直线扫描转换算法是一种将数学图形转换为像素的绘制算法,主要包括以下三种常见方法:
- DDA(数字差分分析法)
- Bresenham(布雷森汉姆算法)
- 中点算法(Midpoint Algorithm)
绘制圆外接五角星、圆内接正方形、圆外切椭圆 的场景,这些图形分别可以与以下算法关联:
文末附完整代码
1. 绘制圆外接五角星
相关算法:DDA 或 Bresenham(直线段)
- 理由:
五角星由多条直线段组成,直线扫描转换算法可以使用 DDA 或 Bresenham 来实现直线段的绘制。- DDA 算法:通过增量计算生成点坐标,效率较低,但逻辑简单。
- Bresenham 算法:通过整数运算绘制直线,效率高且实现高效。
- 适用场景:
- 如果需要强调像素级别的性能优化(例如低分辨率的嵌入式设备),可以使用 Bresenham。
- 在普通应用程序中,使用 Qt 提供的绘图方法(如
addPolygon)内部可能已优化为类似算法。 -
// 使用DDA算法绘制直线 void Widget::drawLineDDA(QGraphicsScene *scene, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { int dx = x2 - x1; // 计算x方向的差 int dy = y2 - y1; // 计算y方向的差 int steps = std::max(abs(dx), abs(dy)); // 选择更大的方向进行扫描 float xInc = dx / float(steps); // 计算每步x的增量 float yInc = dy / float(steps); // 计算每步y的增量 float x = x1, y = y1; // 设置起始点 for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++) { scene->addRect(x, y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::black)); // 绘制一个像素点 x += xInc; // 更新x坐标 y += yInc; // 更新y坐标 } } // 绘制圆外接五角星图像 void Widget::on_btn_drawStar_clicked() { on_btn_clearDrawing_clicked(); // 清空当前绘制的图像 const int points = 5; // 五角星有五个顶点 double angleIncrement = 2 * M_PI / points; // 计算每个顶点的角度间隔 double startAngle = -M_PI_2; // 从顶部开始绘制五角星 // 计算五角星顶点的坐标 int starCoords[5][2]; for (int i = 0; i < points; ++i) { double angle = startAngle + i * angleIncrement; // 计算当前顶点的角度 starCoords[i][0] = x + radius * cos(angle); // x 坐标 starCoords[i][1] = y + radius * sin(angle); // y 坐标 } // 按五角星的顶点连接顺序绘制线段 for (int i = 0; i < points; ++i) { int nextIndex = (i + 2) % points; // 跳过一个顶点连接(非相邻顶点) drawLineDDA(scene, starCoords[i][0], starCoords[i][1], starCoords[nextIndex][0], starCoords[nextIndex][1]); // 绘制线段 } // 绘制外接圆 scene->addEllipse(x - radius, y - radius, 2 * radius, 2 * radius, QPen(Qt::blue, 2)); }

2. 绘制圆内接正方形
相关算法:DDA 或 Bresenham(直线段)、中点圆算法
- 理由:
- 绘制内接正方形时:
正方形由四条直线段构成,因此可以用 DDA 或 Bresenham 绘制。 - 如果附带绘制圆:
外接圆可以通过 中点圆算法 来实现高效的圆形扫描转换。
- 绘制内接正方形时:
- 适用场景:
- 中点圆算法:
它通过判断某一点与圆的误差函数关系(决策变量)确定圆周点,避免了复杂的浮点运算,非常高效。 - Bresenham 直线算法:用于绘制正方形边界时效率较高。
-
// 使用中点圆算法绘制圆 while (x <= y) { plotCirclePoints(centerX, centerY, x, y); // 绘制八个对称点 if (d < 0) { d += 2 * x + 3; // 如果判别值小于0,更新x,保持y不变 } else { d += 2 * (x - y) + 5; // 如果判别值大于等于0,更新y,同时减少y y--; } x++; // 更新x坐标 } } // 绘制圆内接正方形图像 void Widget::on_btn_drawRect_clicked() { on_btn_clearDrawing_clicked(); // 清空当前绘制的图像 int side = radius * sqrt(2) / 2; // 正方形的边长,使用勾股定理求得 drawLineDDA(scene, x - side, y - side, x + side, y - side); // 上边 drawLineDDA(scene, x + side, y - side, x + side, y + side); // 右边 drawLineDDA(scene, x + side, y + side, x - side, y + side); // 下边 drawLineDDA(scene, x - side, y + side, x - side, y - side); // 左边 scene->addEllipse(x - radius, y - radius, 2 * radius, 2 * radius, QPen(Qt::blue, 2)); // 绘制外接圆 }
- 中点圆算法:

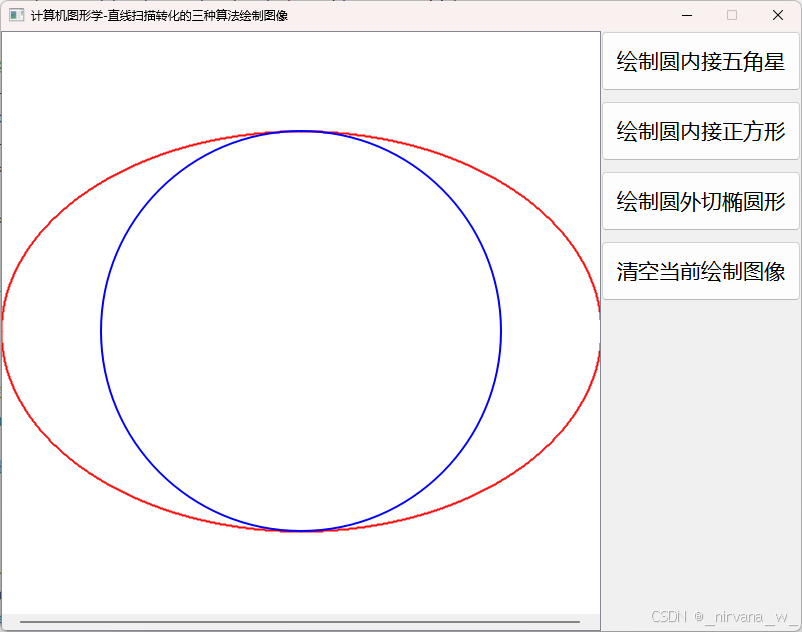
3. 绘制圆外切椭圆
相关算法:中点椭圆算法
- 理由:
- 绘制外切圆时可以使用 中点圆算法。
- 椭圆本身可以通过 中点椭圆算法 来绘制,类似中点圆算法,使用决策变量判断椭圆的下一个像素点,分为两个区域(长轴区和短轴区)计算。
- 适用场景:
- 中点椭圆算法 是高效绘制椭圆的标准方法,避免了复杂的浮点运算。
- 如果只是简单绘图(非像素级),Qt 的
addEllipse方法可能已集成类似的优化。 -
// 使用中点椭圆算法绘制椭圆 void Widget::drawMidpointEllipse(QGraphicsScene *scene, int centerX, int centerY, int a, int b) { int x = 0, y = b; double a2 = a * a, b2 = b * b; double d = b2 - a2 * b + 0.25 * a2; // 初始判别值 // 绘制椭圆的对称点 auto plotEllipsePoints = [&](int cx, int cy, int x, int y) { scene->addRect(cx + x, cy + y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red)); scene->addRect(cx - x, cy + y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red)); scene->addRect(cx + x, cy - y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red)); scene->addRect(cx - x, cy - y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red)); }; // 第一阶段:沿y轴递减 while (b2 * x <= a2 * y) { plotEllipsePoints(centerX, centerY, x, y); // 绘制四个对称点 if (d < 0) { d += b2 * (2 * x + 3); // 如果判别值小于0,更新x } else { d += b2 * (2 * x + 3) + a2 * (-2 * y + 2); // 如果判别值大于等于0,更新y并减少y y--; } x++; // 更新x坐标 } // 第二阶段:沿x轴递增 d = b2 * (x + 0.5) * (x + 0.5) + a2 * (y - 1) * (y - 1) - a2 * b2; while (y >= 0) { plotEllipsePoints(centerX, centerY, x, y); // 绘制四个对称点 if (d > 0) { d += a2 * (-2 * y + 3); // 如果判别值大于0,更新y } else { d += b2 * (2 * x + 2) + a2 * (-2 * y + 3); // 如果判别值小于等于0,更新x x++; } y--; // 更新y坐标 } }
总结
| 图形类型 | 涉及算法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 圆外接五角星 | DDA 或 Bresenham | 五角星由直线段构成,适合用直线扫描算法绘制。 |
| 圆内接正方形 | DDA 或 Bresenham + 中点圆算法 | 正方形由直线构成,圆的绘制适合用中点圆算法。 |
| 圆外切椭圆 | 中点椭圆算法 | 椭圆外切圆的绘制适合使用中点圆算法和中点椭圆算法。 |
完整代码文件(3个文件)
main.cpp
#include "widget.h"
#include <QApplication>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QApplication a(argc, argv);
Widget w;
w.show();
return a.exec();
}
widget.h
#ifndef WIDGET_H
#define WIDGET_H
// 引入图形项类,用于图形场景的绘制
#include <QGraphicsEllipseItem>
#include <QGraphicsPolygonItem>
#include <QGraphicsScene>
// 引入鼠标滚轮事件类,用于缩放图像
#include <QWheelEvent>
// 引入QWidget类,用于创建GUI窗口
#include <QWidget>
// 引入数学库,用于数值计算
#include <math.h>
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui {
class Widget; // 声明Widget类
}
QT_END_NAMESPACE
// 定义Widget类继承自QWidget类,表示图形窗口
class Widget : public QWidget
{
Q_OBJECT // 必须定义Q_OBJECT宏,用于Qt的信号和槽机制
public:
// 构造函数,初始化窗口,parent为父窗口,默认值为nullptr
Widget(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
// 析构函数,释放资源
~Widget();
protected:
void wheelEvent(QWheelEvent *event) override; // 重写缩放事件
void mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event) override; // 鼠标按下事件
void mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event) override; // 鼠标移动事件
void mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event) override; // 鼠标释放事件
private slots:
// 按钮点击槽函数,用于绘制五角星
void on_btn_drawStar_clicked();
// 按钮点击槽函数,用于绘制矩形
void on_btn_drawRect_clicked();
// 按钮点击槽函数,用于绘制椭圆
void on_btn_drawEllipse_clicked();
// 按钮点击槽函数,用于清除绘制内容
void on_btn_clearDrawing_clicked();
// DDA 或 Bresenham,此处使用数值微分法DDA实现:圆外接五角星,五角星由直线段构成,适合用直线扫描算法绘制。
void drawLineDDA(QGraphicsScene *scene, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2);
// DDA 或 Bresenham + 中点圆算法,此处使用中点画线法实现:圆内接正方形,正方形由直线构成,圆的绘制适合用中点圆算法。
void drawMidpointCircle(QGraphicsScene *scene, int centerX, int centerY, int radius);
// 中点椭圆算法实现绘制圆外切椭圆,椭圆外切圆的绘制适合使用中点圆算法和中点椭圆算法。
void drawMidpointEllipse(QGraphicsScene *scene, int centerX, int centerY, int a, int b);
private:
Ui::Widget *ui; // UI界面的指针,用于访问界面元素
QGraphicsScene *scene; // 图形场景,用于绘制图形
int x, y, radius; // 圆心坐标和半径,用于绘制圆
bool isDragging; // 标记是否正在拖动视图
QPoint lastMousePos; // 上次鼠标位置
};
#endif // WIDGET_H
widget.cpp
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
// 构造函数,初始化UI和场景
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent) // 调用父类QWidget的构造函数
, ui(new Ui::Widget) // 创建UI对象
, scene(new QGraphicsScene(this)) // 创建QGraphicsScene对象,指定parent为当前对象
, isDragging(false) // 初始化拖动标志
{
ui->setupUi(this); // 设置UI界面
ui->graphicsView_drawing->setScene(scene); // 将图形视图设置为当前场景
ui->graphicsView_drawing->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing); // 启用抗锯齿
ui->graphicsView_drawing->setDragMode(QGraphicsView::ScrollHandDrag); // 设置拖动模式
x = ui->graphicsView_drawing->width() / 2; // 圆心的x坐标为图形视图宽度的中心
y = ui->graphicsView_drawing->height() / 2; // 圆心的y坐标为图形视图高度的中心
radius = ui->graphicsView_drawing->width() / 3; // 半径为图形视图宽度的三分之一
}
// 析构函数,释放UI对象
Widget::~Widget()
{
delete ui; // 释放UI内存
}
void Widget::wheelEvent(QWheelEvent *event)
{
int delta = event->angleDelta().y();
qreal scaleFactor = (delta > 0) ? 1.2 : 0.8;
// 获取当前缩放因子
qreal currentScale = ui->graphicsView_drawing->transform().m11();
// 设置缩放的最大最小值
if ((scaleFactor > 1 && currentScale < 5) || (scaleFactor < 1 && currentScale > 0.1)) {
ui->graphicsView_drawing->scale(scaleFactor, scaleFactor);
}
// 保持视图居中
ui->graphicsView_drawing->centerOn(scene->sceneRect().center());
}
void Widget::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{ // 鼠标左键按下时,记录位置并开始拖动
if (event->button() == Qt::LeftButton) {
isDragging = true;
lastMousePos = event->pos(); // 记录当前鼠标位置
setCursor(Qt::ClosedHandCursor); // 改变鼠标为拖动状态
}
}
void Widget::mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
if (isDragging) {
// 计算鼠标移动的距离
QPoint delta = event->pos() - lastMousePos;
ui->graphicsView_drawing->translate(delta.x(), delta.y()); // 移动视图
lastMousePos = event->pos(); // 更新鼠标位置
}
}
void Widget::mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{ // 鼠标左键释放时,停止拖动
if (event->button() == Qt::LeftButton) {
isDragging = false;
setCursor(Qt::ArrowCursor); // 恢复鼠标为箭头状态
}
}
// 绘制圆外接五角星图像
void Widget::on_btn_drawStar_clicked()
{
on_btn_clearDrawing_clicked(); // 清空当前绘制的图像
const int points = 5; // 五角星有五个顶点
double angleIncrement = 2 * M_PI / points; // 计算每个顶点的角度间隔
double startAngle = -M_PI_2; // 从顶部开始绘制五角星
// 计算五角星顶点的坐标
int starCoords[5][2];
for (int i = 0; i < points; ++i) {
double angle = startAngle + i * angleIncrement; // 计算当前顶点的角度
starCoords[i][0] = x + radius * cos(angle); // x 坐标
starCoords[i][1] = y + radius * sin(angle); // y 坐标
}
// 按五角星的顶点连接顺序绘制线段
for (int i = 0; i < points; ++i) {
int nextIndex = (i + 2) % points; // 跳过一个顶点连接(非相邻顶点)
drawLineDDA(scene,
starCoords[i][0],
starCoords[i][1],
starCoords[nextIndex][0],
starCoords[nextIndex][1]); // 绘制线段
}
// 绘制外接圆
scene->addEllipse(x - radius, y - radius, 2 * radius, 2 * radius, QPen(Qt::blue, 2));
}
// 绘制圆内接正方形图像
void Widget::on_btn_drawRect_clicked()
{
on_btn_clearDrawing_clicked(); // 清空当前绘制的图像
int side = radius * sqrt(2) / 2; // 正方形的边长,使用勾股定理求得
drawLineDDA(scene, x - side, y - side, x + side, y - side); // 上边
drawLineDDA(scene, x + side, y - side, x + side, y + side); // 右边
drawLineDDA(scene, x + side, y + side, x - side, y + side); // 下边
drawLineDDA(scene, x - side, y + side, x - side, y - side); // 左边
scene->addEllipse(x - radius, y - radius, 2 * radius, 2 * radius, QPen(Qt::blue, 2)); // 绘制外接圆
}
// 绘制圆外切椭圆图像
void Widget::on_btn_drawEllipse_clicked()
{
on_btn_clearDrawing_clicked(); // 清空当前绘制的图像
double aspectRatio = 1.5; // 椭圆的长短轴比例(1.5表示长轴是短轴的1.5倍)
int a = radius * aspectRatio; // 长轴
int b = radius; // 短轴
drawMidpointEllipse(scene, x, y, a, b); // 绘制椭圆
scene->addEllipse(x - radius, y - radius, 2 * radius, 2 * radius, QPen(Qt::blue, 2)); // 绘制外接圆
}
// 清空当前绘制的图像
void Widget::on_btn_clearDrawing_clicked()
{
scene->clear(); // 清除图形场景中的所有项
}
// 使用DDA算法绘制直线
void Widget::drawLineDDA(QGraphicsScene *scene, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
int dx = x2 - x1; // 计算x方向的差
int dy = y2 - y1; // 计算y方向的差
int steps = std::max(abs(dx), abs(dy)); // 选择更大的方向进行扫描
float xInc = dx / float(steps); // 计算每步x的增量
float yInc = dy / float(steps); // 计算每步y的增量
float x = x1, y = y1; // 设置起始点
for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++) {
scene->addRect(x, y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::black)); // 绘制一个像素点
x += xInc; // 更新x坐标
y += yInc; // 更新y坐标
}
}
// 使用中点圆算法绘制圆
void Widget::drawMidpointCircle(QGraphicsScene *scene, int centerX, int centerY, int radius)
{
int x = 0, y = radius; // 初始化圆的初始坐标
int d = 1 - radius; // 初始判别值
// 绘制圆的对称点
auto plotCirclePoints = [&](int cx, int cy, int x, int y) {
scene->addRect(cx + x, cy + y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
scene->addRect(cx - x, cy + y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
scene->addRect(cx + x, cy - y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
scene->addRect(cx - x, cy - y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
scene->addRect(cx + y, cy + x, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
scene->addRect(cx - y, cy + x, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
scene->addRect(cx + y, cy - x, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
scene->addRect(cx - y, cy - x, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::blue));
};
// 使用中点圆算法绘制圆
while (x <= y) {
plotCirclePoints(centerX, centerY, x, y); // 绘制八个对称点
if (d < 0) {
d += 2 * x + 3; // 如果判别值小于0,更新x,保持y不变
} else {
d += 2 * (x - y) + 5; // 如果判别值大于等于0,更新y,同时减少y
y--;
}
x++; // 更新x坐标
}
}
// 使用中点椭圆算法绘制椭圆
void Widget::drawMidpointEllipse(QGraphicsScene *scene, int centerX, int centerY, int a, int b)
{
int x = 0, y = b;
double a2 = a * a, b2 = b * b;
double d = b2 - a2 * b + 0.25 * a2; // 初始判别值
// 绘制椭圆的对称点
auto plotEllipsePoints = [&](int cx, int cy, int x, int y) {
scene->addRect(cx + x, cy + y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red));
scene->addRect(cx - x, cy + y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red));
scene->addRect(cx + x, cy - y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red));
scene->addRect(cx - x, cy - y, 1, 1, QPen(Qt::red));
};
// 第一阶段:沿y轴递减
while (b2 * x <= a2 * y) {
plotEllipsePoints(centerX, centerY, x, y); // 绘制四个对称点
if (d < 0) {
d += b2 * (2 * x + 3); // 如果判别值小于0,更新x
} else {
d += b2 * (2 * x + 3) + a2 * (-2 * y + 2); // 如果判别值大于等于0,更新y并减少y
y--;
}
x++; // 更新x坐标
}
// 第二阶段:沿x轴递增
d = b2 * (x + 0.5) * (x + 0.5) + a2 * (y - 1) * (y - 1) - a2 * b2;
while (y >= 0) {
plotEllipsePoints(centerX, centerY, x, y); // 绘制四个对称点
if (d > 0) {
d += a2 * (-2 * y + 3); // 如果判别值大于0,更新y
} else {
d += b2 * (2 * x + 2) + a2 * (-2 * y + 3); // 如果判别值小于等于0,更新x
x++;
}
y--; // 更新y坐标
}
}
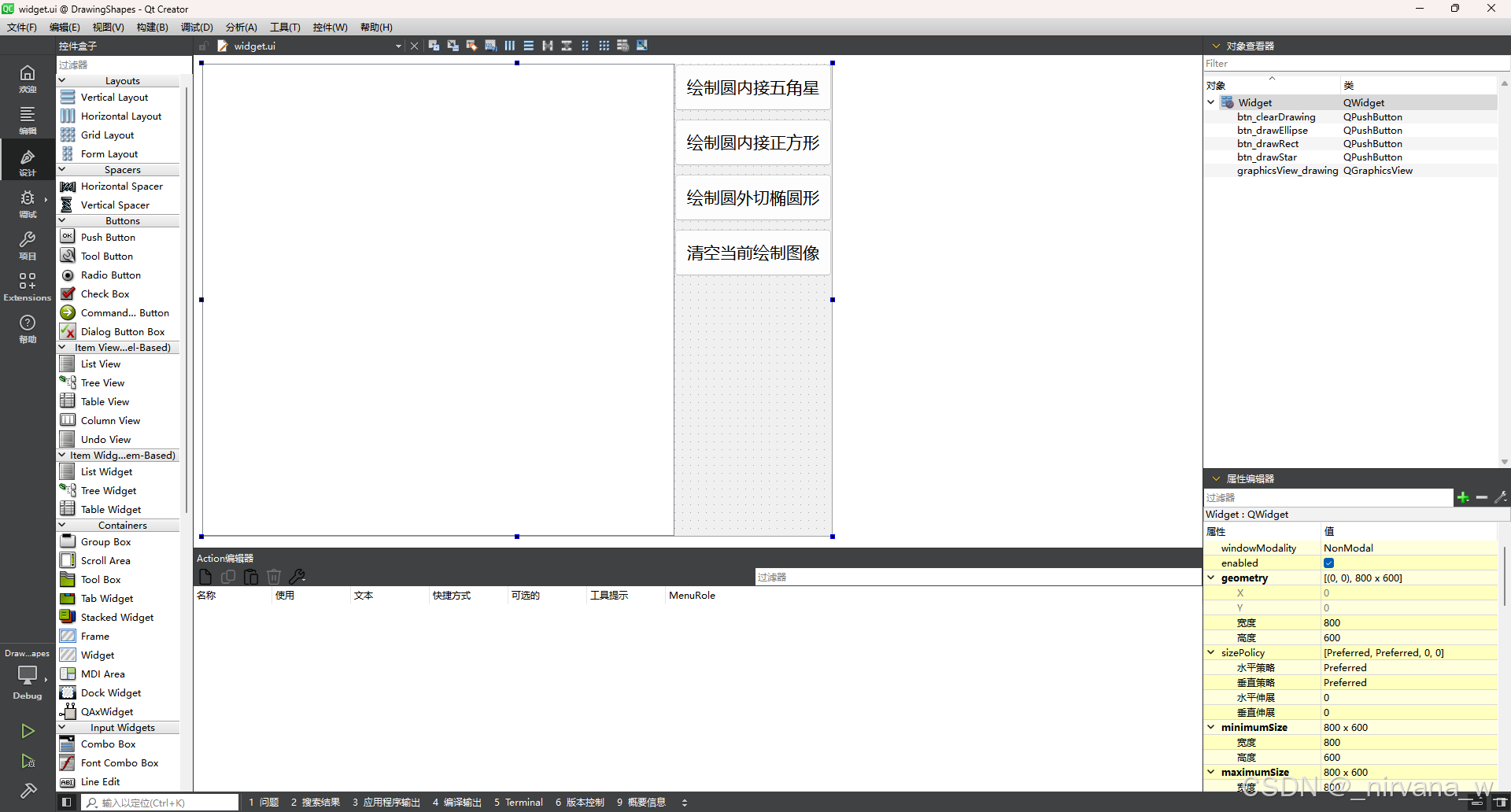
附界面设计文件截图



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










