Abstract
Multimodal summarization with multimodal output (MSMO) generates a summary with both textual and visual content.Multimodal news report contains heterogeneous contents, which makes MSMO nontrivial. Moreover, it is observed that different modalities of data in the news report correlate hierarchically. Traditional MSMO methods indistinguishably handle different modalities of data by learning a representation for the whole data, which is not directly adaptable to the heterogeneous contents and hierarchical correlation. In this paper, we propose a hierarchical cross-modality semantic correlation learning model (HCSCL) to learn the intra- and intermodal correlation existing in the multimodal data. HCSCL adopts a graph network to encode the intra-modal correlation. Then, a hierarchical fusion framework is proposed to learn the hierarchical correlation between text and images.Furthermore, we construct a new dataset with relevant image annotation and image object label information to provide the supervision information for the learning procedure. Extensive experiments on the dataset show that HCSCL significantly outperforms the baseline methods in automatic summarization metrics and fine-grained diversity tests.
翻译:
多模态摘要生成(MSMO)旨在同时生成包含文本和视觉内容的摘要。多模态新闻报道含有异质内容,这使得MSMO具有挑战性。此外,观察到新闻报道中不同模态的数据之间存在层次相关性。传统的MSMO方法通过学习整个数据的表示来处理不同模态的数据,这并不直接适用于异质内容和层次相关性。在本文中,我们提出了一种层次跨模态语义相关性学习模型(HCSCL),以学习多模态数据中存在的模内和跨模态相关性。HCSCL采用图网络对模内相关性进行编码。然后,提出了一种分层融合框架来学习文本和图像之间的层次相关性。此外,我们构建了一个新的数据集,其中包含相关的图像注释和图像对象标签信息,以提供学习过程的监督信息。在数据集上的大量实验表明,HCSCL在自动摘要指标和细粒度多样性测试中明显优于基线方法。
总结:
直接融合数据的不同模态,会忽略它们之间的潜在相关性和内部结构的异质性
Introduction
Usually, the visual image and text article have heterogeneous structures. Directly mapping visual input and textual input as global vectors (Zhu et al 2018; Li et al 2020b; Zhu et al 2020) is not effective to learn the important information for both modalities from each other, and even noisy information is added to decrease the performance of summarization. Previous experiments (Zhu et al 2018) have shown that multimodal input models may decrease summarization metric scores compared to text-only input models. Our experiments also show that some multimodal input model methods perform worse than traditional text-only input models.Therefore, one of the core problems of MSMO is how to effectively learn from each other modalities of data to obtain high-quality summaries.
翻译:
通常情况下,视觉图像和文本文章具有异质性结构。直接将视觉输入和文本输入映射为全局向量并不能有效地从对方那里学习到两种模式的重要信息,甚至会有噪声信息加入,降低摘要的性能。我们的实验还表明,一些多模态输入模型方法比传统的纯文本输入模型表现得更差。因此,MSMO的核心问题之一是如何有效地相互学习数据的模式,从而获得高质量的摘要。
总结:
如何做到利用模态之间异质的信息很关键
Meanwhile, the correlation between the visual content and text article presents unique characteristics, providing clues to learning the important information from the two modalities complementarily to improve MSMO. As shown in Figure 1, the low-level objects in an image constitute the high-level semantics called scenes through the interaction between them. Therefore, by analyzing the objects and hence the scenes, we can know what the image describes from different levels. In the other data space, words are also the basic textual information in an article, while the combination of words, called sentences, present more abstract semantics information. Besides the intra-modal correlation, the semantics objects in the image and article are correlated in different levels. For example, in Figure 1, each person in the image may be related to a name in the article, and the football sport in the image is also described by a sentence in the article. By learning the inter-modal correlation, it can be known what is the important information in both of the modalities. Moreover, even there are some incomplete descriptions in one modality, it can be learned from the other modality by exploiting the inter-modal correlation.As shown in Figure 1, we can generate the more complete information about the relation between the player “Mascherano” and the event “block Robben’s shot”. Therefore, by exploiting the hierarchical cross-modality correlation, we can extract the important information from both image and article more effectively.
翻译:
同时,视觉内容和文字文章之间的关联性呈现出独特的特点,图像中的低层次物体通过它们之间的相互作用构成了被称为场景的高层次语义。在另一个数据空间中,单词也是一篇文章中的基本文本信息,而单词的组合,称为句子,呈现出更抽象的语义信息。除了模态内的关联,图像和文章中的语义对象在不同的层次上也有关联。例如,在图1中,图像中的每个人可能与文章中的一个名字相关,并且图像中的足球运动也由文章中的一个句子描述。通过学习模态间的相关性,可以知道两种模态中哪些是重要的信息。此外,即使一种模态中有一些不完整的描述,也可以利用模态间的相关性从另一种模态中学习。如图1所示,我们可以生成更完整的球员“马斯切拉诺”与事件“挡罗本射门”之间的关系信息。因此,利用层次交叉模态相关,可以更有效地从图像和文章中提取重要信息。
总结:
模态信息由语义对象在不同层次的关联组成,因此学习模态内与模态间的相关性很重要
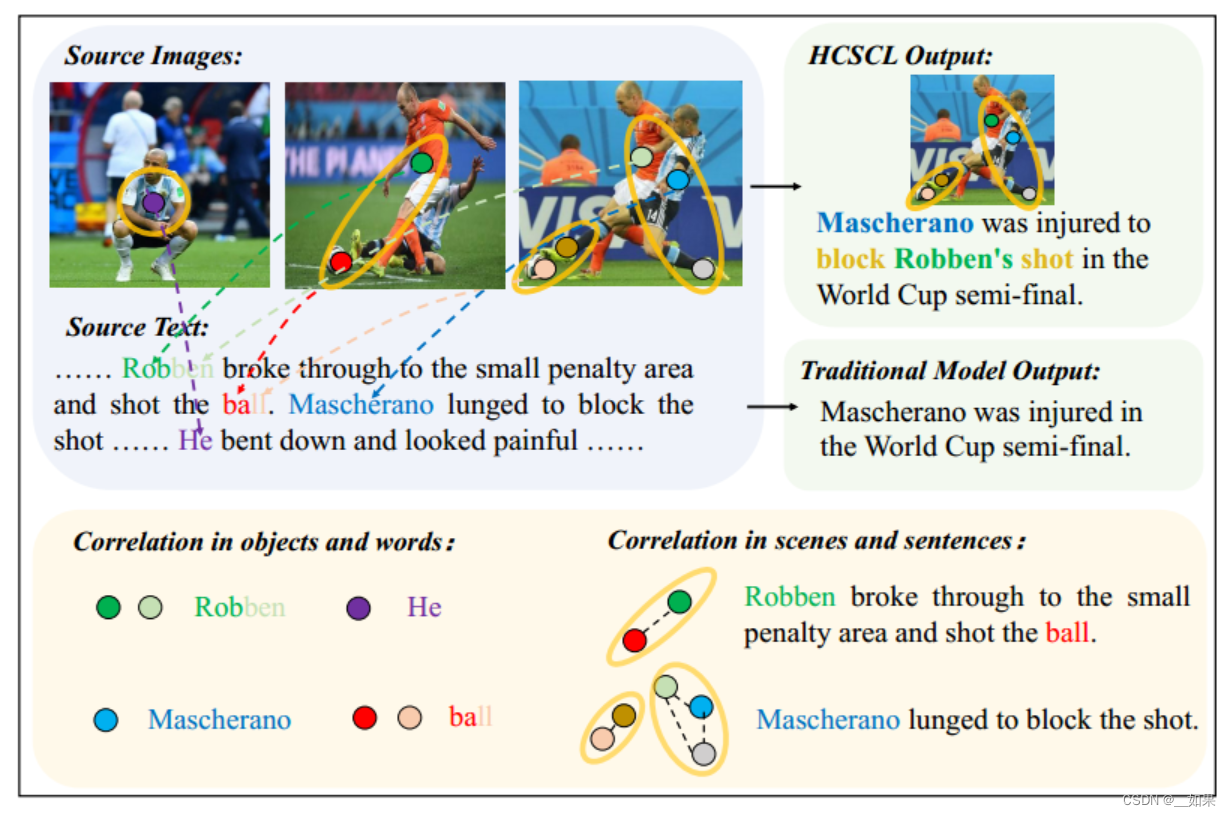
However, there is still a great challenge to learn the hierarchical cross-modality correlation. First, different modalities have different feature spaces and structures among the elements. It is nontrivial to learn an effective representation to reflect both the different content and structure information.Second, much noisy information might exist, while some important information might be missed in one of the modalities. However, there is no explicit knowledge about the correlation between different modalities of data.
翻译:
然而,学习层次跨模态相关性仍是一个巨大的挑战。首先,不同模态具有不同的特征空间和元素间的结构。学习一种有效的表示来反映不同的内容和结构信息并非易事。其次,可能存在许多噪声信息,而在某一模态中可能遗漏了一些重要信息。然而,对于不同模态数据之间的相关性,并没有明确的先验知识。
To tackle the challenge, we propose a novel Hierarchical Cross-Modality Semantic Correlation Learning model (HCSCL) to learn the intra- and inter-modality correlation for MSMO. In particular, two modality encoders are proposed to learn the intra-modal correlation for image and article, respectively. Then, a hierarchical fusion framework is proposed to learn the hierarchical correlation between image and article. A hierarchical attention method is proposed to combine the different levels of features learned by the hierarchical fusion framework to generate the summary. Furthermore, we construct a new dataset1 with relevant image annotation to provide the supervision information for the learning procedure. Extensive experiments on the dataset show that HCSCL significantly outperforms the baseline methods in automatic summarization metrics and fine-grained diversity tests. Our main contributions are as follows:
• We propose a hierarchical learning model HCSCL to learn the intra- and inter-modality correlation in the multimodal data. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that guides multimodal summarization by exploiting the fine-grained semantics and their correlation information inside the multimodal data.
• We propose a multimodal visual graph learning method to capture the structure and the content information and reinforce the inter-modality interaction.
• We construct a large-scale multimodal summarization dataset with relevant image annotations and object labels to evaluate the performance of MSMO.
翻译:
为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的层次跨模态语义相关性学习模型(HCSCL),用于学习MSMO的模内和跨模态相关性。特别是,我们提出了两个模态编码器,分别用于学习图像和文章的模内相关性。然后,提出了一种分层融合框架,用于学习图像和文章之间的层次相关性。我们提出了一种分层注意力方法,将分层融合框架学到的不同层次的特征结合起来,以生成摘要。此外,我们构建了一个新的数据集1,其中包含了相关的图像注释,以提供学习过程的监督信息。在数据集上的大量实验表明,HCSCL在自动摘要指标和细粒度多样性测试中显著优于基线方法。我们的主要贡献如下:
• 我们提出了一个层次学习模型HCSCL,用于学习多模态数据中的模内和跨模态相关性。据我们所知,这是第一个通过利用多模态数据内的细粒度语义及其相关性信息来指导多模态摘要的工作。
• 我们提出了一种多模态视觉图学习方法,以捕捉结构和内容信息,并加强跨模态交互。
• 我们构建了一个大规模的多模态摘要数据集,其中包含了相关的图像注释和对象标签,以评估MSMO的性能。
总结:
提出一种分层注意力用来融合不同层次的特征
Model
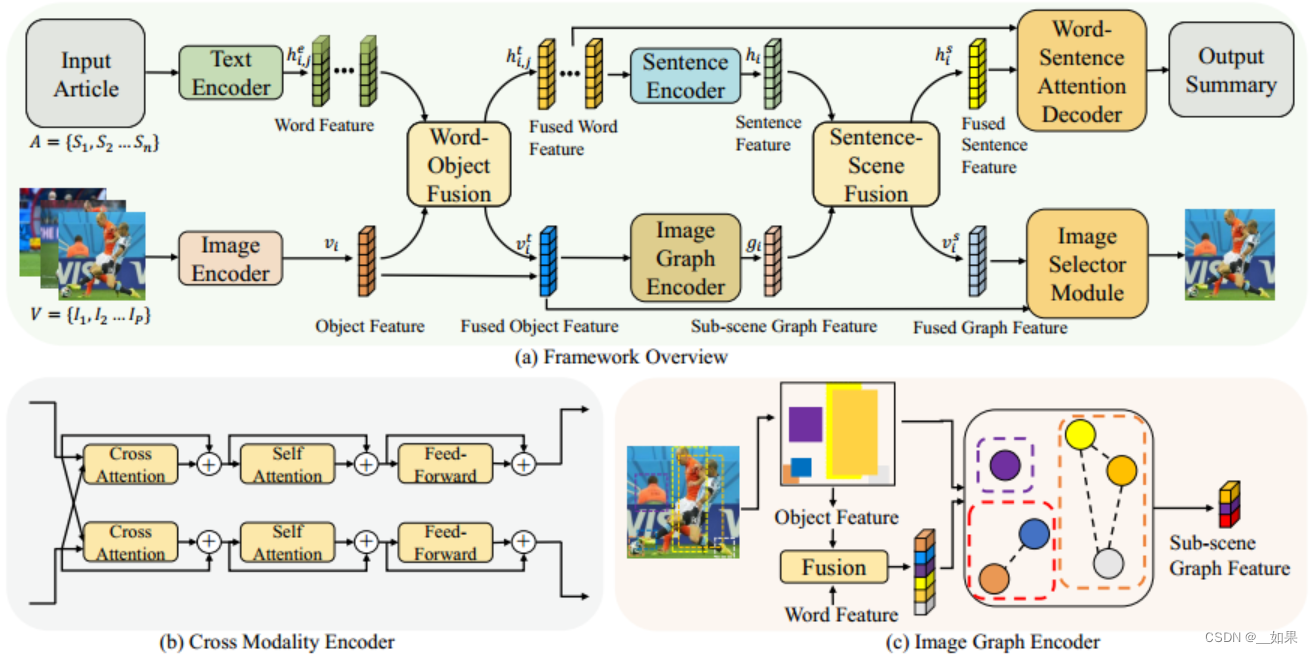
HCSCL包括三个模块:模态特征编码器用于编码每个模态,层次化的语义关联融合模块用于学习模态内和模态间的层次化关联,多模态输出总结器利用层次化的关联来生成多模态摘要
Modality Feature Encoder
使用LSTM编码文章句子,使用Faster-RCNN提取图片中的物体特征
Hierarchical Semantic Correlation Fusion
将模态特征传入层次化的语义关联融合模块,在两个层面上学习相关性:单词-物体融合和句子-场景融合。单词-物体融合采用一个基于注意力的跨模态编码器(CME)学习模态间的关系。CME由三部分组成:交叉注意力层、自注意力层和前馈层。其中每个子层中也加入了残差连接和LayerNorm。三个步骤重复次,即可得到融合后的单词表征和融合后的物体表征。句子-场景融合包括两方面,一方面,将单词表征传入LSTM模型得到整个句子的表征。另一方面,图像中物体的一部分被关联起来,形成一个场景来表示一个更抽象的概念或活动。首先,基于图像编码器提取物体边界框,为每两个物体计算一个IOU得分。接下来,构建一个带有邻接矩阵A的关系图,如果IOU分数超过了 阈值, = 1,否则 = 0。然后按照如下公式计算物体i相对于物体j的特征分数:
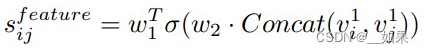
再结合IOU分数和特征分数得到有向边的权重:
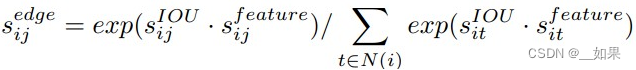
最后,结合邻接矩阵A得到一系列子场景图的表征:
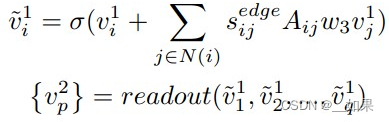 其中,readout函数的公式如下:
其中,readout函数的公式如下:
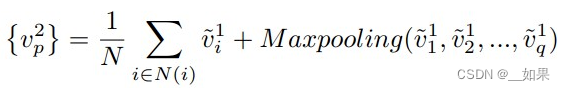
最后,通过CME计算得到句子-场景融合特征和。
Multimodal Output Summarizer
多模态输出摘要器会生成文本摘要,附带一张最相关的图片。文本摘要生成方面,使用分层注意力机制。在时间片t-1时,传入融合后的句子特征{},得到hidden state ,然后按如下公式分别计算i-th句子的权重和j-th单词在i-th句子的权重。
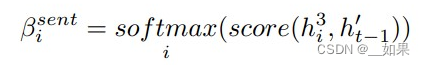
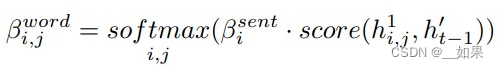
然后,按照如下公式计算时间t时的context 和预测的单词。
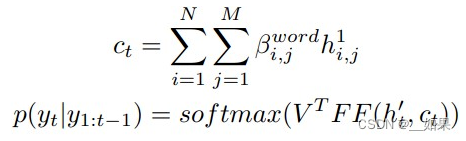
图像选择方面,最相关的图像应该在物体层面和场景层面都与摘要语义相匹配。首先,隐藏的状态特征被用于计算与物体和场景的相关分数。使用物体-场景门机制计算两种特征的权重,加权后得到每张图片的相关分数。选择分数最高的图片最为选择的图片。具体公式如下:
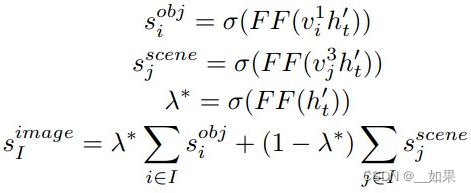
Results and Analysis
To validate the effectiveness of our model, we compare our model with three kinds of baselines: Traditional Textual Model, Multimodal Summarization model, and Multimodal Summarization Output Model. Table 3 shows the result of comparative models on the dataset. We can obtain several conclusions from this table. First, it shows that HCSCL achieves state-of-the-art performance in almost all evaluation metrics. HCSCL outperforms baselines 1.51%, 0.76% in terms of Rouge-1, Rouge-2 and 1.48%, 1.27%, 0.75%, 0.20% in terms of BLEU-1, BLEU-2, BLEU-3, BLEU-4 and 22.32% in IP. It demonstrates the superiority of the hierarchical cross-modality correlation learning model. By exploiting the intra-modality correlation learning and the intermodality feature aligning, the visual content can reinforce a specific part of the representation of text content, and the text content can reinforce to select the relevant image. Second, in Rouge-L, HCSCL (40.94) is slightly worse than the text output model MSE (41.79). After analyzing the cases, we find that the text outputs of HCSCL are more relevant to image semantics. Therefore, the longest common subsequence (RL) is less matched with the text description, affecting this metric’s evaluation.
翻译:
为了验证我们模型的有效性,我们将我们的模型与三种基线模型进行了比较:传统文本模型、多模态摘要模型和多模态摘要输出模型。表3显示了比较模型在数据集上的结果。我们可以从这张表中得出几个结论。首先,它表明HCSCL在几乎所有评估指标上都取得了最先进的性能。HCSCL在Rouge-1、Rouge-2上分别优于基线1.51%、0.76%,在BLEU-1、BLEU-2、BLEU-3、BLEU-4上分别优于1.48%、1.27%、0.75%、0.20%,在IP上优于22.32%。这证明了层次跨模态相关性学习模型的优越性。通过利用模内相关性学习和跨模态特征对齐,视觉内容可以加强文本内容的特定部分的表示,文本内容可以加强选择相关的图像。其次,在Rouge-L指标上,HCSCL(40.94)略逊于文本输出模型MSE(41.79)。在分析了案例后,我们发现HCSCL的文本输出与图像语义更相关。因此,最长公共子序列(RL)与文本描述的匹配度较低,影响了这个指标的评估。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








