A. Wrong Subtraction
Little girl Tanya is learning how to decrease a number by one, but she does it wrong with a number consisting of two or more digits. Tanya subtracts one from a number by the following algorithm:
- if the last digit of the number is non-zero, she decreases the number by one;
- if the last digit of the number is zero, she divides the number by 10 (i.e. removes the last digit).
You are given an integer number n n n. Tanya will subtract one from it k k k times. Your task is to print the result after all k k k subtractions.
It is guaranteed that the result will be positive integer number.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integer numbers n n n and k k k ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 9 2 \le n \le 10^9 2≤n≤109, 1 ≤ k ≤ 50 1 \le k \le 50 1≤k≤50) — the number from which Tanya will subtract and the number of subtractions correspondingly.
Output
Print one integer number — the result of the decreasing n n n by one k k k times.
It is guaranteed that the result will be positive integer number.
Example
input1
514 4
output1
50
input2
1000000000 9
output2
1
Tutorial
根据题意直接模拟即可,时间复杂度为
O
(
k
)
O(k)
O(k)
Solution
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
)
var in = bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
var out = bufio.NewWriter(os.Stdout)
func solve() {
var n, k int
fmt.Fscan(in, &n, &k)
for k > 0 {
if n % 10 > 0 {
n--
} else {
n /= 10
}
k--
}
fmt.Println(n)
}
func main() {
defer out.Flush()
solve()
}
B. Two-gram
Two-gram is an ordered pair (i.e. string of length two) of capital Latin letters. For example, “AZ”, “AA”, “ZA” — three distinct two-grams.
You are given a string s s s consisting of n n n capital Latin letters. Your task is to find any two-gram contained in the given string as a substring (i.e. two consecutive characters of the string) maximal number of times. For example, for string s s s = “BBAABBBA” the answer is two-gram “BB”, which contained in s s s three times. In other words, find any most frequent two-gram.
Note that occurrences of the two-gram can overlap with each other.
Input
The first line of the input contains integer number n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 100 2 \le n \le 100 2≤n≤100) — the length of string s s s. The second line of the input contains the string s s s consisting of n n n capital Latin letters.
Output
Print the only line containing exactly two capital Latin letters — any two-gram contained in the given string s s s as a substring (i.e. two consecutive characters of the string) maximal number of times.
Example
input1
7
ABACABA
output1
AB
input2
5
ZZZAA
output2
ZZ
Note
In the first example “BA” is also valid answer.
In the second example the only two-gram “ZZ” can be printed because it contained in the string “ZZZAA” two times.
Tutorial
使用计数器记录每个长度为2的子字符串出现的次数,最后取出现最多的字符串即可
Solution
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
)
var in = bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
var out = bufio.NewWriter(os.Stdout)
func solve() {
var n int
var s, ans string
fmt.Fscan(in, &n, &s)
mp, l, cnt := make(map[string]int), len(s), 0
for i := 1; i < l; i++ {
mp[s[i - 1:i + 1]]++
}
for str, times := range mp {
if times > cnt {
ans, cnt = str, times
}
}
fmt.Println(ans)
}
func main() {
defer out.Flush()
solve()
}
C. Less or Equal
You are given a sequence of integers of length n n n and integer number k k k. You should print any integer number x x x in the range of [ 1 ; 1 0 9 ] [1; 10^9] [1;109] (i.e. 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le x \le 10^9 1≤x≤109) such that exactly k k k elements of given sequence are less than or equal to x x x.
Note that the sequence can contain equal elements.
If there is no such x x x, print “-1” (without quotes).
Input
The first line of the input contains integer numbers n n n and k k k ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤n≤2⋅105, 0 ≤ k ≤ n 0 \le k \le n 0≤k≤n). The second line of the input contains n n n integer numbers a 1 , a 2 , … , a n a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n a1,a2,…,an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le a_i \le 10^9 1≤ai≤109) — the sequence itself.
Output
Print any integer number x x x from range [ 1 ; 1 0 9 ] [1; 10^9] [1;109] such that exactly k k k elements of given sequence is less or equal to x x x.
If there is no such x x x, print “-1” (without quotes).
Example
input1
7 4
3 7 5 1 10 3 20
output1
6
input2
7 2
3 7 5 1 10 3 20
output2
-1
Note
In the first example 5 5 5 is also a valid answer because the elements with indices [ 1 , 3 , 4 , 6 ] [1, 3, 4, 6] [1,3,4,6] is less than or equal to 5 5 5 and obviously less than or equal to 6 6 6.
In the second example you cannot choose any number that only 2 2 2 elements of the given sequence will be less than or equal to this number because 3 3 3 elements of the given sequence will be also less than or equal to this number.
Tutorial
先将数组排序,取子序列问题就转换为了取子区间,接下来就直接分多种情况讨论即可:
- 当 k = n k = n k=n 时,数组中最大的值即可满足题意
- 当 k = 0 k = 0 k=0 时,需要判断 a i a_i ai 是否为 1 1 1,如果为 1 1 1,那么无法找到一个数 x x x 满足 1 ≤ x ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le x \le 10^9 1≤x≤109 的同时还满足题意的,如果 a i a_i ai 不为 1 1 1,那么 x x x 直接取 1 1 1 即可
- 其他情况时,直接找到数组中第 k k k 个数和第 k + 1 k + 1 k+1 个数进行判断即可,如果 a i = a i + 1 a_i = a_{i + 1} ai=ai+1 ,此时怎么取 x x x 都无法使满足条件的数刚好等于 k k k,否则 x x x 直接取 a i a_i ai 即可
Solution
package main
import (
"bufio"
. "fmt"
"os"
"sort"
)
var in = bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
var out = bufio.NewWriter(os.Stdout)
func solve() {
var n, k int
Fscan(in, &n, &k)
a := make([]int, n)
for i := range a {
Fscan(in, &a[i])
}
sort.Ints(a)
if k == n {
Println(a[n - 1])
} else if k == 0 {
if a[0] == 1 {
Println(-1)
} else {
Println(1)
}
} else if a[k] == a[k - 1] {
Println(-1)
} else {
Println(a[k - 1])
}
}
func main() {
defer out.Flush()
solve()
}
D. Divide by three, multiply by two
Polycarp likes to play with numbers. He takes some integer number x x x, writes it down on the board, and then performs with it n − 1 n - 1 n−1 operations of the two kinds:
- divide the number x x x by 3 3 3 ( x x x must be divisible by 3 3 3);
- multiply the number x x x by 2 2 2.
After each operation, Polycarp writes down the result on the board and replaces x x x by the result. So there will be n n n numbers on the board after all.
You are given a sequence of length n n n — the numbers that Polycarp wrote down. This sequence is given in arbitrary order, i.e. the order of the sequence can mismatch the order of the numbers written on the board.
Your problem is to rearrange (reorder) elements of this sequence in such a way that it can match possible Polycarp’s game in the order of the numbers written on the board. I.e. each next number will be exactly two times of the previous number or exactly one third of previous number.
It is guaranteed that the answer exists.
Input
The first line of the input contatins an integer number n n n ( 2 ≤ n ≤ 100 2 \le n \le 100 2≤n≤100) — the number of the elements in the sequence. The second line of the input contains n n n integer numbers a 1 , a 2 , … , a n a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n a1,a2,…,an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 3 ⋅ 1 0 18 1 \le a_i \le 3 \cdot 10^{18} 1≤ai≤3⋅1018) — rearranged (reordered) sequence that Polycarp can wrote down on the board.
Output
Print n n n integer numbers — rearranged (reordered) input sequence that can be the sequence that Polycarp could write down on the board.
It is guaranteed that the answer exists.
Example
input1
6
4 8 6 3 12 9
output1
9 3 6 12 4 8
input2
4
42 28 84 126
output2
126 42 84 28
Note
In the first example the given sequence can be rearranged in the following way: [ 9 , 3 , 6 , 12 , 4 , 8 ] [9, 3, 6, 12, 4, 8] [9,3,6,12,4,8]. It can match possible Polycarp’s game which started with x = 9 x = 9 x=9.
Tutorial
因为题目保证答案存在,则可以直接判断每个数能除以多少次 3,直接根据除以3的次数从大到小排序即可
Solution
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
def f(x):
ans = 0
while x % 3 == 0:
x //= 3
ans += 1
return -ans
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
a.sort(key=lambda x:(f(x), x))
print(*a)
E. Cyclic Components
You are given an undirected graph consisting of n n n vertices and m m m edges. Your task is to find the number of connected components which are cycles.
Here are some definitions of graph theory.
An undirected graph consists of two sets: set of nodes (called vertices) and set of edges. Each edge connects a pair of vertices. All edges are bidirectional (i.e. if a vertex a a a is connected with a vertex b b b, a vertex b b b is also connected with a vertex a a a). An edge can’t connect vertex with itself, there is at most one edge between a pair of vertices.
Two vertices u u u and v v v belong to the same connected component if and only if there is at least one path along edges connecting u u u and v v v.
A connected component is a cycle if and only if its vertices can be reordered in such a way that:
- the first vertex is connected with the second vertex by an edge,
- the second vertex is connected with the third vertex by an edge,
- …
- the last vertex is connected with the first vertex by an edge,
- all the described edges of a cycle are distinct.
A cycle doesn’t contain any other edges except described above. By definition any cycle contains three or more vertices.
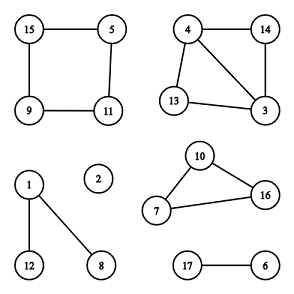
There are 6 6 6 connected components, 2 2 2 of them are cycles: [ 7 , 10 , 16 ] [7, 10, 16] [7,10,16] and [ 5 , 11 , 9 , 15 ] [5, 11, 9, 15] [5,11,9,15].
Input
The first line contains two integer numbers n n n and m m m ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤n≤2⋅105, 0 ≤ m ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 0 \le m \le 2 \cdot 10^5 0≤m≤2⋅105) — number of vertices and edges.
The following m m m lines contains edges: edge i i i is given as a pair of vertices v i v_i vi, u i u_i ui ( 1 ≤ v i , u i ≤ n 1 \le v_i, u_i \le n 1≤vi,ui≤n, u i ≠ v i u_i \ne v_i ui=vi). There is no multiple edges in the given graph, i.e. for each pair ( v i , u i v_i, u_i vi,ui) there no other pairs ( v i , u i v_i, u_i vi,ui) and ( u i , v i u_i, v_i ui,vi) in the list of edges.
Output
Print one integer — the number of connected components which are also cycles.
Example
input1
5 4
1 2
3 4
5 4
3 5
output1
1
input2
17 15
1 8
1 12
5 11
11 9
9 15
15 5
4 13
3 13
4 3
10 16
7 10
16 7
14 3
14 4
17 6
output2
2
Note
In the first example only component [ 3 , 4 , 5 ] [3, 4, 5] [3,4,5] is also a cycle.
The illustration above corresponds to the second example.
Tutorial
用
D
F
S
DFS
DFS 或
B
F
S
BFS
BFS 找到图的连通分量,如果连通分量是一个循环,当且仅当其每个顶点的度数都等于 2,如果不等于 2说明这不是一个循环的连接组件
以下仅提供 D F S DFS DFS 做法
Solution
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
void solve() {
int n, m, u, v, ans = 0;
bool flag;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> g[n + 1];
vector<bool> memo(n + 1, false);
while (m--) {
cin >> u >> v;
g[u].emplace_back(v);
g[v].emplace_back(u);
}
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int u) {
if (memo[u]) {
return;
}
memo[u] = true;
flag |= g[u].size() != 2;
for (int v : g[u]) {
dfs(v);
}
};
for (int u = 1; u <= n; ++u) {
if (not memo[u]) {
flag = false;
dfs(u);
ans += not flag;
}
}
cout << ans;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(15);
solve();
return 0;
}
F. Consecutive Subsequence
You are given an integer array of length n n n.
You have to choose some subsequence of this array of maximum length such that this subsequence forms a increasing sequence of consecutive integers. In other words the required sequence should be equal to [ x , x + 1 , … , x + k − 1 ] [x, x + 1, \dots, x + k - 1] [x,x+1,…,x+k−1] for some value x x x and length k k k.
Subsequence of an array can be obtained by erasing some (possibly zero) elements from the array. You can erase any elements, not necessarily going successively. The remaining elements preserve their order. For example, for the array [ 5 , 3 , 1 , 2 , 4 ] [5, 3, 1, 2, 4] [5,3,1,2,4] the following arrays are subsequences: [ 3 ] [3] [3], [ 5 , 3 , 1 , 2 , 4 ] [5, 3, 1, 2, 4] [5,3,1,2,4], [ 5 , 1 , 4 ] [5, 1, 4] [5,1,4], but the array [ 1 , 3 ] [1, 3] [1,3] is not.
Input
The first line of the input containing integer number n n n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 1 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 1≤n≤2⋅105) — the length of the array. The second line of the input containing n n n integer numbers a 1 , a 2 , … , a n a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n a1,a2,…,an ( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1 0 9 1 \le a_i \le 10^9 1≤ai≤109) — the array itself.
Output
On the first line print k k k — the maximum length of the subsequence of the given array that forms an increasing sequence of consecutive integers.
On the second line print the sequence of the indices of the any maximum length subsequence of the given array that forms an increasing sequence of consecutive integers.
Example
input1
7
3 3 4 7 5 6 8
output1
4
2 3 5 6
input2
9
6 7 8 3 4 5 9 10 11
output2
6
1 2 3 7 8 9
Note
All valid answers for the first example (as sequences of indices):
- [ 1 , 3 , 5 , 6 ] [1, 3, 5, 6] [1,3,5,6]
- [ 2 , 3 , 5 , 6 ] [2, 3, 5, 6] [2,3,5,6]
All valid answers for the second example:
- [ 1 , 4 ] [1, 4] [1,4]
- [ 2 , 5 ] [2, 5] [2,5]
- [ 3 , 6 ] [3, 6] [3,6]
All valid answers for the third example:
- [ 1 ] [1] [1]
- [ 2 ] [2] [2]
- [ 3 ] [3] [3]
- [ 4 ] [4] [4]
All valid answers for the fourth example:
- [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 ] [1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9] [1,2,3,7,8,9]
Tutorial
根据题意可知,需要找到最大长度的某个子序列,使该子序列形成连续整数的递增序列,看到这里就应该想到解决这题需要动态规划
初始状态下每个数的状态都应该是0,每到一个数
x
x
x 它的计数状态都应该由
x
+
1
x + 1
x+1 的计数状态转移过来,由此可以得到状态转移方程:
d
p
[
a
i
]
=
m
a
x
(
d
p
[
a
i
]
,
d
p
[
a
i
−
1
]
+
1
)
dp[a_i] = max(dp[a_i], dp[a_i - 1] + 1)
dp[ai]=max(dp[ai],dp[ai−1]+1)
最后找出最长的那条路,直接依次输出即可
Solution
package main
import (
"bufio"
. "fmt"
"os"
)
var in = bufio.NewReader(os.Stdin)
var out = bufio.NewWriter(os.Stdout)
func solve() {
var n int
Fscan(in, &n)
cnt, mx := 0, 0
a, dp := make([]int, n), map[int]int{}
for i := range a {
Fscan(in, &a[i])
dp[a[i]] = dp[a[i] - 1] + 1
if dp[a[i]] > cnt {
cnt = dp[a[i]]
mx = a[i]
}
}
Println(cnt)
mx -= cnt - 1
for i, x := range(a) {
if x == mx {
Printf("%d ", i + 1)
mx++
}
}
Println()
}
func main() {
defer out.Flush()
solve()
}





















 1887
1887

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








