator->()
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
// ……
Node* _node;
HT* _ht;
};
- HashTable:
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
class HashTable
{
// 声明 _HTIterator 为HashTable类的友元
// 可以让 _HTIterator 结构体访问哈希表中的私有成员和保护成员
//template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
//friend struct _HTIterator;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
friend struct _HTIterator;
public:
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
//typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, T&, T*, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;
// const迭代器复用普通迭代器代码
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, Hash, KeyOfT> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
return iterator(_tables[i], this);
}
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this);
}
// const迭代器
const_iterator begin() const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
if (_tables[i])
return const_iterator(_tables[i], this);
}
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
}
// ……
std::vector<Node*> _tables;// 指针数组
size_t _n = 0;
};
- unordered_map:
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const std::pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
// 普通迭代器
typedef typename bucketHash::HashTable<K, std::pair<const K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
// const迭代器
typedef typename bucketHash::HashTable<K, std::pair<const K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
// const迭代器
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
// ……
private:
bucketHash::HashTable < K, std::pair<const K, V>, Hash, MapKeyOfT> _ht;
};
- unordered_set:
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
// 注意typename的使用
typedef typename bucketHash::HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename bucketHash::HashTable<K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _ht.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _ht.end();
}
std::pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Insert(key);
}
private:
bucketHash::HashTable <K, K, Hash, SetKeyOfT> _ht;
};
unordered_set的普通迭代器与set的迭代器一样也不能修改key,所以普通迭代器(unordered_set层)也是const迭代器(HashTable层)
测试unordered_map:
void TestMap()
{
std::string arr[] = { "cherry" };
unordered_map<std::string, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
// it是const迭代器,countMap.begin()是普通迭代器无法转换
nb::unordered_map<std::string, int>::const_iterator it = countMap.begin();// Error
while (it != countMap.end())// Error:没有匹配的运算符
{
std::cout << it->first << " " << it->second << std::endl;
++it;
}
}
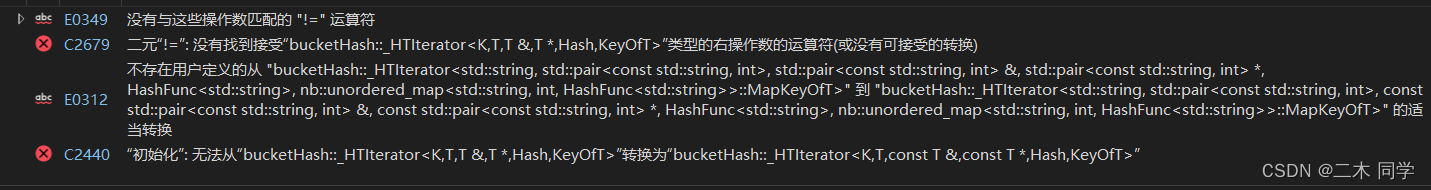
这里如果我们实现一个像RBTree迭代器一样的特殊构造那么就可以解决。
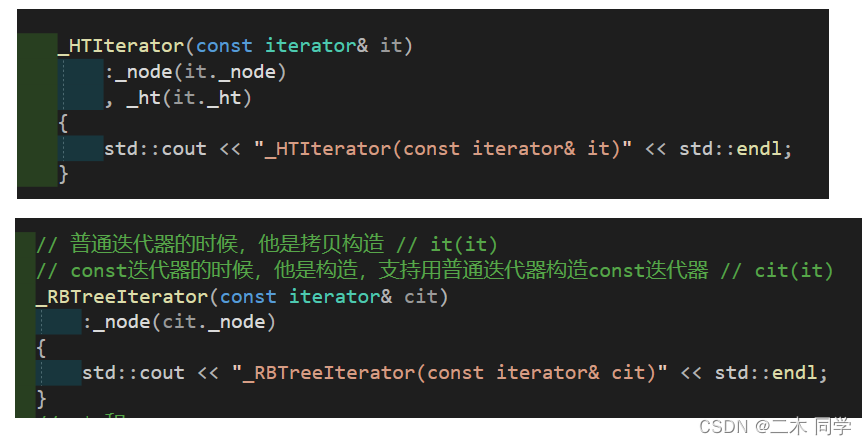
再测试就没有问题:
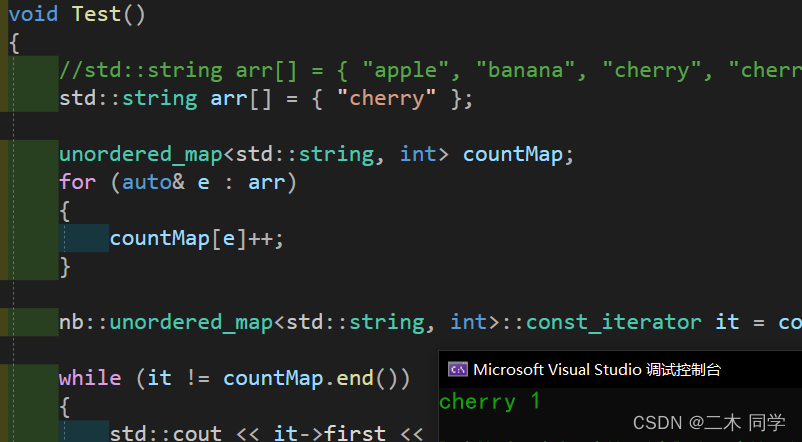
再来测试unordered_set:
void test()
{
nb::unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(13);
nb::unordered_set<int>::const_iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
也没问题:
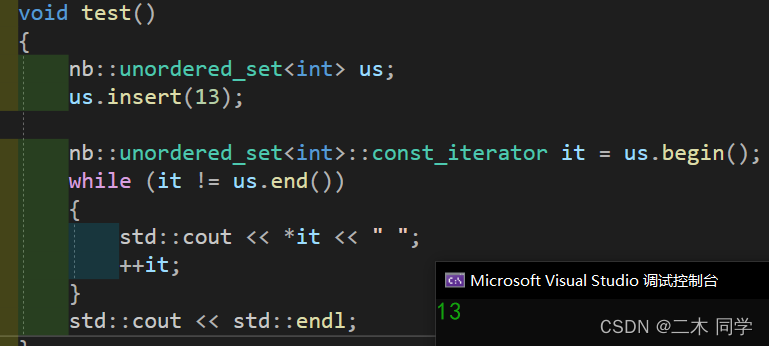
再看一段测试代码:
void func(const unordered_set<int>& us)
{
unordered_set<int>::const_iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
cout << *it << endl;
++it;
}
}
void test()
{
unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(10);
func(us);
}
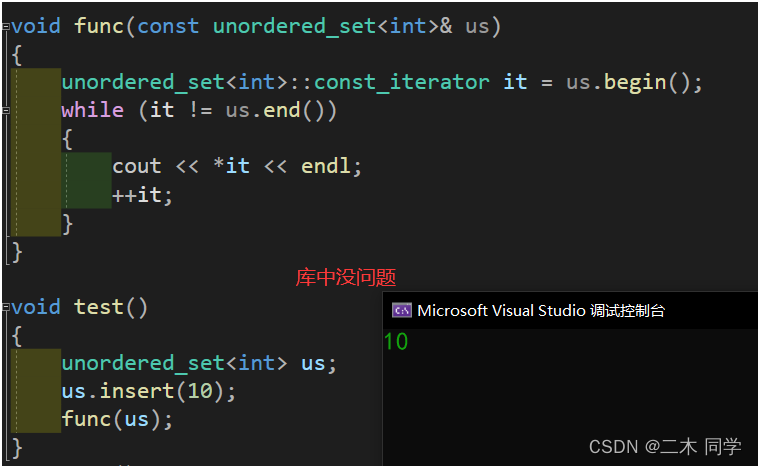
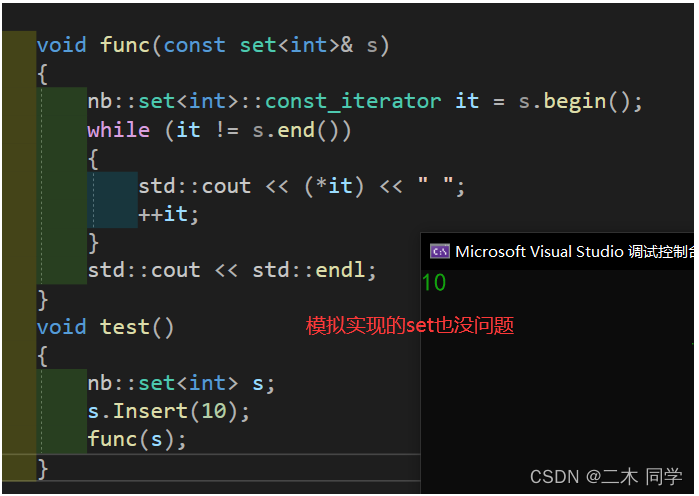
再看看我们模拟实现的unordered_set:
void func(const unordered_set<int>& us)
{
nb::unordered_set<int>::const_iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void test()
{
nb::unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(10);
}
结果编译错误:
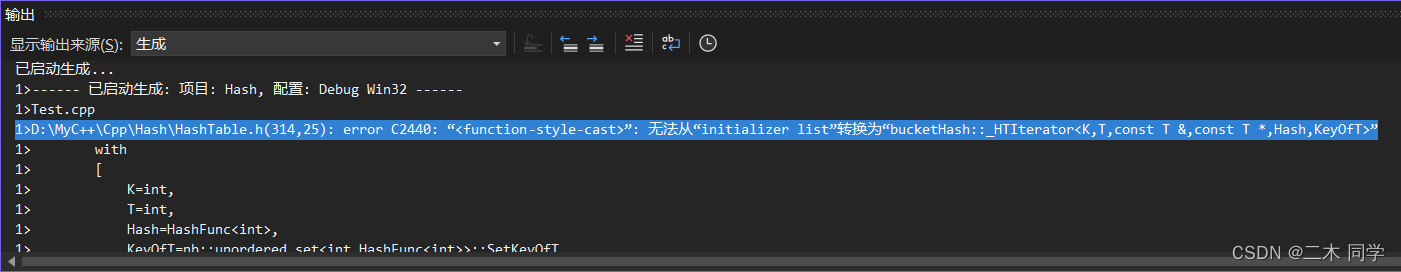

错误分析:
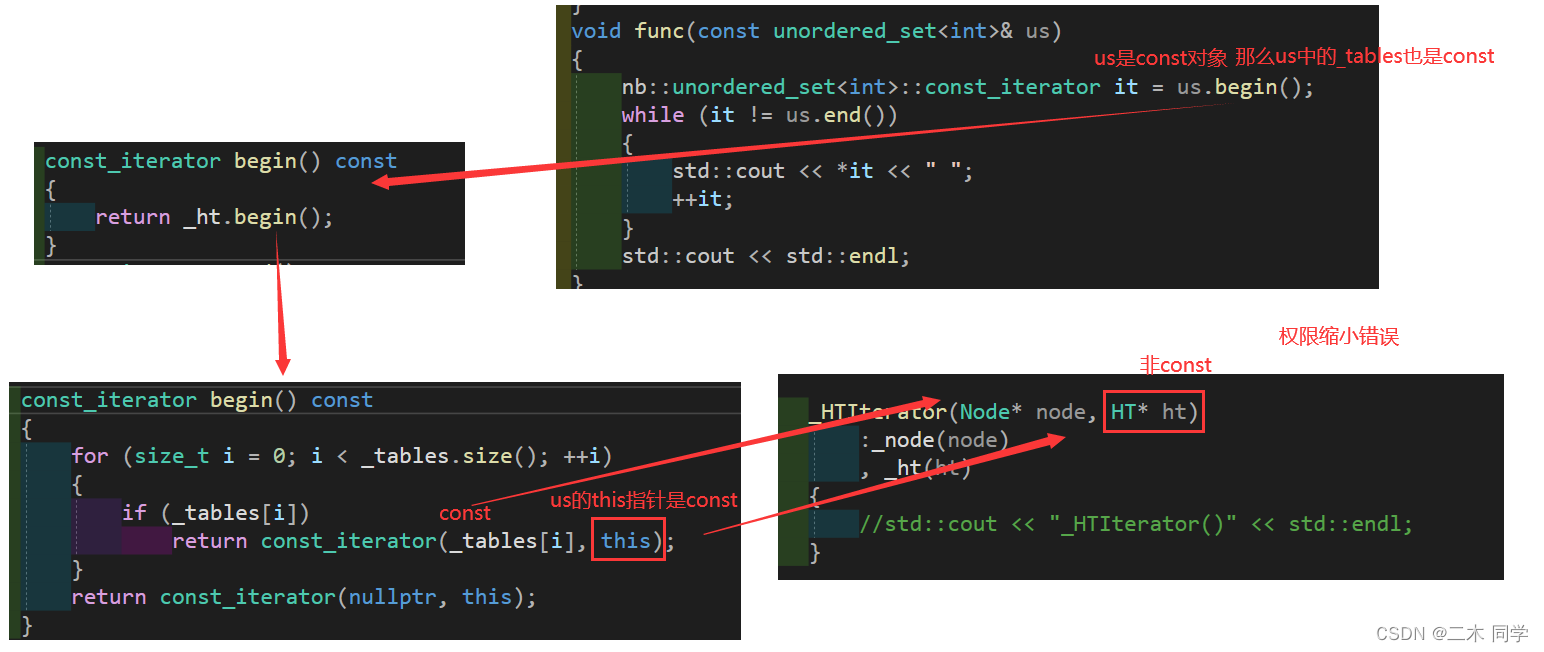
那把迭代器的构造改成const Node*和const HT*?
答案是不行,因为这样一改,迭代器的成员变量也要跟着改,这样迭代器就只能被const对象使用了。
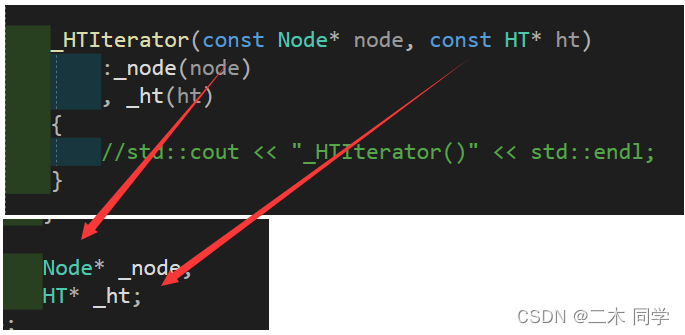
所以普通迭代器和const迭代器需要分开实现。这样一来有多处代码需要改动具体见代码,当然本文的实现肯定是没有STL库中的好,我们只需要知道底层实现逻辑即可,而不是造一个更好的轮子。
// const迭代器类
template<class K, class T, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
//template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class Hash, class KeyOfT>
struct const_HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;
typedef const_HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> const_iterator;
typedef const_HTIterator<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
//typedef _HTIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, Hash, KeyOfT> Self;
//typedef _HTIterator<K, T, T&, T*, Hash, KeyOfT> iterator;
typedef HashTable<K, T, Hash, KeyOfT> HT;
const_HTIterator(const Node* node, const HT* ht)
:_node(node)
, _ht(ht)
{
//std::cout << "_HTIterator()" << std::endl;
}
// 普通迭代器构造const迭代器
const_HTIterator(const iterator& it)
:_node(it._node)
, _ht(it._ht)
{
std::cout << "iterator --> const_iterator" << std::endl;
}
const T& operator*()
//Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
const T* operator->()
//Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_next) // node下一个不为空走到下一个节点
{
_node = _node->_next;
}
else // node的下一个为空找非空桶
{
// 计算哈希地址
size_t hashi = Hash()(KeyOfT()(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();
++hashi;
while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())
{
if (_ht->_tables[hashi])//找到非空桶
{
_node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
break;
}
else
{
++hashi;
}
}
// 所有桶走完了,走到end
if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())
_node = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator != (const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator == (const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
const Node* _node;
const HT* _ht;
};
unordered_map和unordered_set的模拟实现-GitHub
如有错误,望指正🌹























 680
680











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










