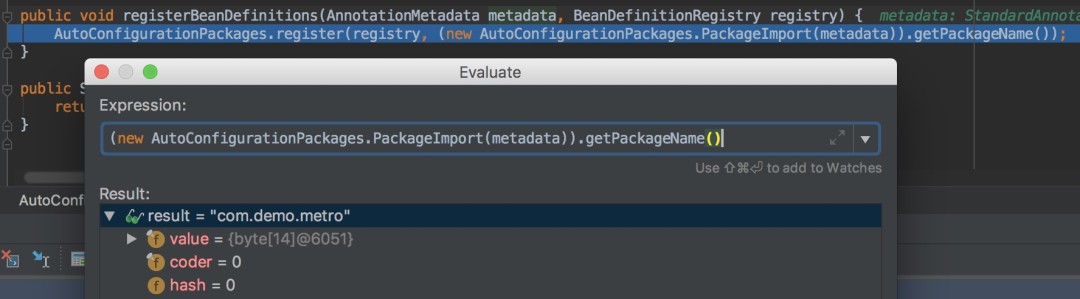
就是通过以上这个方法获取扫描的包路径,可以debug查看具体的值:
img
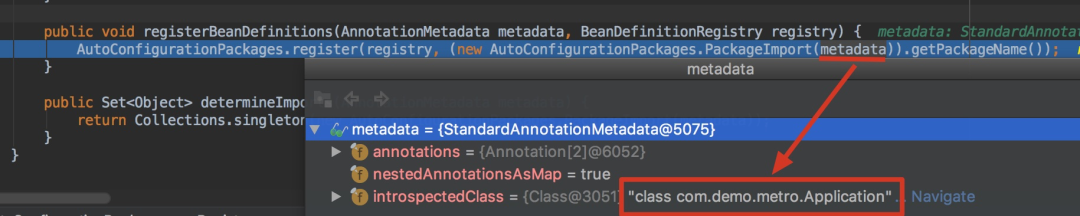
那metadata是什么呢,可以看到是标注在@SpringBootApplication注解上的DemosbApplication,也就是我们的主配置类Application:
img
其实就是将主配置类(即@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及子包里面所有组件扫描加载到Spring容器。因此我们要把DemoApplication放在项目的最高级中(最外层目录)。
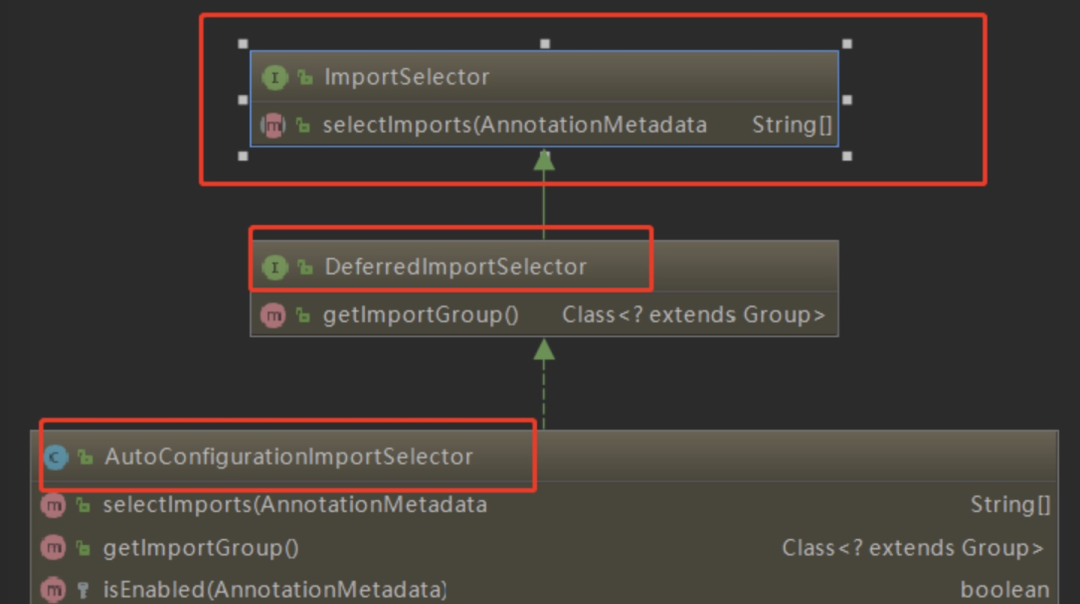
看看注解@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class),@Import注解就是给Spring容器中导入一些组件,这里传入了一个组件的选择器:AutoConfigurationImportSelector。
img
可以从图中看出AutoConfigurationImportSelector 继承了 DeferredImportSelector 继承了 ImportSelector,ImportSelector有一个方法为:selectImports。将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器中。
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
} else {
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry =
this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
}
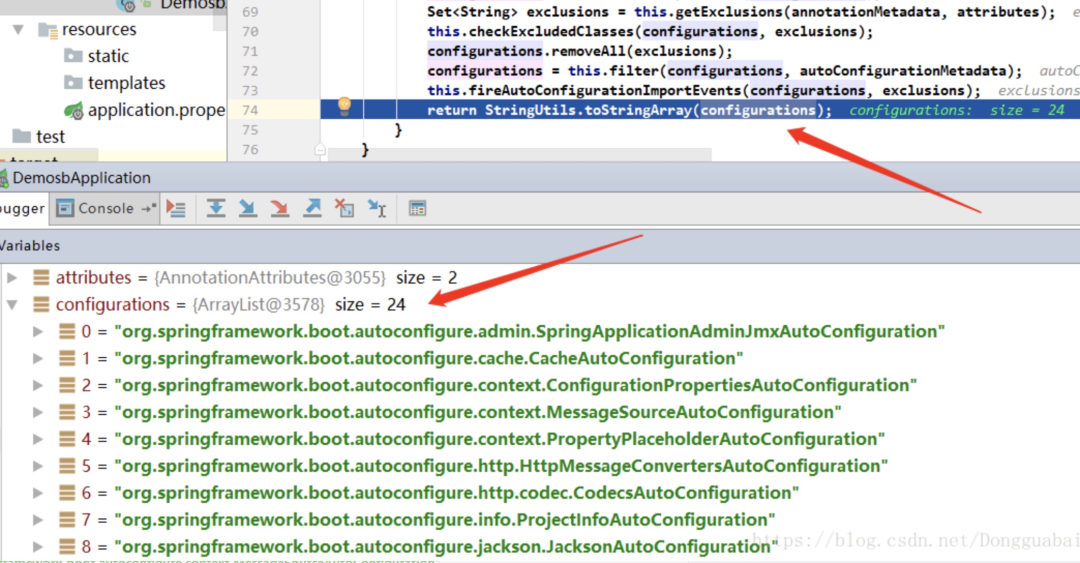
会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration);就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件。
img
有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作。那是如何获取到这些配置类的呢,看看下面这个方法:
protected AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry
getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
} else {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = this.filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}
我们可以看到getCandidateConfigurations()这个方法,他的作用就是引入系统已经加载好的一些类,到底是那些类呢:
protected List getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
“No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.”);
return configurations;
}
public static List loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
会从META-INF/spring.factories中获取资源,然后通过Properties加载资源:
private static Map<String, List> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
Enumeration urls = classLoader !=
null ? classLoader.getResources(“META-INF/spring.factories”) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(“META-INF/spring.factories”);
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<?, ?> entry = (Map.Entry)var6.next();
String factoryClassName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
int var10 = var9.length;
for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) {
String factoryName = var9[var11];
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var13) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]”, var13);
}
}
}
可以知道SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效,帮我们进行自动配置工作。以前我们需要自己配置的东西,自动配置类都帮我们完成了。如下图可以发现Spring常见的一些类已经自动导入。
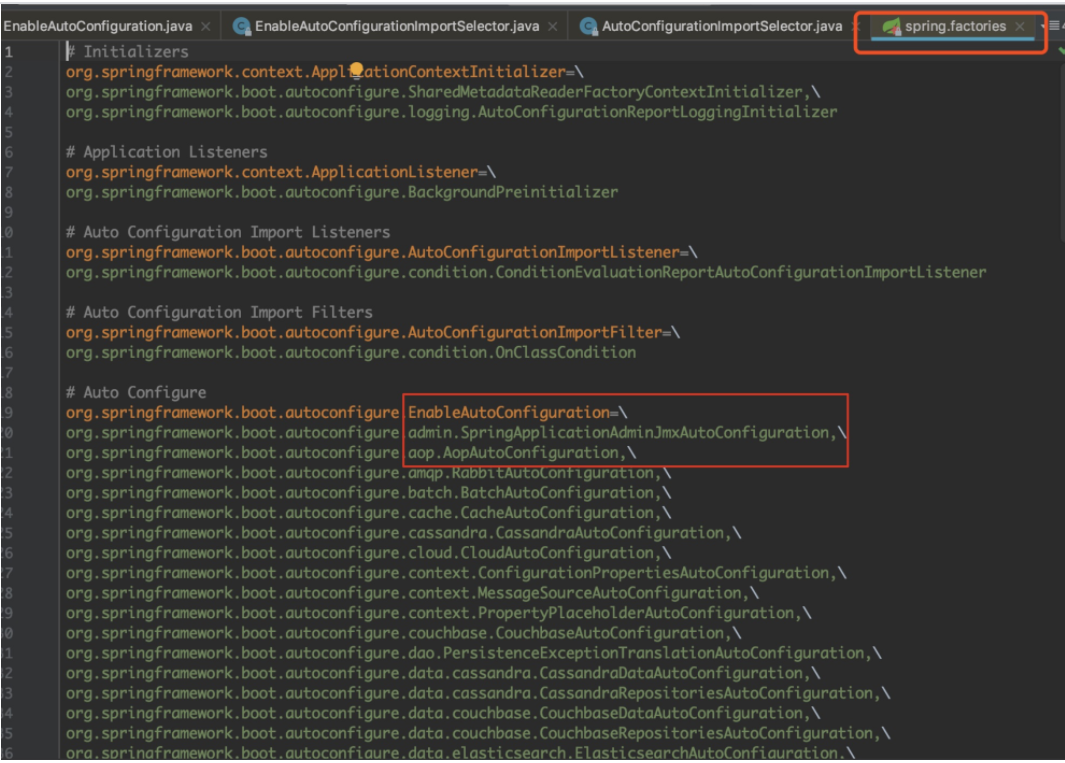
img
接下来看@ComponentScan注解,@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }),这个注解就是扫描包,然后放入spring容器。
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class})})
public @interface SpringBootApplication {}
总结下@SpringbootApplication:就是说,他已经把很多东西准备好,具体是否使用取决于我们的程序或者说配置。
接下来继续看run方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
来看下在执行run方法到底有没有用到哪些自动配置的东西,我们点进run:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String… args) {
//计时器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
//监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
//准备上下文
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
//预刷新context
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新context
this.refreshContext(context);
//刷新之后的context
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
那我们关注的就是 refreshContext(context); 刷新context,我们点进来看。
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
我们继续点进refresh(context);
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
他会调用 ((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();方法,我们点进来看:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset ‘active’ flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring’s core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore…
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
由此可知,就是一个spring的bean的加载过程。继续来看一个方法叫做 onRefresh():
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
他在这里并没有直接实现,但是我们找他的具体实现:
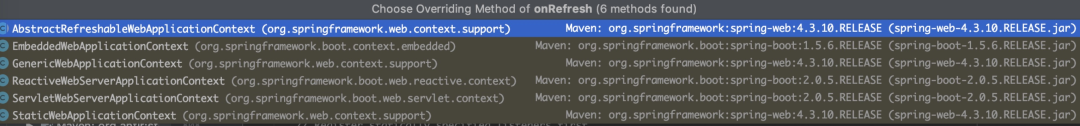
img
比如Tomcat跟web有关,我们可以看到有个ServletWebServerApplicationContext:
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(“Unable to start web server”, ex);
}
}
可以看到有一个createWebServer();方法他是创建web容器的,而Tomcat不就是web容器,那是如何创建的呢,我们继续看:
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(“Cannot initialize servlet context”,
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}
factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());他是通过工厂的方式创建的。
public interface ServletWebServerFactory {
WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer… initializers);
}
可以看到 它是一个接口,为什么会是接口。因为我们不止是Tomcat一种web容器。

img
我们看到还有Jetty,那我们来看TomcatServletWebServerFactory:
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer… initializers) {
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir(“tomcat”);
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
那这块代码,就是我们要寻找的内置Tomcat,在这个过程当中,我们可以看到创建Tomcat的一个流程。
如果不明白的话, 我们在用另一种方式来理解下,大家要应该都知道stater举点例子。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-freemarker
首先自定义一个stater。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.1.4.RELEASE
com.zgw
gw-spring-boot-starter
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数Java工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年Java开发全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Java开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且会持续更新!
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以扫码获取!!(备注Java获取)

面试结束复盘查漏补缺
每次面试都是检验自己知识与技术实力的一次机会,面试结束后建议大家及时总结复盘,查漏补缺,然后有针对性地进行学习,既能提高下一场面试的成功概率,还能增加自己的技术知识栈储备,可谓是一举两得。
以下最新总结的阿里P6资深Java必考题范围和答案,包含最全MySQL、Redis、Java并发编程等等面试题和答案,用于参考~
重要的事说三遍,关注+关注+关注!


更多笔记分享

《互联网大厂面试真题解析、进阶开发核心学习笔记、全套讲解视频、实战项目源码讲义》点击传送门即可获取!
293709182)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-te7J7zly-1713293709182)]
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Java开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且会持续更新!
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以扫码获取!!(备注Java获取)

面试结束复盘查漏补缺
每次面试都是检验自己知识与技术实力的一次机会,面试结束后建议大家及时总结复盘,查漏补缺,然后有针对性地进行学习,既能提高下一场面试的成功概率,还能增加自己的技术知识栈储备,可谓是一举两得。
以下最新总结的阿里P6资深Java必考题范围和答案,包含最全MySQL、Redis、Java并发编程等等面试题和答案,用于参考~
重要的事说三遍,关注+关注+关注!
[外链图片转存中…(img-TeAwrHZF-1713293709183)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-di3ZQWp7-1713293709183)]
更多笔记分享
[外链图片转存中…(img-z6SuhdV0-1713293709183)]
《互联网大厂面试真题解析、进阶开发核心学习笔记、全套讲解视频、实战项目源码讲义》点击传送门即可获取!






















 186
186











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








