1.节点流
字节节点流: 万能流
FileInputStream: 文件字节输入流
FileOutputStream: 文件字节输出流
字符节点流: 对文本文件进行读写: word文档不是文本文件
FileReader :文件字符输入流
FileWriter :文件字符输出流
1.1 FileInputStream: 文件字节输入流
构造方法:
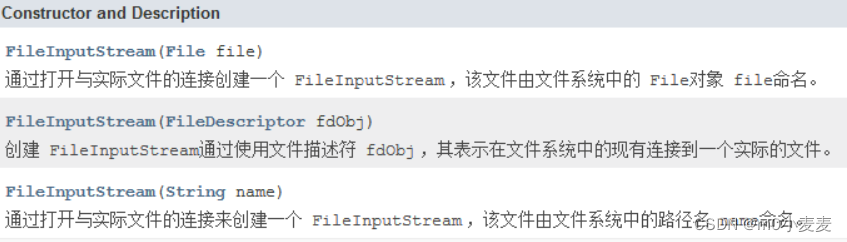
常用方法:
-
-
voidclose()关闭此文件输入流并释放与流相关联的任何系统资源。
-
-
-
intread()从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。intread(byte[] b)从该输入流读取最多b.length个字节的数据为字节数组。intread(byte[] b, int off, int len)从该输入流读取最多len字节的数据为字节数组。
-
注意事项:
字节输入流的read()方法如果读到文件末尾, 返回-1
//read() 一次只读一个字节 编码 返回的读到内容编码 //read(byte[] b) 把读到字节缓存到byte数组中 返回的是 读到的字节长度
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("d:/hello.txt");//1.创建IO流对象
int rs = -1;//设一个标志值,如果返回-1则表示文件已读完毕
byte[] b = new byte[5];
while((rs=fis.read(b)) != -1){
//read() 一次只能读一个字节
//read(byte[] b) 把读到字节缓存到byte数组中 返回的是 读到的字节长度
//System.out.print((char)rs);//把byte[] 转换为字符串
System.out.println(rs);
//String(byte[], offset, len)
// 从byte[] 数组中指定offset下标开始, 读len个字节
String s = new String(b,0,rs);
System.out.println(s);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(fis != null){//如果文件不为空则关闭
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.2FileOutp
utStream: 文件字节输出流
构造函数:

常用方法:
-
-
voidwrite(byte[] b)将b.length个字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流。voidwrite(byte[] b, int off, int len)将len字节从位于偏移量off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流。
-
注意事项:
如果构造函数中的
file参数的文件不存在, 会自动创建文件, 但是如果目录不存在, 无法创建如果在创建对象时没有指定append参数, 默认值:
false,表示不追加,即每次往文件写内容, 先把文件的内容清空,再写(覆盖之前的文件内容),如果手动设置append的参数为true, 表示追加
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("d:/a.txt",true);//1.创建IO对象
String str = "\nhello world\n";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();//需要把字符串转换为byte数组
fos.write(bytes);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(fos!=null){//如果文件不为空则关闭
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
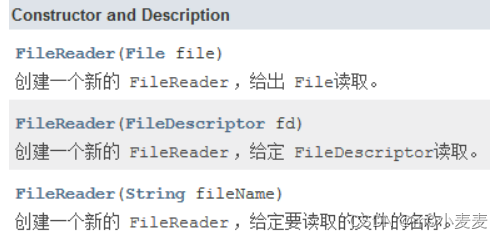
1.3 FileReader :文件字符输入流
构造函数:
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("d:/hello.txt");//1.创建IO流对象
int rs = -1;//设一个标志值,如果返回-1则表示文件已读完毕
while((rs = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)rs);
}
} catch (
FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (
IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(fr != null){
fr.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
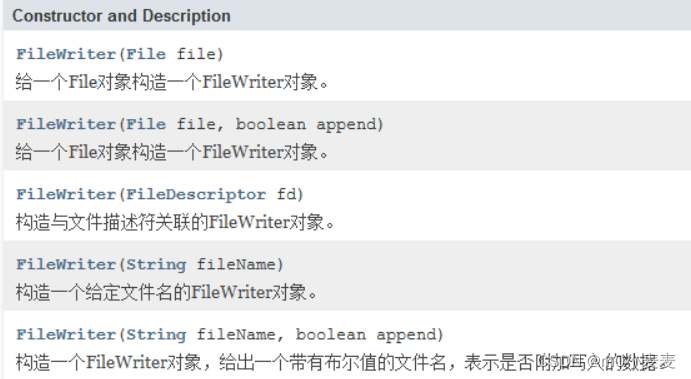
1.4FileWriter :文件字符输出流
构造方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("d:/a.txt",true);//1.创建IO对象
String str = "\n你好 世界\n";
fw.write(str);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(fw!=null){
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.缓冲流(处理流)
2.1BufferedReader: 缓冲字符输入流
构造方法:

处理流: 单独使用, 一定需要接在其他流上, 节点流
ObjectOutputStream oos = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; fos = new FileOutputStream("stu.txt"); oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);BufferedWriter 缓冲输出流: 有一个缓冲区: 8KB
write() 写入到缓冲区,
如果缓冲区满了, 自动把缓冲区的内容写到文件
如果手动调用flush() , 立即把缓冲区的内容写到文件
BufferedWriter 的close() 方法, 关闭流之前, 先刷新缓冲区
2.2转换流
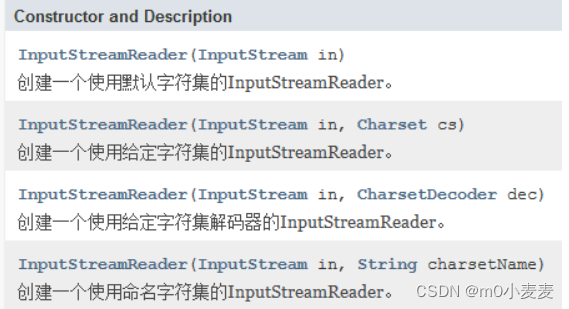
InputStreamReader : 把一个字节输入流转换为字符输入流
构造方法:
OutputStreamWriter: 把一个字节输出流转换为字符输出流
构造方法:
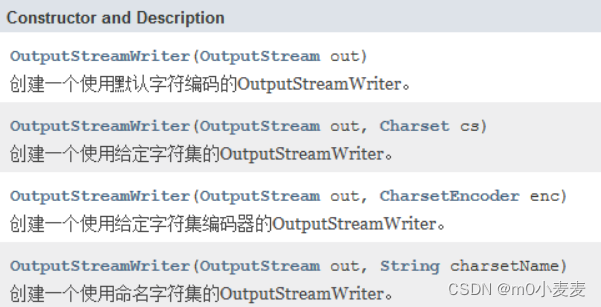
2.3打印流
只有输出流, 打印输出流: 额外提供了一个打印方法: print() println()
字节打印流: PrintStream
字符打印流: PrintWriter
PrintStream和PrintWriter提供了重载的print()、println()方法用于多种数据类型的输出。
PrintStream和PrintWriter不会抛出异常,用户通过检测错误状态获取错误信息。






















 157
157











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








