理论基础
前序遍历:中左右
中序遍历:左中右
后序遍历:左右中
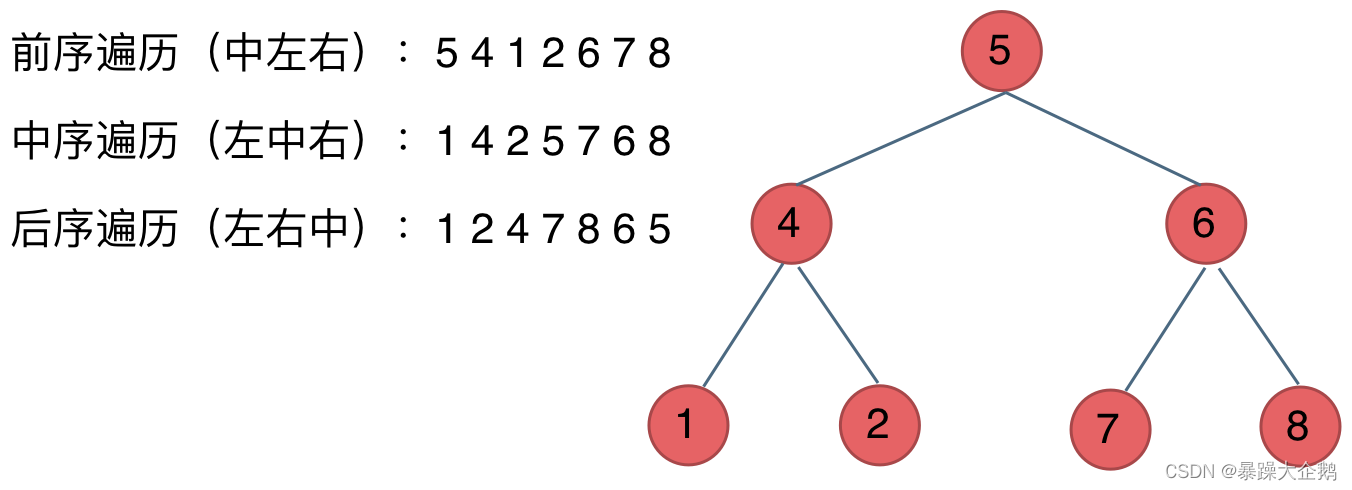
遍历完全二叉树
//遍历完全二叉树-先序、中序、后序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
void preorder(int t){
printf("%d ", t);
if (t * 2 <= n){
preorder(t * 2);
}
if (t * 2 + 1 <= n){
preorder(t * 2 + 1);
}
}
void inorder(int t){
if (t * 2 <= n){
inorder(t * 2);
}
printf("%d ", t);
if (t * 2 + 1 <= n){
inorder(t * 2 + 1);
}
}
void postorder(int t){
if (t * 2 <= n){
postorder(t * 2);
}
if (t * 2 + 1 <= n){
postorder(t * 2 + 1);
}
printf("%d ", t);
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
preorder(1);
printf("\n");
inorder(1);
printf("\n");
postorder(1);
printf("\n");
return 0;
} 遍历一般二叉树
//遍历一般二叉树-先序、中序、后序
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
struct node{
int l, r, fa;
} a[1100];
void preorder(int t){
printf("%d ", t);
if (a[t].l){
preorder(a[t].l);
}
if (a[t].r){
preorder(a[t].r);
}
}
void inorder(int t){
if (a[t].l){
inorder(a[t].l);
}
printf("%d ", t);
if (a[t].r){
inorder(a[t].r);
}
}
void postorder(int t){
if (a[t].l){
postorder(a[t].l);
}
if (a[t].r){
postorder(a[t].r);
}
printf("%d ", t);
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x){
a[i].l = x;
a[x].fa = i;
}
if (y){
a[i].r = y;
a[y].fa = i;
}
}
preorder(1);
printf("\n");
inorder(1);
printf("\n");
postorder(1);
printf("\n");
return 0;
} 二叉树的最近公共祖先-解法一
//二叉数的最近公共祖先-解法一
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
struct node{
int l, r, fa;
} a[1100];
int u, v;
int temp1[1100], temp2[1100];
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x){
a[i].l = x;
a[x].fa = i;
}
if (y){
a[i].r = y;
a[y].fa = i;
}
}
cin >> u >> v;
int l1 = 0;
while (u != 1){
temp1[++l1] = u;
u = a[u].fa;
}
temp1[++l1] = 1;
int l2 = 0;
while (v != 1){
temp2[++l2] = v;
v = a[v].fa;
}
temp2[++l2] = 1;
int ans;
for (int i = l1, j = l2; i && j; i--, j--){
if (temp1[i] == temp2[j]){
ans = temp1[i];
}
else {
break;
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
} 二叉树的最近公共祖先-解法二
//二叉数的最近公共祖先-解法二
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, u, v;
struct node{
int l, r, fa, deep;
} a[1100];
queue<node> q;
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x){
a[i].l = x, a[x].fa = i;
}
if (y){
a[i].r = y, a[y].fa = i;
}
}
q.push(a[1]);//BFS遍历deep
while (!q.empty()){
if (q.front().l){
q.push(a[q.front().l]);
a[q.front().l].deep = q.front().deep + 1;
}
if (q.front().r){
q.push(a[q.front().r]);
a[q.front().r].deep = q.front().deep + 1;
}
q.pop();
}
cin >> u >> v;
if (a[u].deep < a[v].deep){
swap(u, v);
}
int count = a[v].deep - a[u].deep;
while (count--){
u = a[u].fa;
}
while (u != v){
u = a[u].fa;
v = a[v].fa;
}
printf("%d\n", u);
return 0;
} 二叉树子树和-暴力解法
//二叉树子树和-暴力
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, u, v;
int ans;
struct node{
int l, r, fa, value;
} a[1100];
void preorder(int x){
ans++;
if (a[x].l){
preorder(a[x].l);
}
if (a[x].r){
preorder(a[x].r);
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x){
a[i].l = x, a[x].fa = i;
}
if (y){
a[i].r = y, a[y].fa = i;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a[i].value;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
ans = 0;
preorder(i);
printf("%d ", ans);
}
return 0;
} 二叉树子树和-递归解法
//二叉树子树和-递归
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, u, v;
struct node{
int l, r, fa, value;
} a[1000010];
int ans[1000010];
int dfs(int x){
int count = a[x].value;
if (a[x].l){
count += dfs(a[x].l);
}
if (a[x].r){
count += dfs(a[x].r);
}
ans[x] = count;
return count;
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x){
a[i].l = x, a[x].fa = i;
}
if (y){
a[i].r = y, a[y].fa = i;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a[i].value;
}
dfs(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
}
return 0;
} 





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








